2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(677d) Integrating Physical Principles with Machine Learning for Predicting Field-Enhanced Catalysis
Authors
Runze Zhao - Presenter, University of Massachusetts Lowell
Qiang Li, University of Massachusetts Lowell
Zhu Cheng, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Fanglin Che, University of Massachusetts Lowell
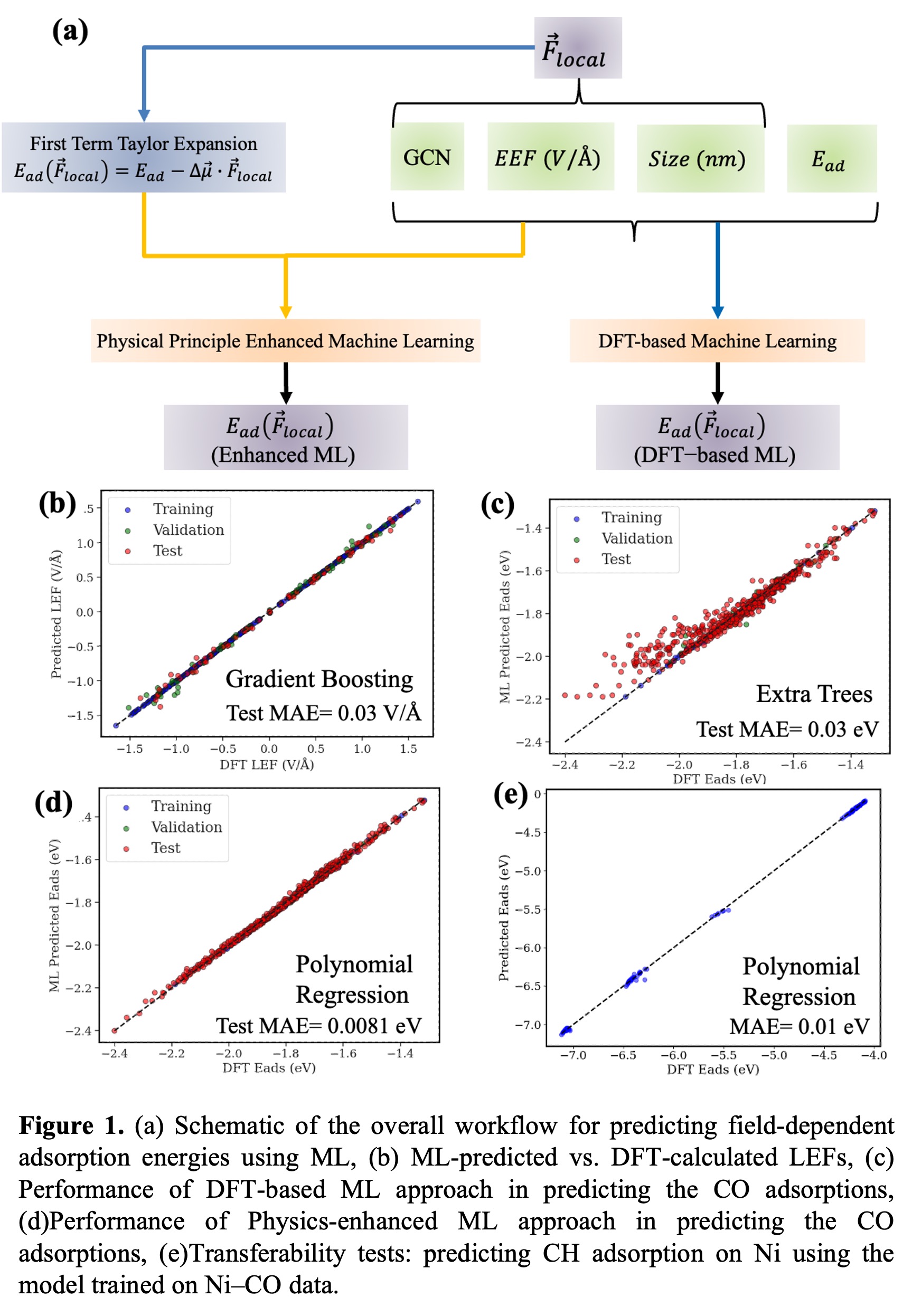
Field-dipole interactions can significantly alter the energetics of polarized species on catalyst nanoparticles (NPs) for renewable energy technologies, potentially boosting the efficiency of desired reactions by several orders of magnitude compared to conventional heating. However, strong local electric fields (LEFs) around sharp NP edges and the field-dependent adsorption on these NPs are not yet well-understood, and the computational costs to study these effects are extremely high. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel workflow (Figure 1a) that combines density functional theory (DFT) calculations, DFT-based CO vibrational Stark effects, and physics principles enhanced machine learning (ML) for rapid prediction of LEFs and adsorption energies1. Our ML model accurately estimates LEFs based on NP size, generalized coordination number (GCN), and external electric fields (EEFs), achieving near-DFT accuracy (MAE ~0.03 V/Å, Figure 1b) with significantly reduced computational cost. Purely data-driven ML models predict adsorption energies under varying EEFs with moderate accuracy (MAE ~0.03 eV, Figure 1c). By incorporating physical laws through first-order Taylor expansions, our physics-enhanced ML model achieves significantly improved accuracy (MAE ~0.0081 eV, Figure 1d) with fewer data points. Our ML models also exhibit strong transferability to previously unseen systems, such as accurately forecasting field-dependent CH adsorption on Ni surfaces (MAE ~0.01 eV, Figure 1e). Analysis reveals that EEF, GCN, and NP size are the primary determinants of LEFs, with low-coordinated sites and smaller nanoparticles enhancing LEFs approximately four-fold compared to flat surfaces, significantly influencing catalytic energetics. By integrating ab initio modeling with ML, our method rapidly and accurately forecasts field-driven adsorption energetics at various NP sites, opening new avenues for fundamentally guided catalyst design rather than empirical trial-and-error approaches.
Reference:
(1) Zhao, R.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Che, F. Integrating Physical Principles with Machine Learning for Predicting Field-Enhanced Catalysis. JACS Au 2025. DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00901.