Introduction: Macrophages play a central role in many immune-mediated diseases and can be polarized toward anti-inflammatory or pro-inflammatory phenotypes, making them promising targets for chronic inflammatory diseases. In response to certain pro-inflammatory stimuli, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), macrophages engulf excess LDL, become metabolically dysfunctional, and contribute to disease progression. These lipid-laden macrophages, known as foamy macrophages, are key drivers in several inflammatory diseases including atherosclerosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Methods: To target foamy macrophages, we have previously developed chimeric proteins comprised of an LDL binding antibody fragment (Fab) fused to the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. We have found that these protein fusions successfully limit vascular inflammation in atherosclerotic mice. Here, we elucidate the mechanisms by which Fab-IL-10 alters the phenotype of foamy macrophages.
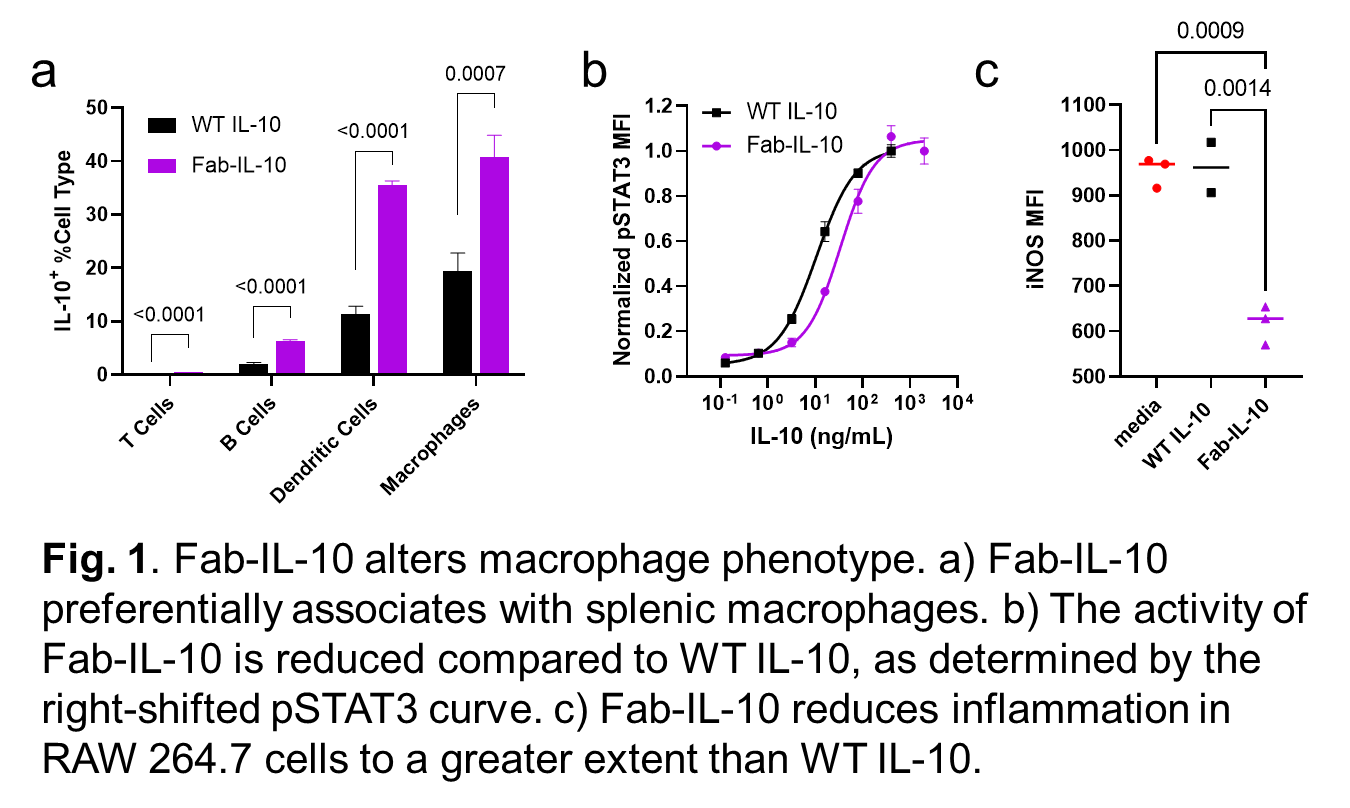
Results: Fab-IL-10 preferentially co-localizes with dendritic cells and macrophages in atherosclerotic mice over other immune cell populations (Fig. 1a) and further associates with splenic macrophages from atherosclerotic mice more strongly than those from healthy mice. In vitro, the initial phosphorylation of STAT3 is reduced for Fab-IL-10 compared to native IL-10 in RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells (Fig. 1b). However, Fab-IL-10 suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in these cells to a greater extent (Fig. 1c).
Conclusions: By evaluating the interactions between Fab-IL-10 and lipid-laden macrophages, we can elucidate mechanistic insights to inform the design of future engineered cytokine therapeutics.