2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(584bf) Structure Sensitivity in CO2 Methanation over Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts
Authors
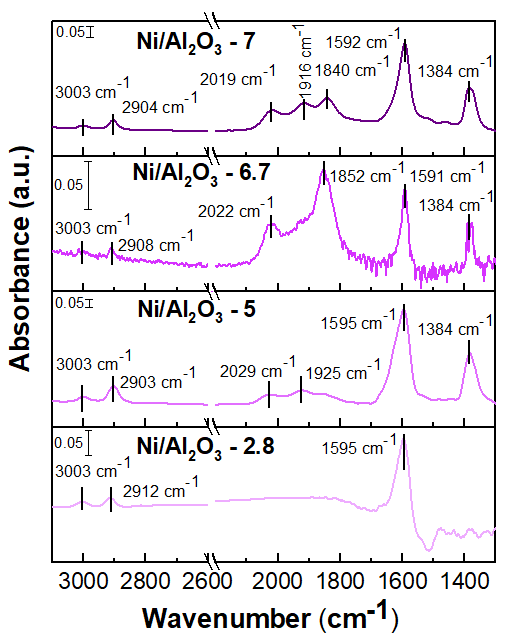
Ni/Al2O3 catalysts with average particle sizes ranging from 2.8 to 7 nm were synthesized using colloidal synthesis, strong electrostatic adsorption, and incipient wetness impregnation. The particle sizes were characterized using CO chemisorption and TEM/STEM. Methanation reactivity was found to increase with Ni nanoparticle size, correlating with higher H2 consumption in H2-TPR measurements. However, CO2-TPD results indicated that reactivity was not directly linked to catalyst basicity. In situ FTIR analysis revealed that only formate species were present on smaller Ni particles under reaction conditions, while both CO and formate species were observed for larger Ni particles. For the most active catalysts with large particles, formyl species on also appeared within the first 10 minutes, alongside CO and formate. We suggest that the changing density of interfacial Ni-Al2O3 sites leads to this observed performance.
Figure Caption. FTIR spectra of Ni-based catalysts supported on Al2O3 under CO2 methanation conditions. All catalysts were reduced in situ at 477 °C for 2 hrs prior to switching to the CO2, H2, Ar mixture at 300° C. The spectra shown were collected after 10 hrs. of reaction and a background of the reduced catalysts under H2/Ar flow is subtracted.