2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(288e) Enhancing Optical Properties and Stability of DNA-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes with Cryoprotectant-Mediated Lyophilization
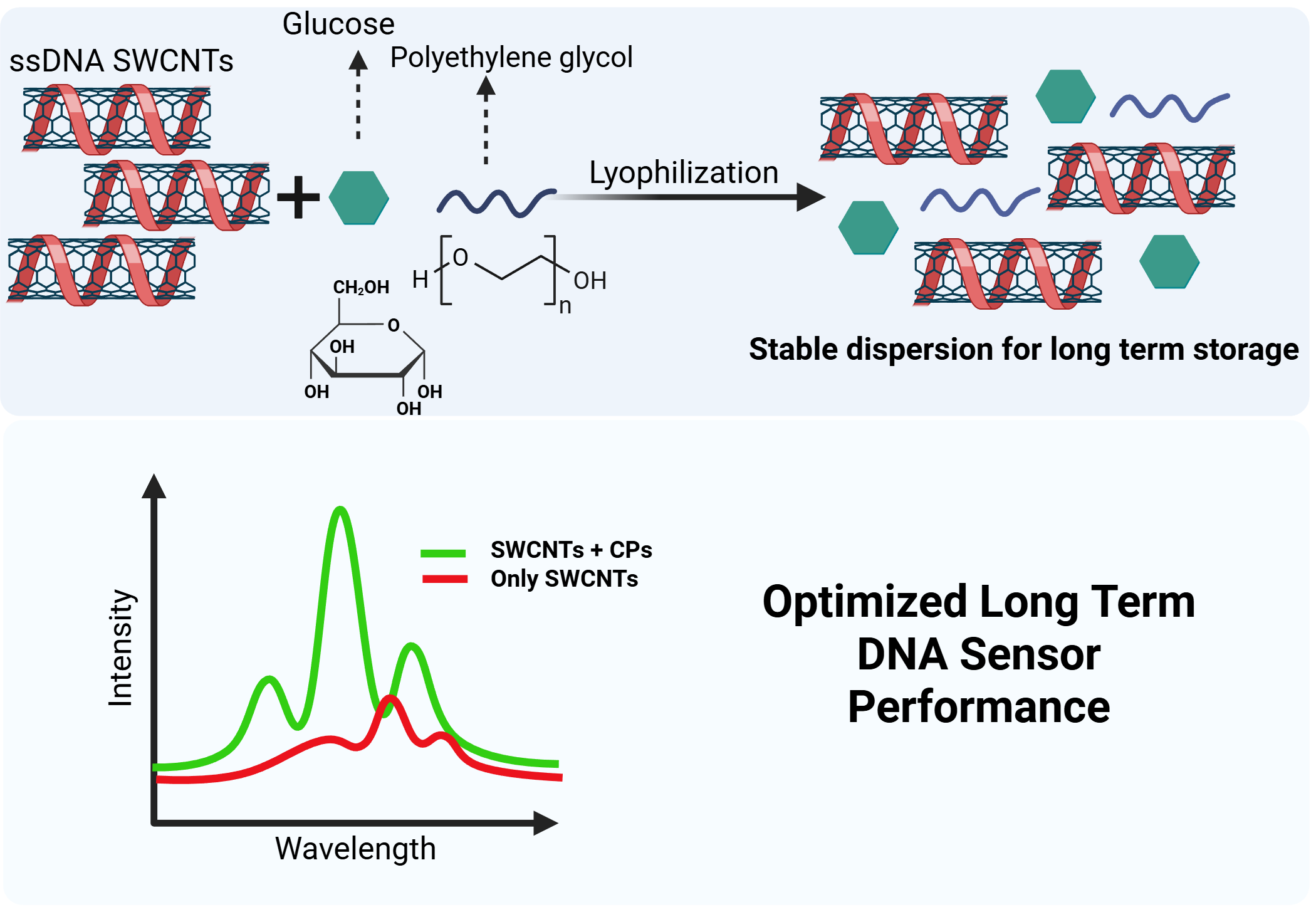
The long-term optical performance and stability of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) functionalized with single-stranded DNA are critical for their application in near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence biological sensing and imaging. However, the aggregation of such DNA-SWCNTs during storage presents a significant challenge. This study explores the use of lyophilization combined with various cryoprotectants (CPs) to enhance the long-term stability and reconstitution of DNA-SWCNTs at room temperature. Five cryoprotectants, including glucose, sucrose, mannitol, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), were evaluated for their ability to maintain desired optical properties and prevent aggregation of SWCNTs through the process of lyophilization and reconstitution. The results indicated that glucose and PEG used in different ratios, provided optimized performance preserving NIR fluorescence and ensuring consistent reconstitution without significant aggregation. Further in vitro studies using murine macrophages demonstrated that lyophilized SWCNTs with glucose-PEG protectants maintained stable and enhanced intracellular optical performance at room temperature, supporting their potential for long-term storage, ease of transport, and use in biomedical applications. The 80:20 glucose: PEG ratio proved to be the most stable, performing best overall, and could be stored at room temperature without degrading the DNA wrapping or stability for up to 12 months. Lyophilizing SWCNTs specifically with 80:20 glucose to PEG ratio not only enhances practical applicability for long term storage but potentially revolutionizes storage and long-term handling of biopolymer suspended SWCNTs specifically for biomedical applications like biosensing and diagnostic tool development. This could in turn lead to more reliable and efficient technologies, significantly impacting healthcare outcomes by enabling more precise detection and monitoring. The findings suggest that the optimized lyophilization protocol with specific cryoprotectant combinations can significantly improve the shelf life and reproducibility of DNA-SWCNT-based sensors, paving the way for their broader application in biological and clinical settings.