2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(643e) Optimizing Reverse Electrodialysis Design and Operation for Renewable Electricity Generation from Salinity Gradients
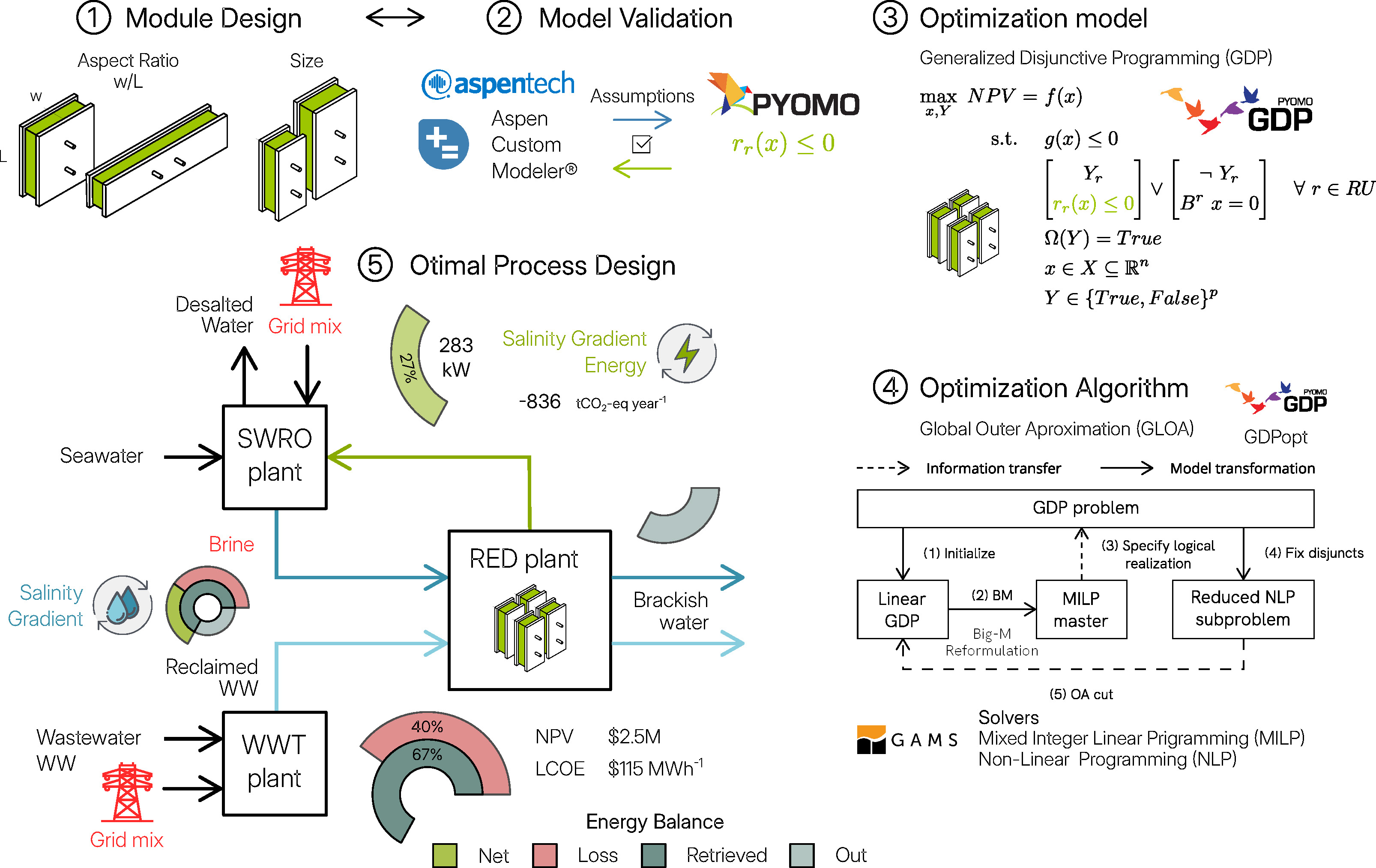
Figure 1 Impact of scaling and shape of RED units on the optimal design and techno-economic assessment of reverse electrodialysis (RED) plant drawing electricity from the salinity gradient between seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) desalination brine and reclaimed wastewater (WW) effluent from a WW treatment plant.
