2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(376c) Joule-Heated Multi-Wire Reactor for Steam-Methane Reforming: Modeling Study for the Commercial-Scale
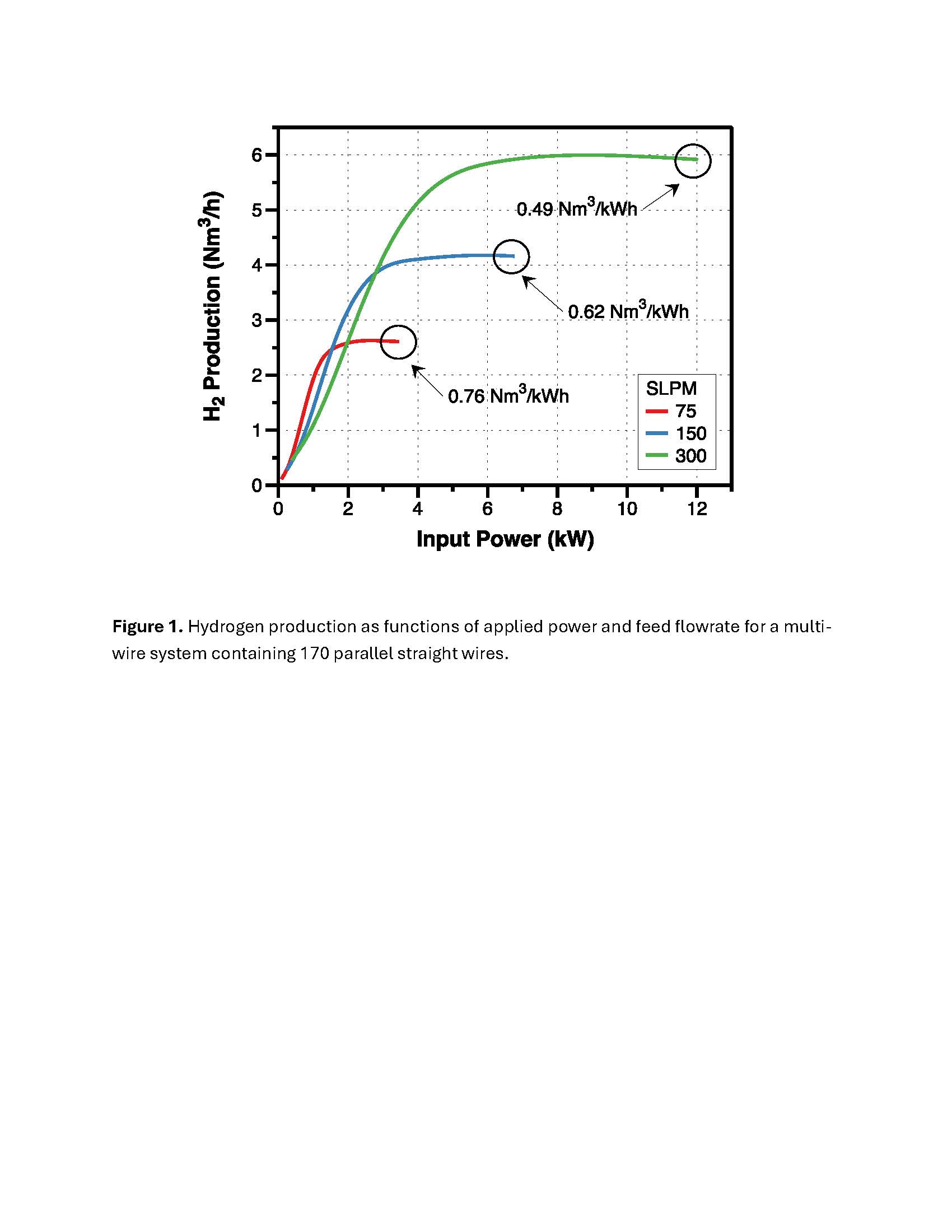
In this modeling study, we examine a potential industrial-scale, multi-wire electrified reactor for SMR, wherein the electrification is through Joule heating. We first determine the optimal thermodynamic conditions to conduct the power-to-hydrogen process. Under both adiabatic and non-adiabatic cases, we then present a detailed parametric study on the effect(s) of process parameters, viz. feed flowrate and temperature, applied power and distribution, catalyst coating configuration, wire material, multi-wire geometric configuration, on key performance indices such as methane conversion, hydrogen production, fluid temperature, and fluid velocity profile. Fig. 1 shows example results of the calculated hydrogen production as a function of input power to a bank of 170 parallel Ni/ZrO2 coated FeCrAl rods. Results shown in Fig. 1 were computed from a multi-physics simulation incorporating weakly compressible laminar flow, mass transfer, and convective heat transfer in the fluid domain; conductive heat transfer with Joule heating in the solid domain of parallel rods; and heterogeneous reactions taking place on the surfaces of the rods. Finally, we present the technical feasibility of the proposed reactor configuration which will have significant relevance to the hydrogen generation sector as it makes attempts to reduce its carbon footprint.