2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(584bo) A Spatial-Resolved Online MS Study on OCM Reaction Catalyzed By Mn-Na2WO4/SiO2 System for Radicals Coupling Mechanistic Insight
Authors
Yong Yang - Presenter, ShanghaiTech University
Ningxujin Ding, ShanghaiTech University
Danyu Wang, ShanghaiTech University
Jie Fan, Zhejiang University
Junyu Lang, ShanghaiTech University
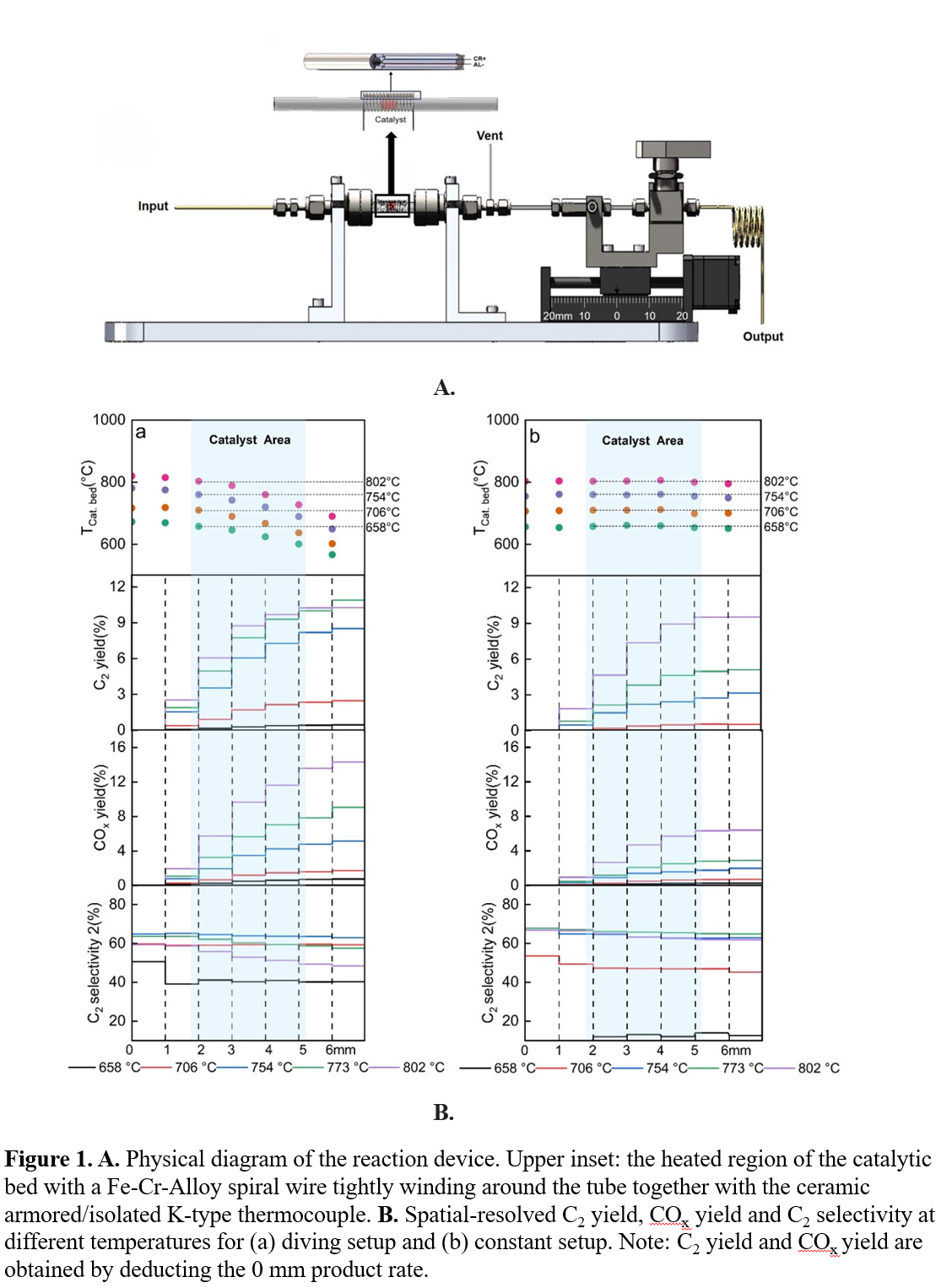
Oxidative coupling of methane (OCM) is a catalytic partial oxidation process that directly converts methane into C2 products. For this high temperature reaction, understanding the radical behavior through experimental investigation is important in correlating the catalytic activity and the products. In this work, a spatial resolution online mass spectrometry (MS) system was developed and applied to a Mn-Na2WO4/SiO2 catalyzed OCM system (Fig. 1. A). In addition to the residue gas analysis, the system obtained the distribution information of the reactants and products in the reactor. At various setting temperatures, all species online MS signals were collected at different positions, mapping the reaction activity covering parameters including temperature, time and space. The distribution behavior of the catalytic activity, selectivity, and apparent activation energy were kinetically analyzed. Selectivity and additional carbon balance analysis strongly supported the radical coupling model of OCM and indicated that after the catalytic bed layer, there is a significant length in the reactor (> 2 mm) filled with radicals. Based on the result, a designed new method by tuning the temperature field in the reactor was found effectively to improve the catalytic activity, especially the C2 yield from 702 to 773 ℃(Fig. 1. B).