2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(189ad) Intrinsically Stable MXene Inks for Electrohydrodynamic Jet-Printed Energy Storage Devices with high Volumetric Capacitance
Authors
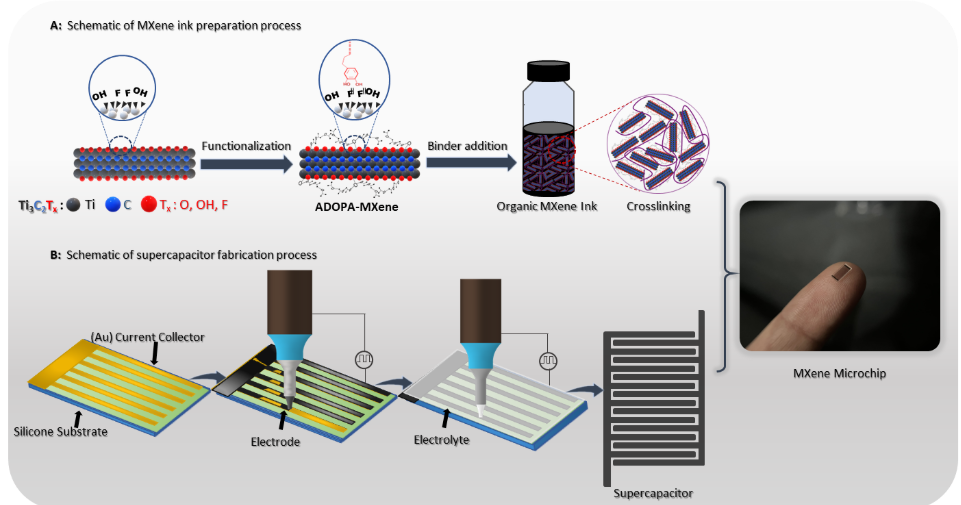
Utilizing the high precision of EHD jet printing, we fabricated interdigitated micro-supercapacitor electrodes achieving an unprecedented feature size of <100 µm width and gap, significantly outperforming existing technologies. The resulting MSC devices exhibited a high volumetric capacitance of above 1500 F/cm³, the highest reported to date for printed supercapacitors. Complementary Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations confirmed strong charge transfer interactions between ADOPA ligands and MXene surfaces, underpinning the ink's exceptional oxidation and dispersion stability.
In summary, this research introduces a robust methodology for developing intrinsically stable MXene inks tailored explicitly for EHD printing, significantly advancing the capabilities and practical scalability of MXene-based printable energy storage devices. The outcomes lay the groundwork for future explorations into high-resolution, scalable, and sustainable printed electronics applications, marking a transformative step forward in microelectronics and energy storage technologies.
Keywords: MXene, Micro-supercapacitor, Electrohydrodynamic jet printing, Oxidation stability, Printable electronics
Figure - Schematic illustration of printable MXene ink synthesis and EHD jet printing of symmetric interdigitated MSC: a) Synthesis of MXene in via series of steps including chemical etching of MXene flakes, surface functionalization of MXene flakes, and ink formulation with binder addition in organic solvent b) EHD jet printing of ADS-MXene(CMC) ink on glass substrate with gold current collectors followed by electrolyte deposition resulting in MXene microchip.