2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(320g) Reverse Water Gas Shift (RWGS) Reaction-Selective and One-Pot Chemical Vapor Deposition (OP-CVD)-Derived Optimized CuOx/CeO2 Catalyst
Authors
Amol Pophali - Presenter, Stony Brook University
Gihan Kwon, Brookhaven National Laboratory
Kwangsuk Yoon, Hanyang University
Hocheol Song, Hanyang University
Tae Jin Kim, Stony Brook University
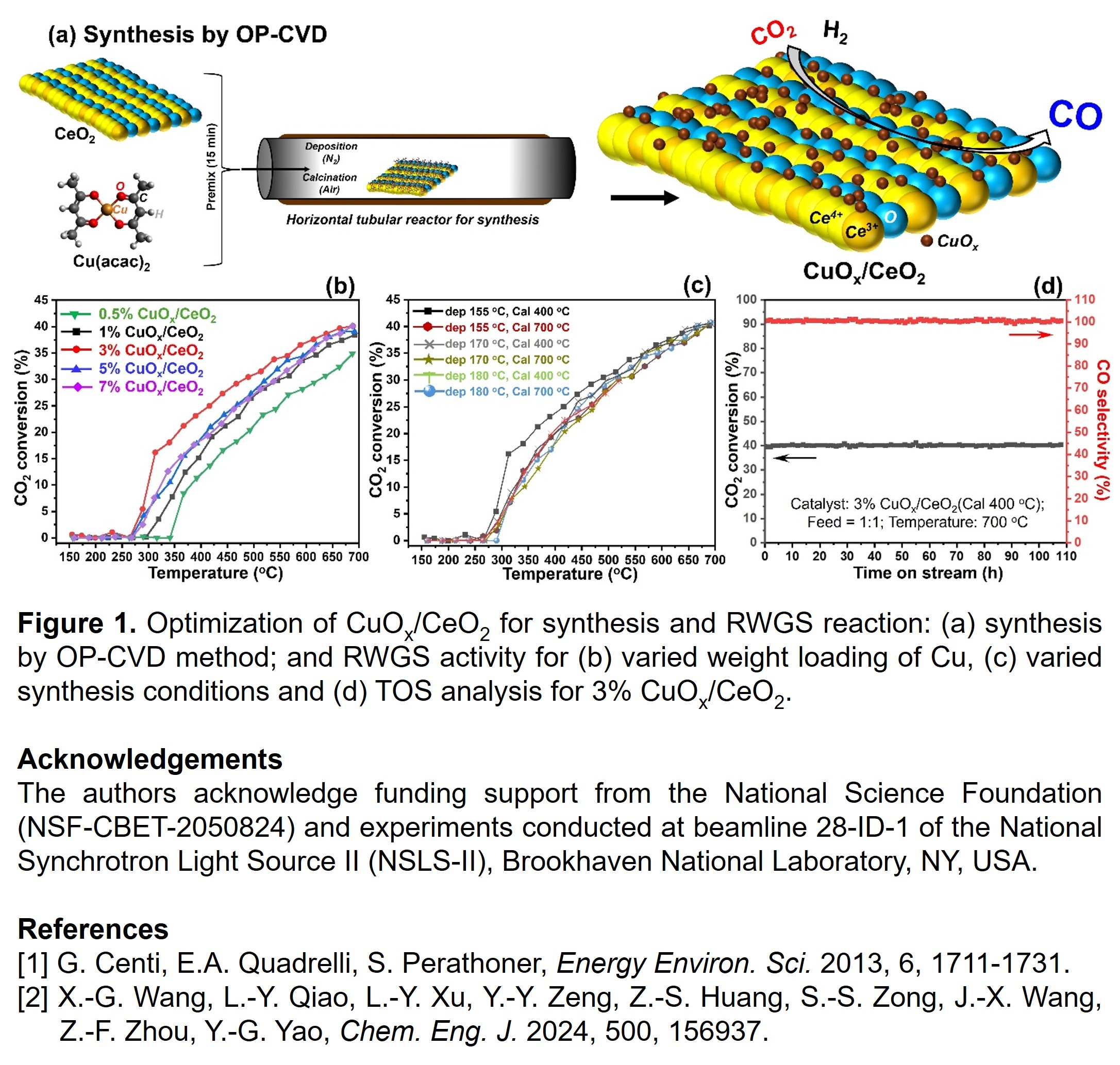
Reducing the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas, is critically important for rebuilding the current ecological system for a sustainable environment. Utilization of CO2 by hydrogenation, H2 as future clean source, via reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction seems a viable option [1]. The thermodynamically unfavorable and endothermic nature of RWGS reaction necessitates a selective catalytic reaction (SCR) for progress under mild conditions [2]. To serve this purpose, supported catalysts provide adequate active sites and high surface utilization. This study focuses on ceria supported copper oxide (CuOx/CeO2) catalysts to overcome the challenges faced by existing synthesis technologies, viz. severe agglomerations, inaccurate Cu loading, non-availability of active sites and surface, and ineffective metal support interaction (MSI), to achieve high catalytic performance. An optimized CuOx/CeO2 catalyst was developed by one-pot chemical vapor deposition (OP-CVD) method with deposition and calcination as major controlling steps. A varied conditions for weight loading of Cu (0.5 – 7 wt%), deposition (155 – 180 oC) and calcination (400 – 700 oC) were used. The prepared catalysts were characterized using BET-PSD, ICP-OES, CO chemisorption, XRD, STEM-EDS, and Raman spectroscopy to understand their structure and physical properties. The RWGS reaction activity results for 3% CuOx/CeO2, prepared at deposition: 155 oC and calcination: 400 oC, in CO2:H2 reactant feed of 1:1 (126,000 ml h-1 gcat-1) showed superior activity and was able to achieve equilibrium CO2 conversion at ~300 oC and thereafter (Figure1). A time on stream (TOS) analysis for 108 h proved the catalyst stability under long working conditions, and in-situ XRD proved catalysts’ structural stability. All the CuOx/CeO2 catalysts showed 100% selectivity for RWGS (only CO), without any methanation side reaction (Figure1). Thus, the work effectively contributed to the development of optimal-synthesized and durable CuOx/CeO2 catalyst by OP-CVD to achieve high RWGS activity with clear structural approach.