2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(389cd) Tuning BEA Zeolite Acidity for Biomass Upgrading Toward Drop-in Biofuels: Computational Modelling to Industrial Scale
Authors
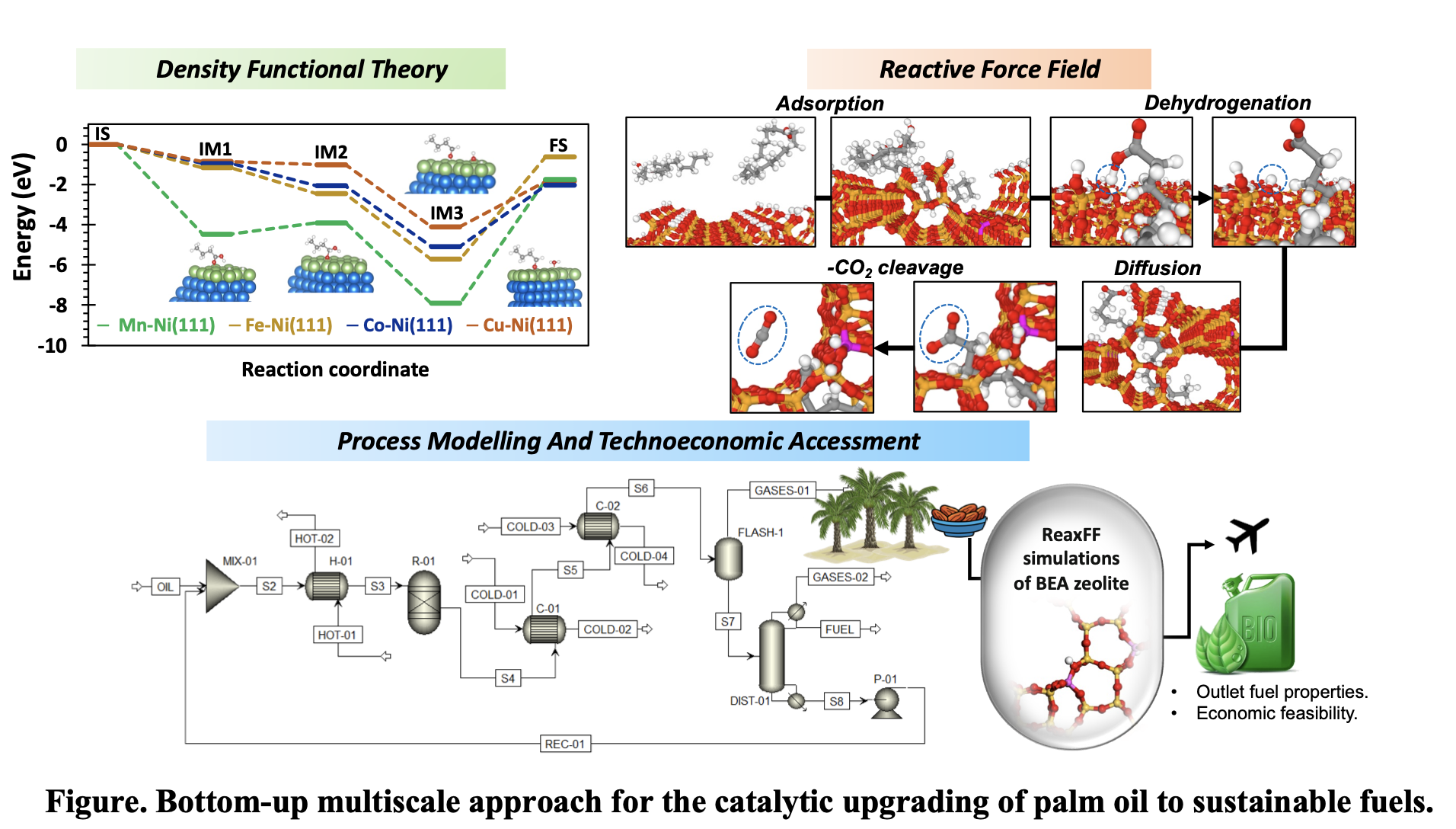
Beyond catalyst design, scaling up biofuel technologies requires a fully integrated approach. We have developed and simulated a full-scale process plant for drop-in biofuels production based on the ReaxFF molecular simulation results, optimizing the heat integration and reactor design [2]. A sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) with 76.75 wt% undecene and a higher heating value (HHV) of 44.96 MJ/kg was achieved. Parameter sensitivity analysis revealed that OPEX is heavily dependent on feedstock cost. Compared to biomass-to-fuel processes in the literature, this work reports a cost-competitive minimum fuel selling price (MFSP) of $3.38 L−1 for SAF production. At the current stage, we are computing the carbon efficiency and water footprint of the plant through life cycle assessment (LCA). Through this pioneering contribution, our research not only transforms biomass waste into high-value fuels but also strengthens the link between scientific discovery and industrial application for fostering improvement in sustainable fuel technologies.
This work has been financed by Khalifa University of Science and Technology under the Research and Innovation Center on CO2 and Hydrogen (RICH) (project RC2-2019-007).
References:
- S. AlAreeqi, D. Bahamon, I. II. Alkhatib, K. Polychronopoulou, L. F. Vega, Advanced Computational Modeling for Biofuel Catalyst Optimization: Enhancing Beta Zeolite Acidity for Oleic Acid Upgrading, Biofuel Res. J. 11 (2024) 2194-2210. https://doi.org/10.18331/BRJ2024.11.3.5
- S. AlAreeqi, I. II. Alkhatib, and L. F. Vega. Palm Oil Biomass to Drop-in Fuels as Alternative to Traditional Jet Fuels: Large-scale Process Modelling and Techno-economic Assessment. Society of Petroleum Engineers. Technical paper presentation at ADIPEC, Abu Dhabi, UAE (2024) SPE-222695-MS. https://doi.org/10.2118/222695-MS