2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(333a) Membraneless Electrochemical Amine Regeneration: A Novel Two-Stage Process for Carbon Capture
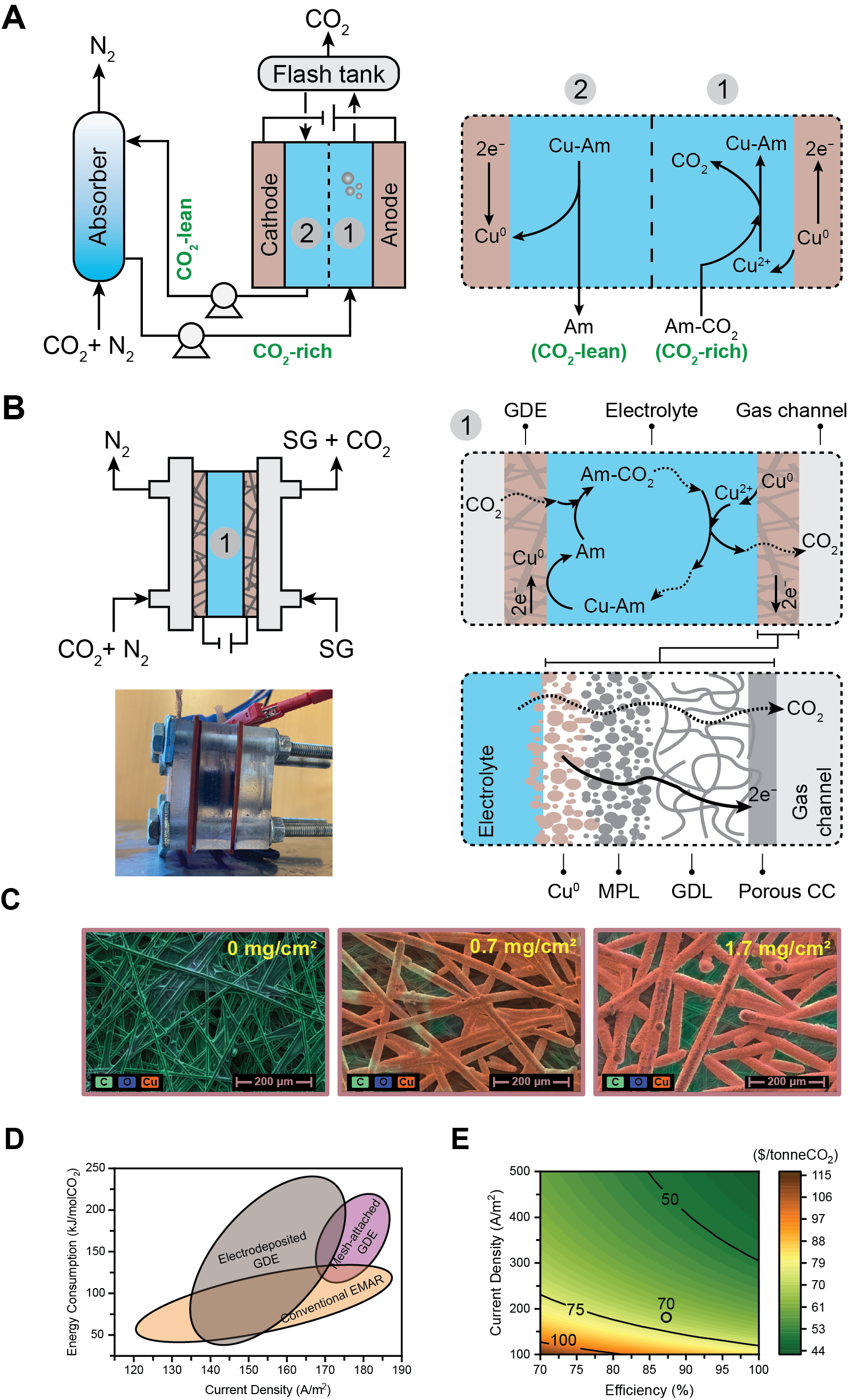
In this study, two types of GDE assemblies were used: mesh-attached and electrodeposited. Electrodeposited GDEs demonstrated superior performance, achieving CO2 removal efficiencies exceeding 90%, compared to 35–55% for mesh-attached GDEs. Copper loading for electrodeposited GDEs, was the determining factor; higher loadings resulted in lower carbon removal efficiency due to the copper layer acting as a physical barrier against CO2 transport. Optimal performance was achieved with a copper loading of 1.7 mg/cm2 on a Toray 060 gas diffusion layer (GDL), delivering 87% removal efficiency, 176 A/m2 current density, and 76 kJ/molCO2 energy consumption for flue gas (0.15 bar partial pressure, released at 1 bar). The detection of CO2 via online gas chromatography confirms the effectiveness of the system in selectively desorbing CO2 without side reactions or the co-transfer of other flue gas components i.e., N2 through the electrolyte.
Techno-economic analysis of the membraneless EMAR system indicated a levelized cost of carbon capture (LCOCC) of approximately $69.7/tonneCO2, about 50% lower than the $137/tonneCO2 for conventional membrane-based systems. Sensitivity analysis suggests that carbon capture costs may be reduced to as low as $50/tonneCO2 with further improvements in current density and removal efficiency. This two-stage EMAR system represents a significant advancement in electrochemical carbon capture technology, offering a simpler configuration, smaller footprint, and substantially lower costs compared to conventional systems, making it a promising solution for scalable point-source carbon capture.
References:
[1] A. Hassan et al., “Reviving the absorbent chemistry of electrochemically mediated amine regeneration for improved point source carbon capture,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 484, p. 149566, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.149566.
[2] M. Wang, R. Shaw, E. Gencer, and T. A. Hatton, “Technoeconomic Analysis of the Electrochemically Mediated Amine Regeneration CO2 Capture Process,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., vol. 59, no. 31, pp. 14085–14095, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02166.
[3] L. E. Clarke, M. E. Leonard, T. A. Hatton, and F. R. Brushett, “Thermodynamic Modeling of CO2 Separation Systems with Soluble, Redox-Active Capture Species,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., vol. 61, no. 29, pp. 10531–10546, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.1c04185.
[4] M. Wang, S. Hariharan, R. A. Shaw, and T. A. Hatton, “Energetics of electrochemically mediated amine regeneration process for flue gas CO2 capture,” International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, vol. 82, pp. 48–58, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2018.12.028.