2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(175n) Functional Characterization of Geraniol Synthase Involved in Monotropein Biosynthesis in Blueberry Using Computational and Molecular Based Approaches
Author
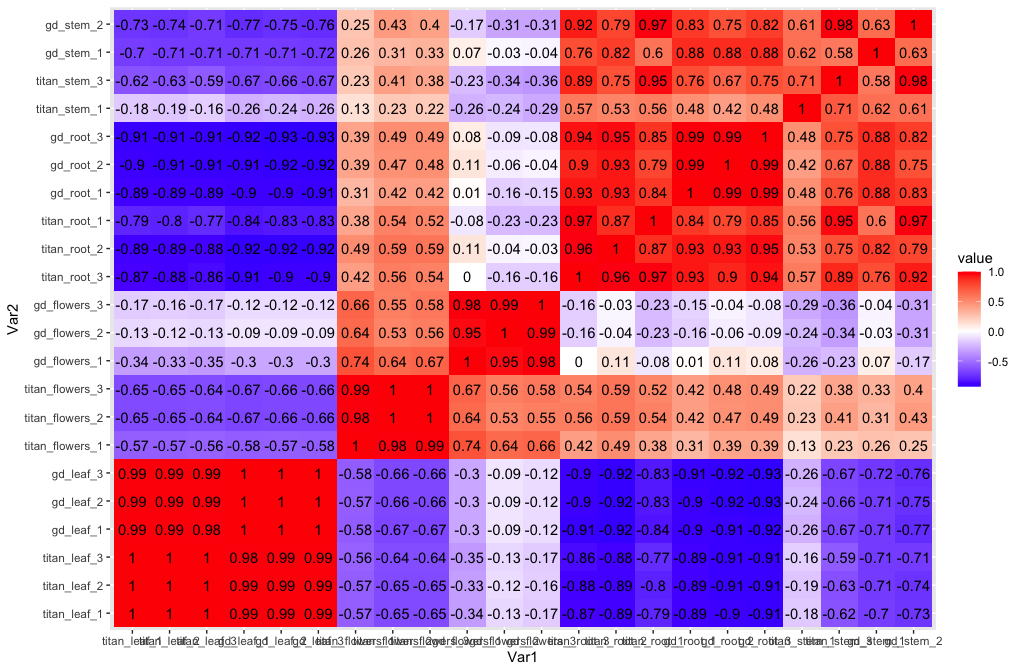
Blueberry is the second most important fruit crop in the US, owing to increased awareness of its health benefits due to the presence of several bioactive compounds. One such plant bioactive compound is monotropein. It has been reported that monotropein is found in only three plant species, namely Monotropa Uniflora, Morinda officinalis (Vaccinium spp). Most work on monotropein has been done in Morinda officinalis where it has been shown to impart several human health benefits. Recent work has also identified monotropein in both wild and cultivated blueberries. However, how monotropein is produced and the type of candidate genes involved in the biosynthesis of monotropein in blueberries has yet to be elucidated. Our research group has used bioinformatics, comparative genomics and protein engineering techniques to functionally characterize the iridoid synthase (ISY) gene which encodes for an enzyme involved in an important cyclization step in monotropein biosynthesis. This further gave u understanding of the key candidate genes involved in the monotropein biosynthesis pathway. Currently, we are focusing on functionally characterizing geraniol synthase (GES) gene, as recent work has found the expression of GES is significantly associated with the production of iridoids in other plant families using both long-reads and short reads from different tissues of blueberry plant. Our overarching goal is to elucidate the biosynthetic pathway of production of monotropein in blueberry to potentially develop biosynthetic pathway for mass and cheap production of monotropein compound, otherwise derived by isolation of compound from Morinda officinalis.