2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(465e) Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Multilayer hBN Formation on Molten Nickel
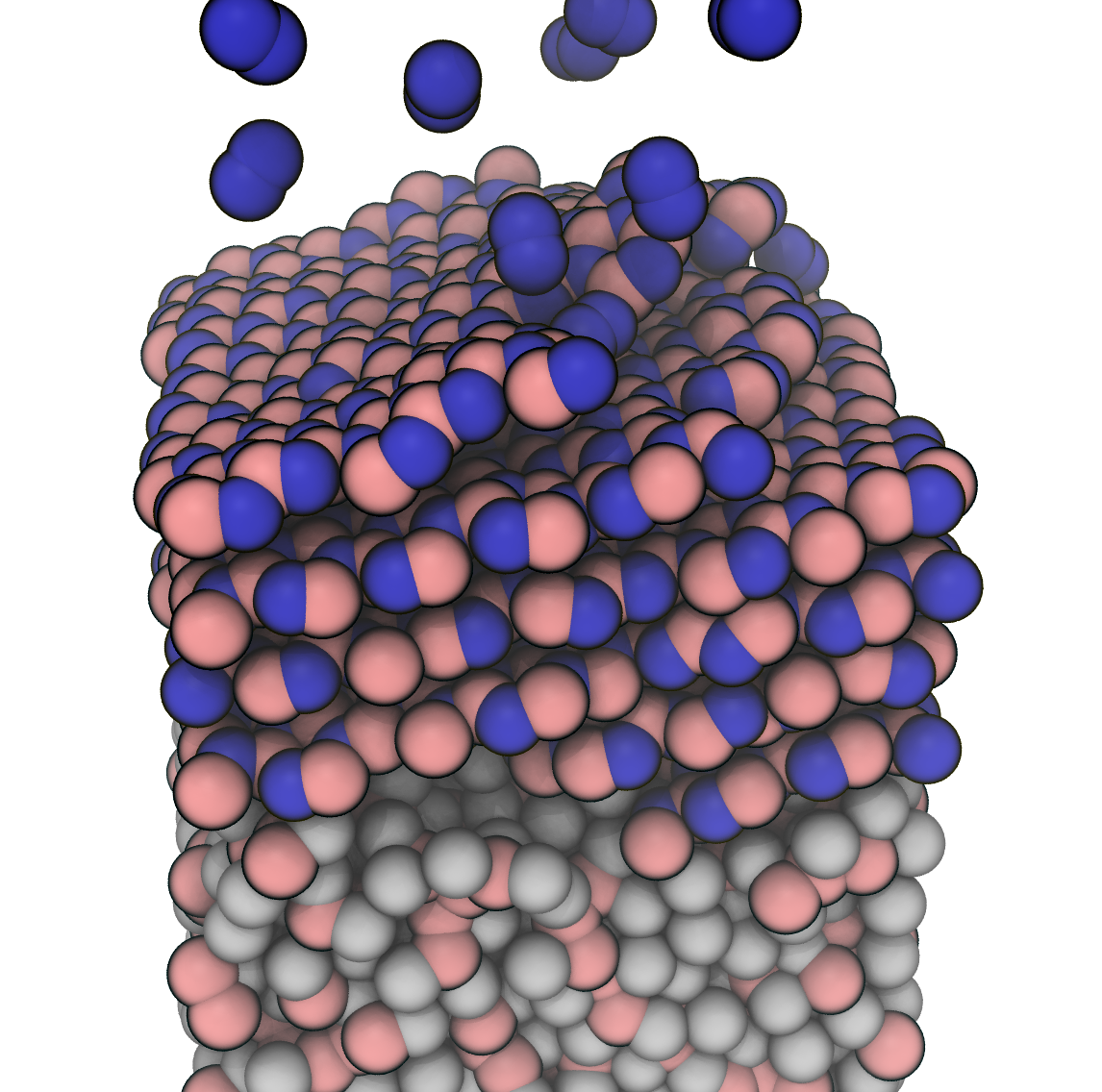
Our findings indicate that applying a fast cooling rate leads to rapid and extensive hBN growth, though the resulting structures tend to be disordered with partial defect formation. Interestingly, despite this disorder, fast cooling conditions yield the highest overall productivity in terms of hBN coverage when compared with constant-temperature scenarios. Additionally, we explore the conditions under which boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) spontaneously form, identifying specific temperature regimes favorable to tubular rather than planar hBN structures.
Furthermore, we analyze how variations in the employed forcefield parameters influence hBN formation, comparing different parameter sets to identify key factors controlling structural quality and productivity. These results provide valuable insights into both the fundamental growth mechanisms of hBN and practical considerations for optimizing synthesis conditions to achieve specific structural and morphological outcomes.