2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(389a) Reproducible Construction of Crosslinked Polymers Via Mosdef: A Workflow for Molecular Simulations
Authors
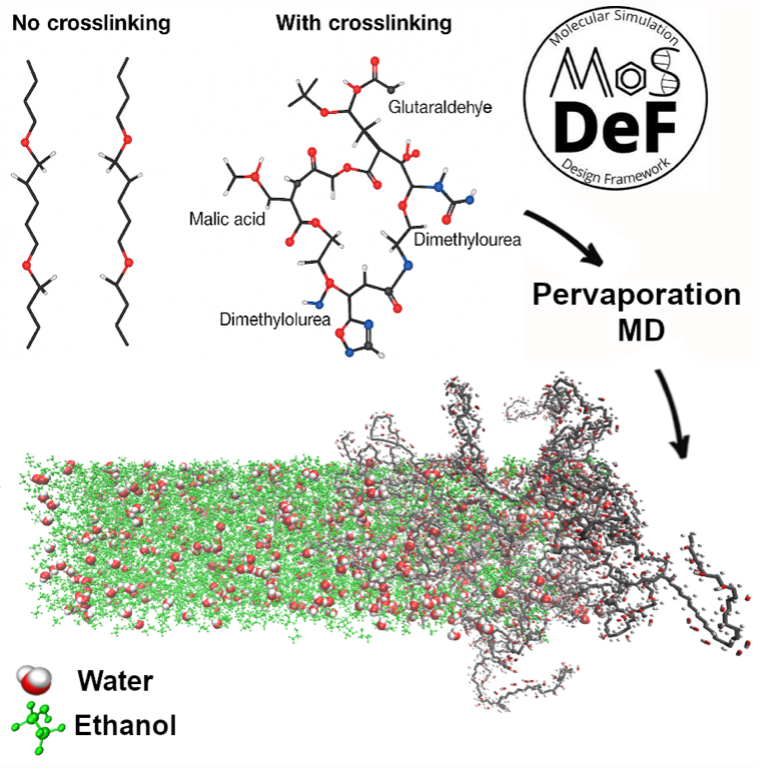
As a validation case, we apply the workflow to generate crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) membranes using glutaraldehyde, malic acid, and dimethylolurea, and evaluate their separation performance in a 90% water–ethanol mixture—motivated by the relevance of ethanol–water separation for renewable energy applications [4]—using pervaporation MD simulations. While both uncrosslinked and crosslinked PVA membranes have been experimentally tested for alcohol enrichment from aqueous mixtures [5,6], the influence of crosslink density and crosslinker identity remains underexplored. The observed transport trends and structural properties align with experimental expectations, demonstrating the robustness and predictive utility of the proposed workflow. This work establishes a generalizable and open-source methodology for systematic generation and evaluation of crosslinked polymers in molecular simulations.
References
- Klein, C. et al. A Hierarchical, Component Based Approach to Screening Properties of Soft Matter. In Foundations of Molecular Modeling and Simulation; Snurr, R. Q., Adjiman, C. S., Kofke, D. A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp 79–92.
- Cummings, P. T. et al. AIChE J. 2021, 67 (3), e17206.
- Thompson, M. W. et al. Phys. 2020, 118 (9–10), e1742938.
- Lively, R. P.; Sholl, D. S. Mater. 2017, 16 (3), 276–279.
- Wu, C. Polymer 2010, 51 (19), 4452–4460.
- Cheng, X. et al. RSC Adv. 2019, 9 (27), 15457–15465.