2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(171d) A Multi-Agent Framework for Enhanced Chemical Process Fault Diagnosis: Integrating Intelligent Analysis, Visualization, and User-Centric Decision Support
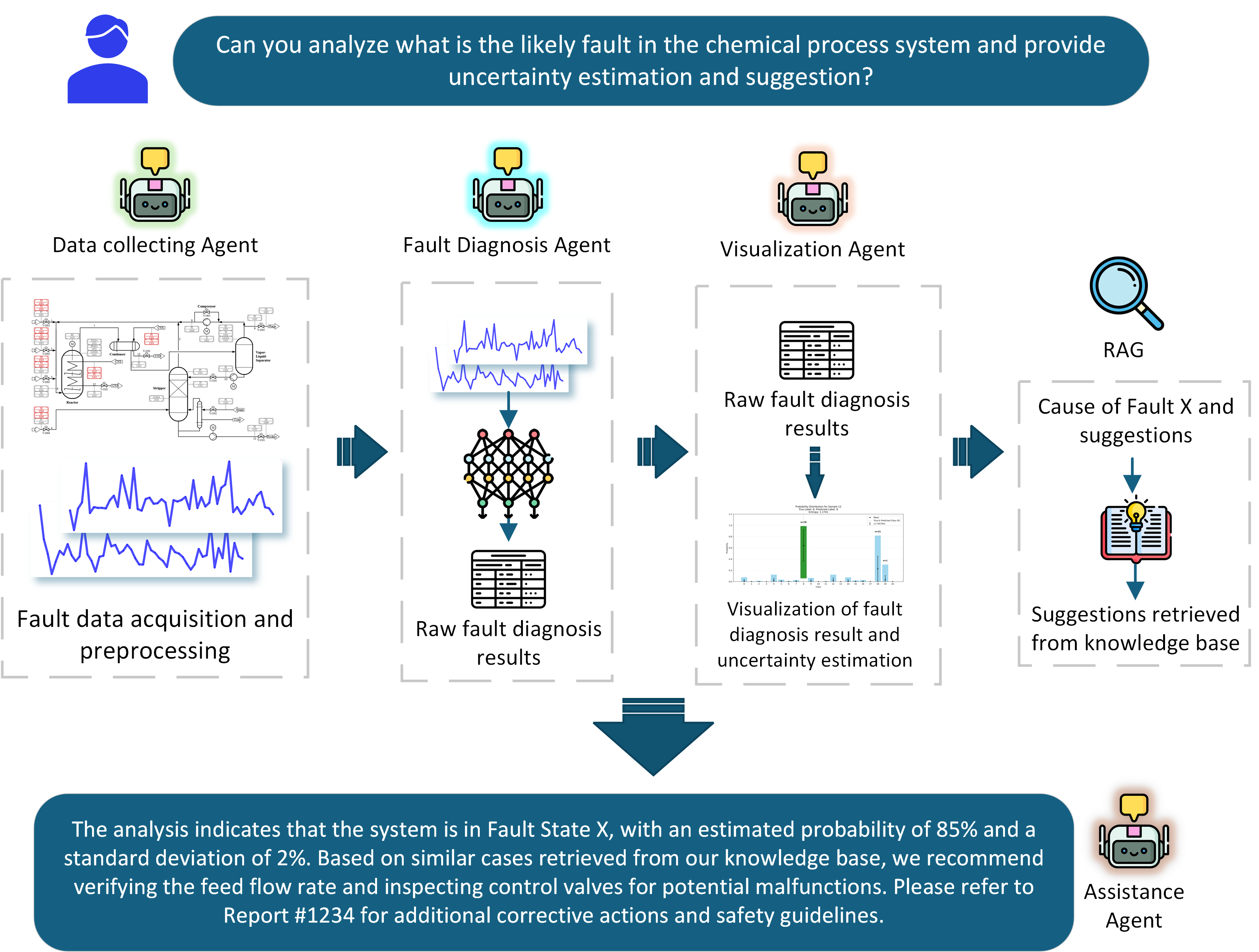
The proposed system follows a well-defined workflow comprising several agents that work in sequence. First, after receiving user input, a data-collecting agent gathers real-time data from the chemical process and performs necessary pre-processing to ensure data quality and consistency. Next, a fault diagnosis agent analyzes the processed data to identify potential faults, producing an initial set of results. Recognizing that these raw outputs are not immediately useful for operators, the framework introduces a visualization agent. This agent converts the complex diagnostic data into simple, easy-to-understand graphical representations such as bar charts, highlighting key aspects of the process state. The final stage of the workflow is handled by an LLM-based assistance agent. This agent synthesizes both the numerical and visual outputs into a plain language summary that clearly explains the diagnosed fault conditions. Importantly, the framework incorporates a RAG module that retrieves relevant historical cases and documented remedies from a knowledge base [3]. By integrating this information, the RAG module provides constructive suggestions, linking current faults to proven corrective actions. As a result, the output not only describes what is wrong but also offers guidance on how to respond.
A case study on the Tennessee Eastman process—a benchmark system in chemical process control—demonstrates the effectiveness of our framework. Compared to traditional methods, the integrated system delivers more meaningful outputs by automatically interpreting complex data and suggesting remedial actions based on past experiences. This enhanced integration significantly reduces the operator’s burden, allowing for quicker and more informed decision-making.
In conclusion, our multi-agent framework, enhanced with LLM capabilities and a RAG module, offers a promising improvement for chemical process fault diagnosis. It transforms raw diagnostic data into comprehensive, actionable insights, ultimately contributing to improved plant safety and operational efficiency.
References:
[1] Bao, Yu, et al. "Chemical process fault diagnosis based on a combined deep learning method." The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering 100.1 (2022): 54-66.
[2] Duan, Zhihua, and Jialin Wang. "Exploration of LLM Multi-Agent Application Implementation Based on LangGraph+ CrewAI." arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.18241 (2024).
[3] Lewis, Patrick, et al. "Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks." Advances in neural information processing systems 33 (2020): 9459-9474.