2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(183as) Enhanced Chemotherapeutic Delivery and Efficacy in Melanoma Treatment Via Magnetite Nanobioconjugates
Authors
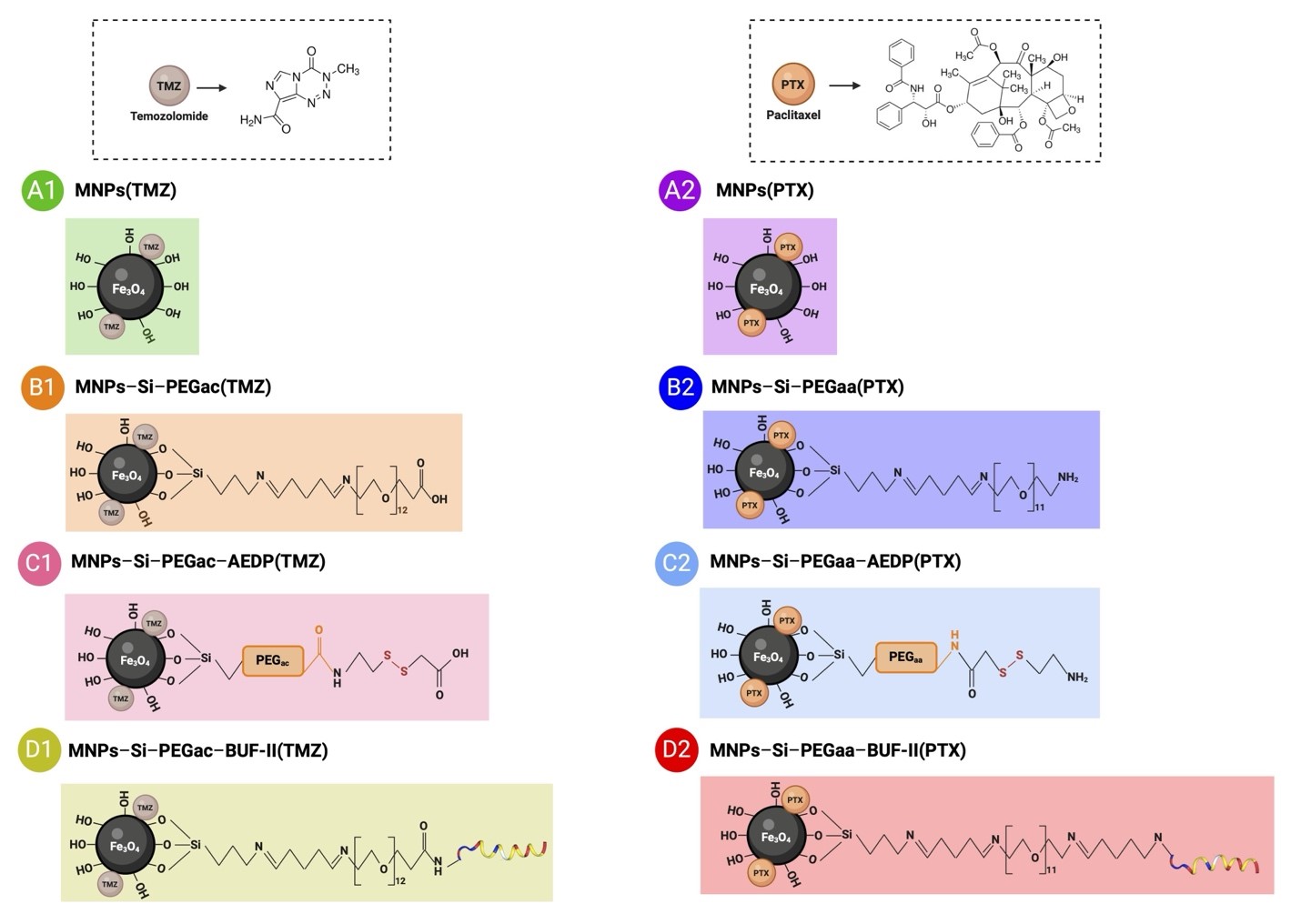
Comprehensive physicochemical characterization, including Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), confirmed successful conjugation and high drug loading efficiencies (32-72% for TMZ, 32-60% for PTX). Biocompatibility studies demonstrated minimal hemolysis and platelet aggregation, supporting their suitability for intravenous administration.
In vitro cytotoxicity studies on A-375 human melanoma cells revealed enhanced therapeutic efficacy of nanobioconjugates compared to free drugs, with cellular uptake mediated by macropinocytosis, caveolin-, and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Additionally, spheroid models confirmed superior penetration and cytotoxic action against 3D melanoma constructs, underscoring the nanobioconjugates’ potential in overcoming drug resistance mechanisms.
These findings highlight magnetite nanobioconjugates as a promising nanocarrier system for targeted melanoma therapy, improving drug solubility, reducing systemic toxicity, and enhancing tumor selectivity. This work contributes to the development of precision nanomedicine strategies, leveraging novel drug carriers and advanced release mechanisms for effective cancer treatment.