2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(693b) Scalable Room-Temperature Oxidation of Graphene for Membranes in Carbon Capture
Authors
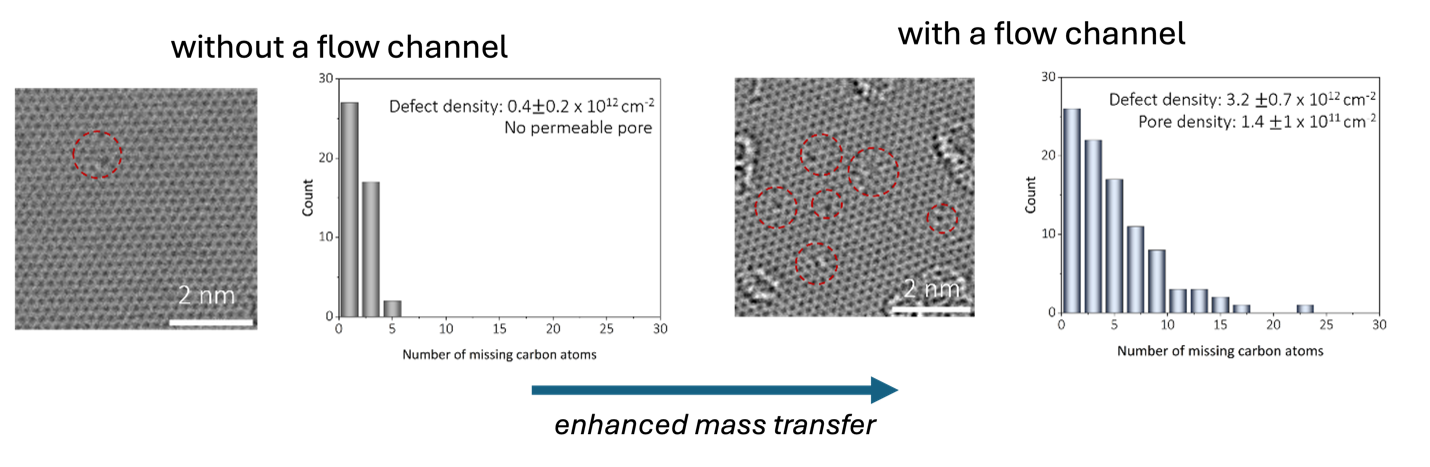
In this work, we present a novel and scalable room-temperature chemical etching method using ozone under confined flow conditions, enabling precise control over pore size and density. Graphene samples were exposed to an O₃/O₂ gas mixture at room temperature within custom-made flow channels (400 and 1000 µm thickness), which enhanced ozone mass transfer and oxidation kinetics by minimizing concentration polarization at the graphene surface. Upon O₃/O₂ gas mixture exposure, epoxy clusters fomed on the graphene lattice. Subsequent photonic gasification with 3.2 eV light for 5 seconds selectively gasified epoxy clusters, forming nanopores with high defect density (up to 3.2 × 10¹² cm⁻²). The enhanced mass transfer increased the degree of oxidation as well as number of defects formed on the graphene lattice, as confirmed by aberration-corrected high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (AC-HRTEM) (Figure 1), Raman, and X-ray photoelectron specreoscopy.
Centimeter-scale membranes prepared from these porous graphene films exhibited highly attractive CO₂ permeance up to 4000 GPU and CO₂/N₂ selectivity of 22. Controlled post-treatment with ozone further improved membrane performance by expanding non-selective pores, increasing CO₂ permeance while maintaining high selectivity. This room-temperature, scalable approach represents a significant advance in graphene membrane fabrication, offering an energy-efficient solution for industrial-scale carbon capture and gas separation applications.
References
[1] S. Huang et al., “Millisecond Lattice Gasification for High-Density CO2- and O2-Sieving Nanopores in Single-Layer Graphene,” Sci. Adv., vol. 7, no. 9, pp. 1–13, 2021, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf0116.
[2] S. Huang et al., “In Situ Nucleation-Decoupled and Site-Specific Incorporation of Å-Scale Pores in Graphene Via Epoxidation,” Adv. Mater., vol. 34, no. 51, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1002/adma.202206627.