2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(72g) Invited Talk: Strengthening Antisense Oligonucleotide-Mediated Anti-Tumor Immunity Via Metal-Organic Framework Gene Delivery
Authors
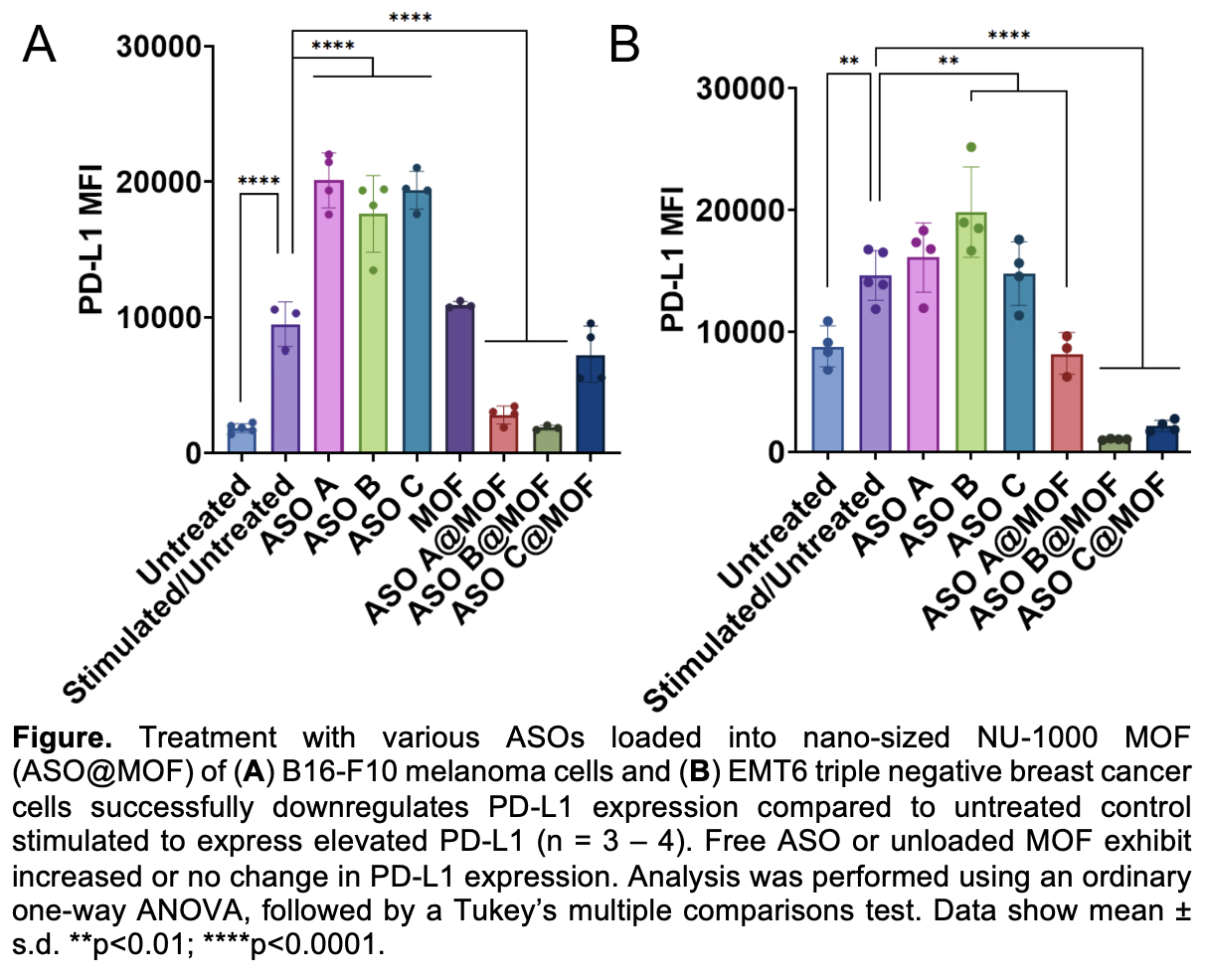
Specifically herein, we synthesized three distinct PD-L1-specific ASOs that were cited in past literature to be specific towards targeting the PD-L1 gene. We loaded the three different sequences individually into 100-200 nm NU-1000 MOFs, averaging ~80% encapsulation efficiency and high loading quantities (ca. 9 nmol/mg MOF) regardless of the oligonucleotide sequence. We successfully sustained the release of encapsulated ASOs up to 7 days ex cellulo, which advantageously positions this platform well for reduced and more infrequent dosing compared to current alternatives. MOF encapsulation increased ASO potency and reduced PD-L1 expression ~3-fold and 2-fold in triple negative breast cancer EMT6 and melanoma B16-F10 cells, respectively. Understanding that PD-L1 is expressed on more than just cancer cells but also on healthy immune cells, we evaluated the impact of MOF-delivered ASOs on PD-L1-expressing immune cells. Here, we observed ca. 12-fold increases in dendritic cell co-stimulatory marker expression, and elevated T cell activation and proliferation compared to untreated cells (4-fold and 10-fold, respectively). These propagated responses were not observed by free ASO treatment. Notably, these changes drove a 3-fold increase in B16-F10 caspase-3 expression, a key mediator for apoptosis. Treatment with free ASO or unloaded MOF did not significantly increase the expression of caspase-3 in tumor cells. This research highlights a two-pronged approach for how MOF encapsulation of PD-L1-specific ASOs can impact both tumor and immune cell activity for enhancing propagated anti-tumor immunity. This work also shows how MOFs can be harnessed to bypass ASO limitations without requiring sequence modifications and reducing the necessary required dose. We offer a broadly applicable platform for improved oligonucleotide delivery for various genes of interest across different cancers.
1Nowak, J.A., Cho, E., Davis, M.A., Zheng, S., Bell, L., Sha, F., Magdalenski, J.S., Farha, O.K., Teplensky, M. H. BioRxiv. 2025/645811.