2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(180ad) A Multi-Scale Framework for Pressure/Vacuum Swing Adsorption System Design Using Machine Learning and Data-Driven Optimization
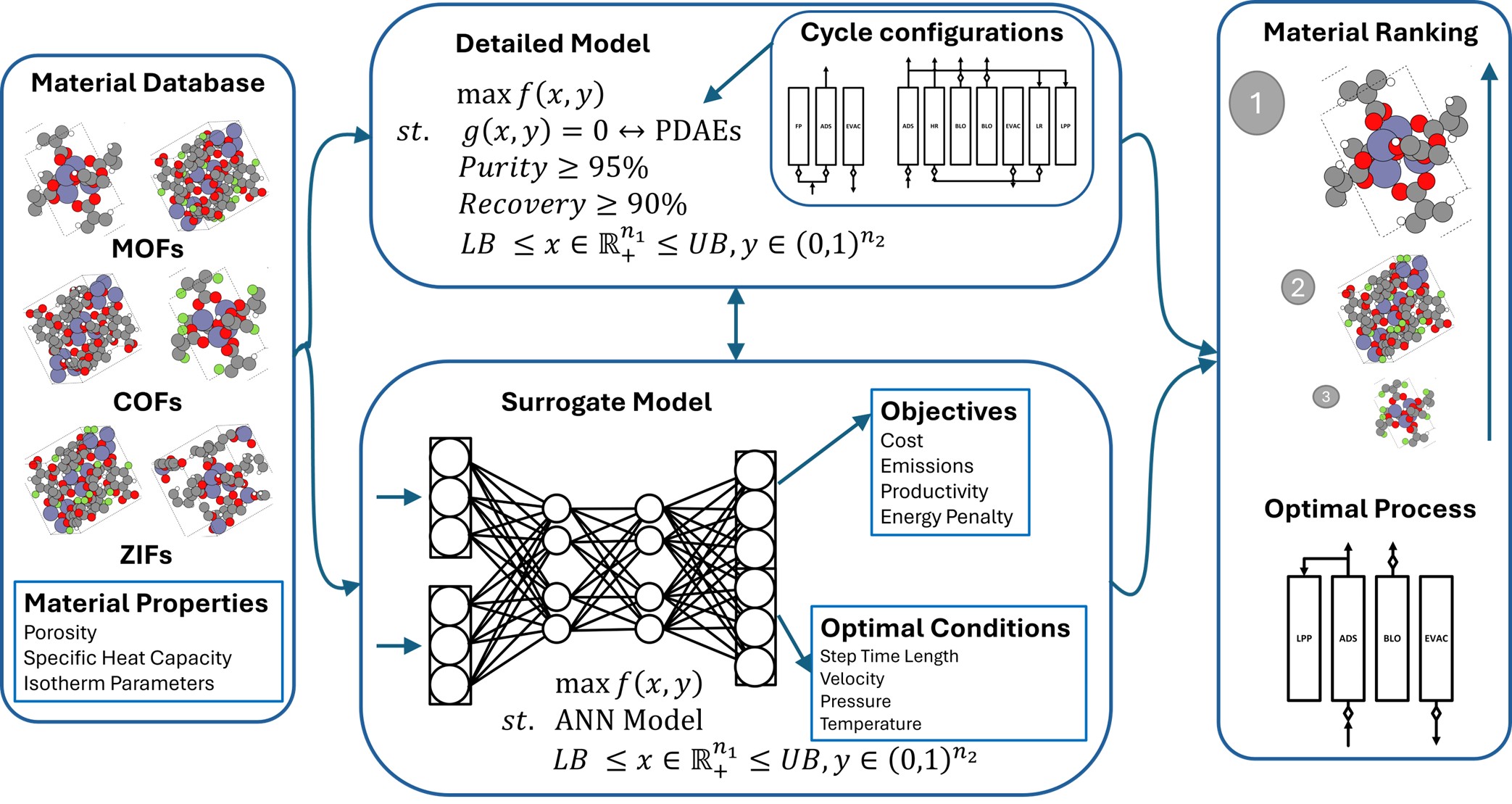
Pressure/Vacuum Swing Adsorption (P/VSA) systems are a promising alternative for energy-efficient gas separation, particularly in carbon capture applications. However, the complexity of sorbent selection, cycle design, and process optimization poses significant challenges. This work presents a multi-scale approach to P/VSA system design that integrates advanced modelling with data-driven optimization. A detailed mathematical framework is developed to incorporate cycle variability and process dynamics, capturing the intricate interplay between material properties and operating conditions. Machine learning techniques accelerate optimization while maintaining accuracy in navigating the large design space and computational challenges. Additionally, sorbent materials are systematically screened using cost and environmental impact criteria. By combining these elements, this study enhances the efficiency and feasibility of adsorption-based gas separation, offering new insights into material selection, process design, and sustainability. The findings contribute to developing next-generation P/VSA systems with improved performance and reduced environmental footprint.