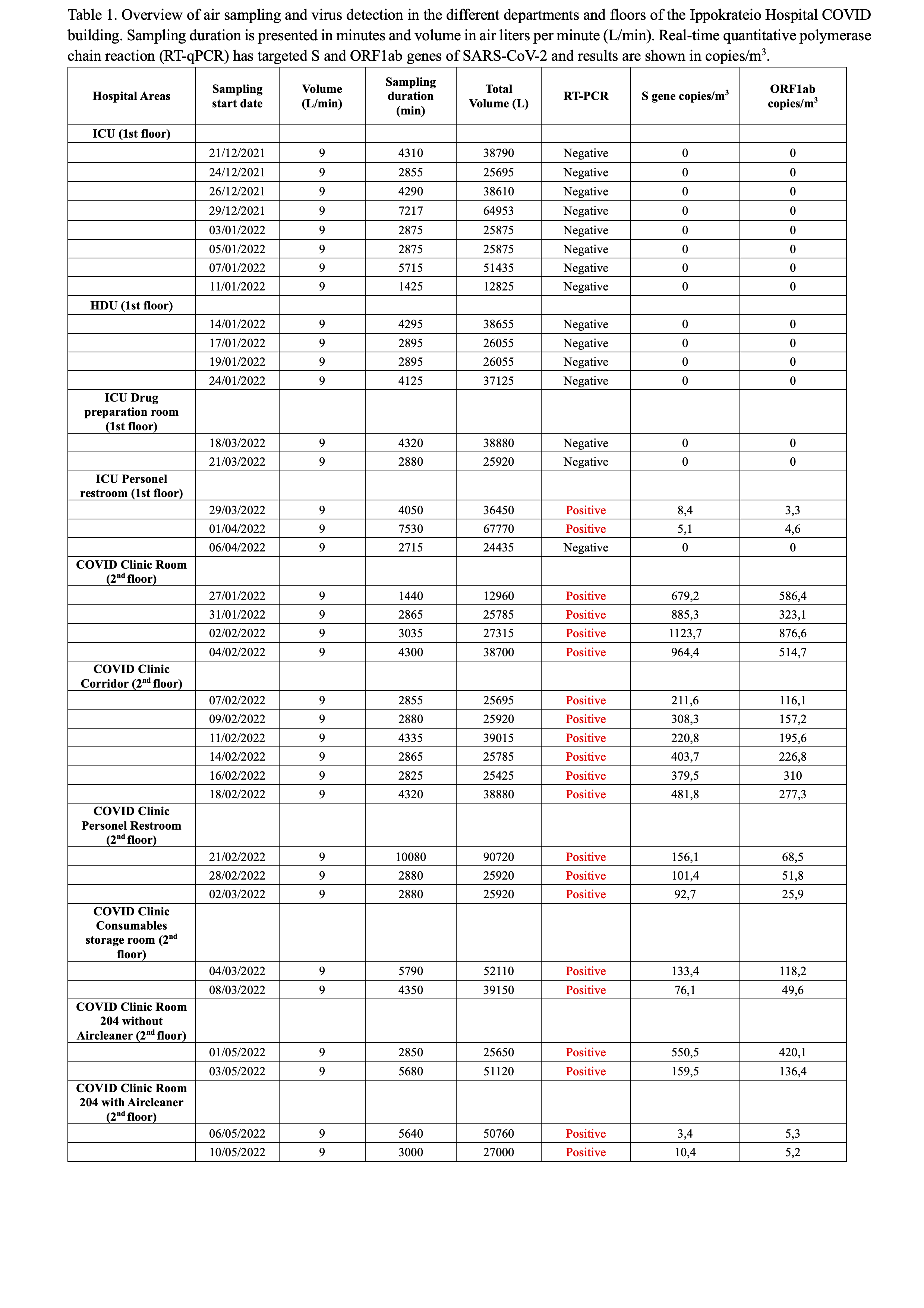
The pandemic of COVID-19 has brought in light the necessity for the development of novel detection methods for airborne transmitted pathogens on the one hand and the importance of effective measures in hospital departments on the other. In this study, Sars-CoV-2 detection has been performed from December 2021 till May 2022 in different departments of the COVID building at the Ippokrateio University Hospital in Thessaloniki, Greece. More specifically, cascade impactors and air pumps with filters were placed at the first floor in the ICU (Intensive Care Unit), the HDU (High-Dependency Unit), in personnel restrooms, in the cloth changing rooms, and in corridors and rooms at the at the COVID second floor. Sampling was performed every 24 or 48 hours till seven days continuously. In addition, in a COVID room with confirmed viral load an air cleaner machine was placed to examine the effect on viral load in hospital environment. Air filters were subjected in RNA extraction using an in-house developed method, and RT-qPCR was performed to detect and quantify viral copies/m
3. Results showed that at the ICU and the HDU departments in which negative pressure air filtration with HEPA filters is applied no viral copies were detected (Table 1). On the contrary, viral load was effectively detected at the COVID floor in rooms and corridors and ranged from 25,9 to 1123,7 copies/m
3. In addition, viral load in the COVID room where an air cleaner was placed showed a reduction of 95,7%. Furthermore, sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 positive samples from January, February and May 2022 showed that during our study Omicron (B.1.1.529) was the dominant variant. In conclusion, in this study SARS-CoV-2 was effectively detected in real-time after extended sampling and ranged between 24 h to 7 days, and it was shown how important and effective are air cleaners as first-line measures against the pathogen airborne transmission in hospital environments.