2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(179e) Surfactant-Enhanced Extraction of Tea Tree Oil By Hydrodistillation Using Alkyl Polyglucoside
Authors
Bing-Hung Chen - Presenter, National Cheng Kung University
Duu-Jong Lee - Presenter, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
Li-Chen Weng, National Cheng Kung University
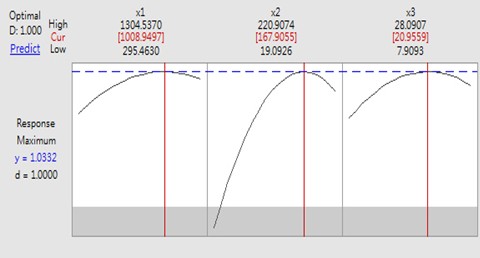
This study is aimed to enhance the extraction yield of tea tree oil (TTO) via hydrodistillation with aqueous solutions of an alkyl polyglucoside surfactant (APG 0810) as extractant. To attain the optimal operating condition for maximal extraction yield of TTO by APG 0810-enhanced hydrodistillation, both design-of-experiments (DoE) and response surface methodology (RSM) approaches were employed [1]. Specifically, a central composite design (CCD) was applied for building a quadratic model for the response variable which was the extraction yield normalized by the yield garnered under the condition corresponding to the center point of CCD. A second-order polynomial equation obtained by fitting experimental data well was used to predict the extraction of tea tree oil. Explicitly, the optimal operating parameters were summarized as follows: (1) liquid extractant containing 1,010 ppm of APG 0810 surfactant, (2) an extraction time at 170 min, and (3) a weight ratio of liquid extractant/solid desiccated leaves in hydrodistll at 21, shown as Figure. The predicted response value was 1.033. To verify the model established by RSM, experiments were conducted under the proximity of optimal extraction condition. The empirical extraction yields were in close agreement with predicted value, even with the hydrodistillation systems composed of tea tree leaves and APG liquid extractant scaled up by three times. More importantly, the TTO obtained in this work by surfactant-enhanced hydrodistillation met the quality requirements stipulated in the standard ISO 4730.