2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(499e) Structure-Function Relationship of Highly Reactive CuOx Cluster on Co3O4 for Selective Formaldehyde Sensing at Low Temperatures
Authors
Frank Krumeich, Particle Technology Laboratory, ETH Zurich
Zhangyi Yao, University College London
Feng Wang, University College London
Andreas Güntner, ETH Zürich
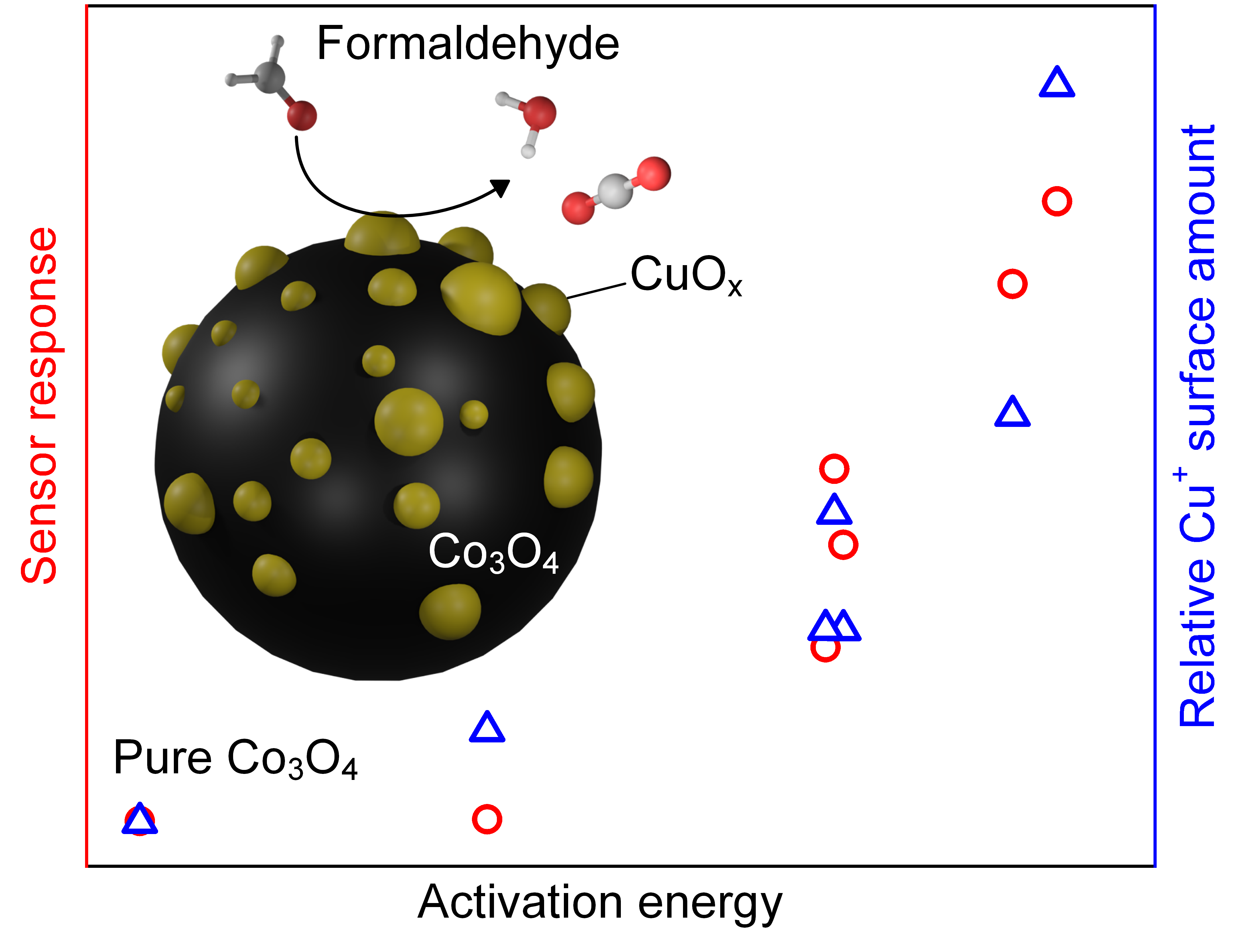
Designing reactive surface clusters at the nanoscale on metal-oxide supports enables selective molecular in low-temperature catalysis and chemical sensing. However, identifying effective material combinations and reactive sites remains a challenge, but of paramount importance for rational sensor/catalyst design. Here [1], the low-temperature oxidation of formaldehyde with CuOx clusters on Co3O4 is showcased yielding an excellent sensor for this critical pollutant. When deploying flame-aerosol technology in the form of flame spray pyrolysis [2], such CuOx clusters are finely dispersed on Co3O4’s surface, while some Cu2+ ions are incorporated into the lattice enhancing thermal stability. Surface-Cu’s speciation is investigated by infrared spectroscopy of adsorbed CO, near-ambient-pressure near edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (Cu L3 edge) temperature-programmed reducibility studies. These identified Cu+ and Cu2+ species in these CuOx clusters as active sites. Remarkably, the Cu+ surface concentration correlated with the apparent activation energy towards formaldehyde oxidation (Spearman’s coefficient ρ = 0.89) and sensor response (0.96), establishing a connection between kinetics and sensory signals. At optimal composition, such sensors detected down to 3 parts-per-billion (ppb) at moderate temperature of 75 °C, superior to state-of-the-art chemiresistors. Further, selectivity to other aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, and inorganic compounds, as well as robustness to humidity and stable performance over 4 weeks are achieved. These sensors are promising as gas detectors in health monitoring, air and food quality control.
References
[1] D’Andria, M.; Krumeich, F.; Yao, Z.; Wang, F.R. & Güntner, A.T., Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2308224.
[2] Güntner, A.T.; Pineau, N. J. & Pratsinis, S.E., Prog. Energ. Combust. Sci. 2022, 90, 100992.