References
[1] S. Chae, H. Kim, J. Gi Hong, J. Jang, M. Higa, M. Pishnamazi, J.Y. Choi, R. Chandula Walgama, C. Bae, I.S. Kim, J.S. Park, Clean power generation from salinity gradient using reverse electrodialysis technologies: Recent advances, bottlenecks, and future direction, Chem. Eng. J. 452 (2023) 139482. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2022.139482.
[2] Q. Chen, I.E. Grossmann, Recent Developments and Challenges in Optimization-Based Process Synthesis, Https://Doi.Org/10.1146/Annurev-Chembioeng-080615-033546 8 (2017) 249–283. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV-CHEMBIOENG-080615-033546.
[3] C. Tristán, M. Fallanza, R. Ibáñez, I. Ortiz, I.E. Grossmann, A generalized disjunctive programming model for the optimal design of reverse electrodialysis process for salinity gradient-based power generation, Comput. Chem. Eng. 174 (2023) 108196. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2023.108196.
[4] C. Tristán, M. Fallanza, I. Ortiz, R. Ibáñez, I.E. Grossmann, Cost-optimal design of reverse electrodialysis process for salinity gradient-based electricity generation in desalination plants, Energy 313 (2024) 134005. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2024.134005.
[5] M. Tedesco, A. Cipollina, A. Tamburini, G. Micale, Towards 1 kW power production in a reverse electrodialysis pilot plant with saline waters and concentrated brines, J. Memb. Sci. 522 (2017) 226–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.09.015.
[6] R.A. Tufa, S. Pawlowski, J. Veerman, K. Bouzek, E. Fontananova, G. di Profio, S. Velizarov, J. Goulão Crespo, K. Nijmeijer, E. Curcio, Progress and prospects in reverse electrodialysis for salinity gradient energy conversion and storage, Appl. Energy 225 (2018) 290–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2018.04.111.
[7] M. Yasukawa, S. Mehdizadeh, T. Sakurada, T. Abo, M. Kuno, M. Higa, Power generation performance of a bench-scale reverse electrodialysis stack using wastewater discharged from sewage treatment and seawater reverse osmosis, Desalination 491 (2020) 114449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114449.
[8] C. Tristán, M. Fallanza, R. Ibáñez, I. Ortiz, Recovery of salinity gradient energy in desalination plants by reverse electrodialysis, Desalination 496 (2020) 114699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114699.
[9] R. Ortiz-Imedio, L. Gomez-Coma, M. Fallanza, A. Ortiz, R. Ibañez, I. Ortiz, Comparative performance of Salinity Gradient Power-Reverse Electrodialysis under different operating conditions, Desalination 457 (2019) 8–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2019.01.005.
[10] W.E. Hart, C.D. Laird, J.-P. Watson, D.L. Woodruff, G.A. Hackebeil, B.L. Nicholson, J.D. Siirola, Pyomo — Optimization Modeling in Python, Second Edi, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58821-6.
[11] Q. Chen, E.S. Johnson, D.E. Bernal, R. Valentin, S. Kale, J. Bates, J.D. Siirola, I.E. Grossmann, Pyomo.GDP: an ecosystem for logic based modeling and optimization development, Optim. Eng. 23 (2022) 607–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-021-09601-7.
[12] S. Lee, I.E. Grossmann, A global optimization algorithm for nonconvex generalized disjunctive programming and applications to process systems, Comput. Chem. Eng. 25 (2001) 1675–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-1354(01)00732-3.
[13] Q. Chen, E.S. Johnson, J.D. Siirola, I.E. Grossmann, Pyomo.GDP: Disjunctive Models in Python, in: Comput. Aided Chem. Eng., Elsevier B.V., 2018: pp. 889–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64241-7.50143-9.