2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(322c) Support Effects in Butadiene Hydrogenation over Cu and PtCu Dilute-Limit Alloys
Authors
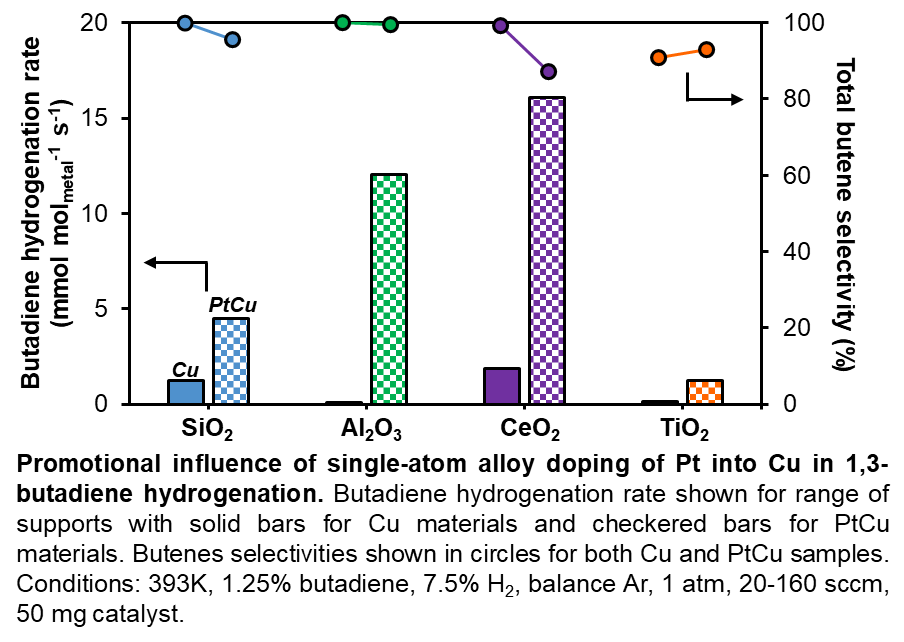
Colloidal methods ensure comparable metal loadings and particle morphologies across anchoring on different supports. Despite this, CeO2- and SiO2-supported Cu exhibited substantially higher butadiene conversions than Cu on Al2O3 and TiO2. While all materials demonstrate high selectivities for butenes at lower temperatures (~90-100%), SiO2 and CeO2-supported catalysts showed higher 1-butene selectivities (up to ~80% near 393 K). The introduction of Pt enhanced butadiene conversion for all materials, though the magnitude of promotion varied strongly with support in the order Al2O3 (170x) >> TiO2 (11x) ~ CeO2 (9x) > SiO2 (4x) at 393 K. The propensity to over-hydrogenate and consequently form butane was also strongly support dependent, with total butene selectivities noticeably dropping below 100% for SiO2 and CeO2 but not for Al2O3. Butene distributions additionally changed for all materials, with increases in 2-butenes vs 1-butenes due to shifts in primary kinetics rather than isomerizations. Overall, these findings highlight that support effects are non-trivial in SAAs, motivating the careful selection of supports when invoking this promotion strategy.