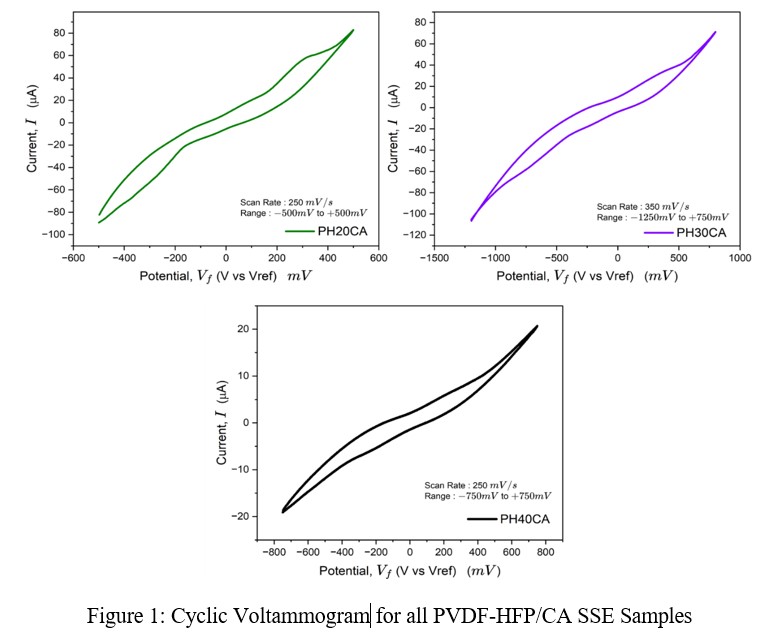
The effects of cellulose on the electrochemical stability of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) solid-state electrolytes (SSE) have been investigated for battery applications [1-2]. Different amounts of CA were filled with PVDF-HFP to fabricate the electrolytes. The biocompatible polymer CA sourced from renewable resources can synergistically interact with the fluorinated polymer PVDF-HFP, which is recognized for its chemical resistance and flexibility, resulting in a stable SSE [3]. The analysis showed that the minimum loading of CA stands out with remarkable electrochemical attributes, boasting a notable DC ionic conductivity of 11.57 mS/cm. SEM analysis revealed distinct microporous structures, with the highest pore area at 223.5 μm² and acceptable surface roughness at 151.9 μm. Loss tangent analysis revealed ion-hopping as the ion migration mechanism. Cyclic voltammetry displayed redox capabilities and an electrochemical stability window (ESW) of approximately 1.0 V as shown in Figure 1, positioning PH20CA as a promising SSE with enhanced electrochemical performance. Comparisons of relative transmittance characteristic peaks with the control sample and other composites reveal a higher interaction intensity and higher stability. These attributes make it a promising candidate for solid-state electrolyte applications with superior electrochemical stability window.
Reference:
1. Gao, C., Li, X., Wei, G. (2022), Cellulose acetate propionate incorporated PVDF-HFP based polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium batteries. Composite Communication 33: 101226 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2022.101226
2. Lalia BS, Abdul SY, Samad YA, Hashaikeh R (2012). Nanocrystalline cellulose-reinforced composite mats for lithium-ion batteries: Electrochemical and thermomechanical performance. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry 17 (2012):. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1894-1
3. Lee H, Song YW, Kim MY, Lee J, Ryu J, Noh Y, Kim S, Kim J, Lim J (2024) Composite solid electrolyte with improved ionic conductivity and high lithium transference number through reduced PVDF-HFP crystallinity, Solid State Ionics, 411, 116571 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2024.116571