2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(400y) Sustainable Recovery of Biobased Food Additive Glutaric Acid Using Vegetable Oils
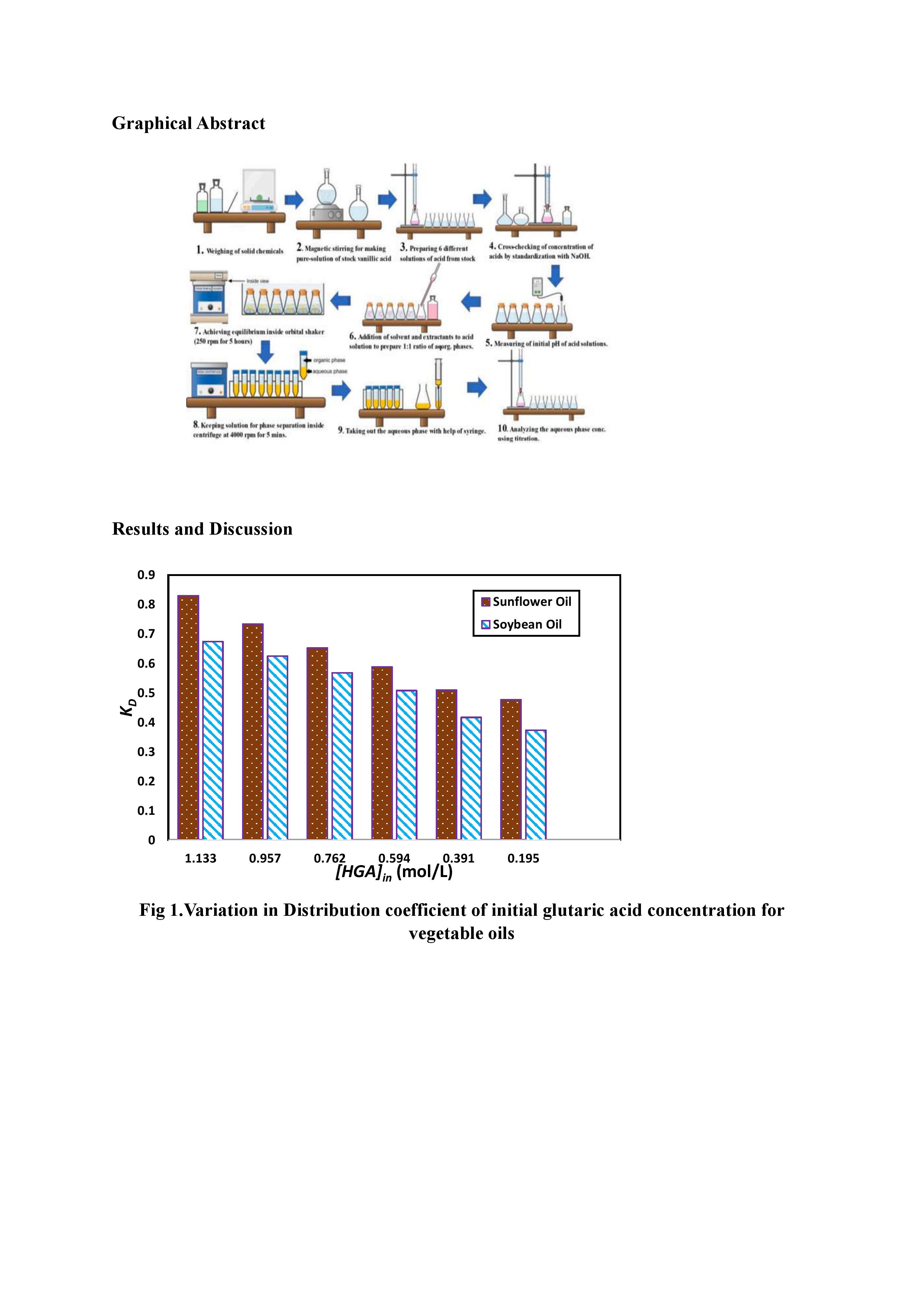
Glutaric acid, a five-carbon dicarboxylic acid, is widely used in the food and beverage industry as both an additive and a flavoring agent. Its acidulant properties help regulate the pH in food products, extending their shelf life and ensuring stability by inhibiting microbial growth. This makes glutaric acid a key ingredient in processed foods, drinks, and condiments where acidity control is essential. As a buffering agent, it also helps maintain a consistent taste and texture in food formulations, making it ideal for use in products like sauces, soft drinks, baked goods, and confectionery. Due to its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature, glutaric acid is considered a safe food additive. It is also increasingly sourced from renewable resources, making it a more sustainable option compared to petrochemical-derived additives. In line with current trends toward natural and eco-friendly food ingredients, biobased glutaric acid is gaining attention as a greener alternative, enhancing both food quality and sustainability in the industry. Traditional recovery processes often require high energy consumption and harsh chemicals, leading to environmental damage and high costs. In contrast, sustainable approaches prioritize reducing environmental impact while ensuring efficiency and quality. Such promising methods are the use of green solvents such as deep eutectic solvents (DES), natural solvents, Ionic liquids, etc. Based on the typical experimental investigation using natural non-toxic solvents, reactive extraction of glutaric acid using tri-octyl amine (TOA) in sunflower and soybean oil was performed. Results were presented in terms of distribution coefficients (0.126 -1.221 for sunflower oil and 0.1097-1.018 for soybean oil), and the extraction efficiency was in the range (13.20 - 74.98 % to 12.89 – 70.47 %) for sunflower and soybean oil respectively. This method minimizes toxic solvent usage, reduces environmental impact, and promotes cleaner production processes, making it ideal for applications in biobased industries.
Keywords: Glutaric acid, Bio-based food additive, reactive extraction, natural solvents.
Introduction
Glutaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid with the molecular formula C5H8O4, is a versatile compound featuring two carboxyl (-COOH) groups connected to a five-carbon linear chain. This configuration gives glutaric acid notable characteristics, such as high-water solubility, a melting range of 97–99°C, and the ability to form esters and amides, making it highly useful in chemical synthesis. It is a white crystalline solid with a mildly acidic pKa=4.31 and can be found naturally or synthesized industrially for various applications [1].
In the food and beverage sector, glutaric acid is gaining recognition as a biobased additive with significant potential. Its inclusion in food products can improve flavor, regulate pH, and enhance preservation [2]. As a buffering agent, it also helps maintain a consistent taste and texture in food formulations, making it ideal for use in products like sauces, soft drinks, baked goods, and confectionery [3]. Furthermore, its biodegradable and non-toxic nature aligns with the increasing demand for sustainable and safe food-grade additives. This makes glutaric acid an appealing replacement for synthetic alternatives, supporting the shift toward environmentally friendly food processing methods. Glutaric acid’s industrial uses are extensive, owing to its reactivity. It is a key precursor in the production of polyesters, polyamides, and other polymers, supporting the manufacture of adhesives, coatings, and biodegradable plastics. Its derivatives also serve as intermediates in pharmaceutical production, including medications for epilepsy and other neurological conditions. In the agrochemical industry, it is utilized in creating plant growth regulators and pesticides [4]. Reactive extraction provides a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to conventional separation techniques for glutaric acid. In the present paper by utilizing trioctyl amine (TOA) in combination with diluents such as sunflower oil and soybean oil, the process can be optimized to enhance recovery efficiency, benefiting the food beverage and pharmaceutical industries. The extraction performance was evaluated based on distribution coefficients, extraction efficiency, loading ratios, and extraction equilibrium complexation constants.
Methodology
The liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) of glutaric acid was carried out using aqueous solutions with initial concentrations ranging from 0.19 to 1.14 mol/L, prepared by dissolving glutaric acid in double-distilled water. Equal volumes (10 mL each) of the aqueous solution and solvent were mixed in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks and shaken at 250 rpm for 3 hours at 298.15 ± 1 K in an orbital shaker incubator (REMI S-24BL). Equilibrated mixtures were then subjected to ultrasound treatment in a 2000 mL sonication bath (Labman, India) at 40 Hz for 30 minutes. Phase separation was achieved via centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes (REMI CENTRIFUGE-4C). A 2 mL sample from the aqueous phase was analyzed using a UV-spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800) at 275 nm, and the organic phase concentration was determined by mass balance. All experiments were repeated for reproducibility.
Conclusion
In the food and beverage industry, sustainable recovery approaches for biobased glutaric acid offer a forward-looking solution for eco-friendly additive production. By employing green solvents, such as natural, nontoxic plant-based oils, this approach significantly reduces environmental impact compared to traditional methods that rely on toxic or fossil-derived solvents. Glutaric acid, a valuable additive with applications in flavor enhancement, preservation, and pH stabilization, can now be produced with greater efficiency and a reduced carbon footprint. The reactive extraction of glutaric acid using sunflower and soybean oil demonstrates a promising, eco-friendly approach for recovering this valuable biobased compound. Both sunflower and soybean oils serve as green, bio-based solvents that effectively dissolve and interact with glutaric acid, reducing the need for toxic or fossil-based organic solvents typically used in extraction.
References
- Uslu, N. P., & Kirbaslar, H. (2009). Experimental and Modelling of Glutaric acid by Trioctylamine. Chem.Eng. Data, 54(12) ,3202-3207. doi:10.1021/je900202f.
- Han, Y.H., Yang, P.Y, Jung S.Y., Joo. H.R. Joo, Song.J. C. Song. (2020) Selective extraction of Glutaric acid from biological production systems using n-butanol. Ind. Eng.Chem,82 98–104.doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2019.09.047.
- H., Gardner, 1968. Acidulants in food processing. In “Handbook of Food Additives,” p. 247. The Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland, Ohio. doi :1007/978-1-4615-2117-4
- S. Parmar, Dicarboxylic Acid, Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition),2014, Pages 76-79. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.01217-3.
- , H. T., Khang.T. U, Baritugo. K. A, Baritugo, S, Hyun.M, Kang. K.H. Kang (2019) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of Glutaric acid, a C5 dicarboxylic acid platform active, Metabolic Engineering.51,99–109.doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2018.08.007.