2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(392b) Integrated Optimization of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Networks: A Mixed-Integer Programming Framework for Strategic Vendor and Transportation Management
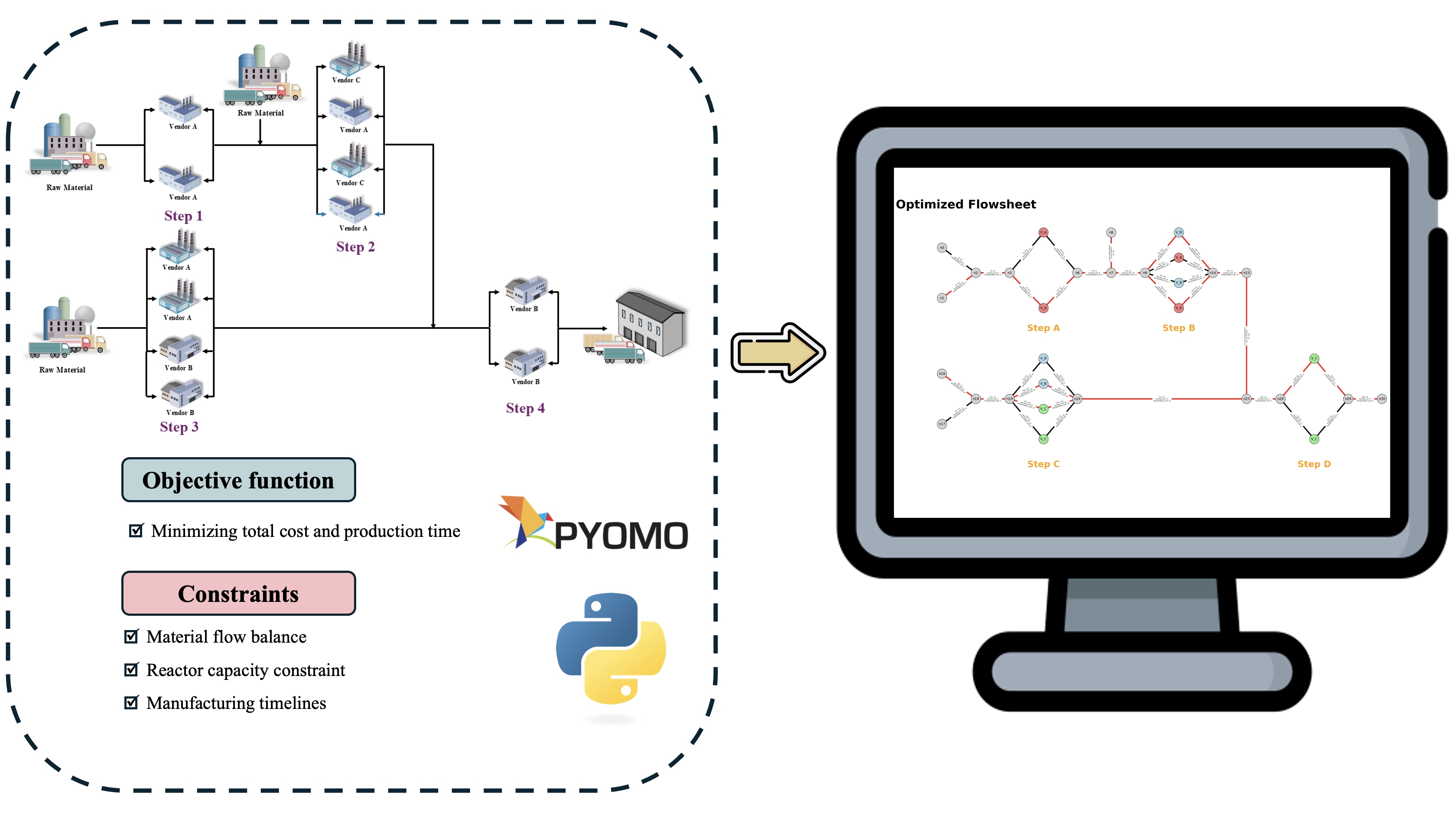
This research applies a mathematical programming approach, integrating planning and transportation within the pharmaceutical supply chain context.3,4 The multi-stage manufacturing process is modeled as a series of steps, each potentially handled by different vendors with distinct processing times and costs. We formulated this scenario as a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) problem, using variables representing material flows and vendor-task assignments. The objective is to minimize either total cost or overall production time, thereby evaluating the network efficiency.
Key constraints include material flow balance, vendor capacity limitations, total product demand, and manufacturing timelines. The formulation also accounts for transportation between vendors handling sequential tasks and considers scenarios where multiple vendors collectively meet product demands. Additionally, the developed framework provides functionality for visualizing the process network based on available vendors and their capabilities.5
The framework generates a ranked portfolio of optimal solutions for user assessment. As an open-source tool implemented entirely in Python, available at [https://github.com/SECQUOIA/Pharma-optimization-flowsheet] 6, it significantly supports practical decision-making by addressing real-world industrial problems. Various scenarios were evaluated using both open-source and commercial MILP solvers, demonstrating the flexibility, scalability, and practicality of this approach.
Reference:
1. Ritchey, L. CMO Quality Management Insights . Pharmaceutical Outsourcing - The Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biopharmaceutical Contract Services 26, 20–21 (2025).
2. Shah, N. Pharmaceutical supply chains: key issues and strategies for optimisation. Comput Chem Eng 28, 929–941 (2004).
3. Wang, J., Liu, Z. & Li, F. Integrated production and transportation scheduling problem under nonlinear cost structures. Eur J Oper Res 313, 883–904 (2024).
4. Ye, Y., Liang, S. & Zhu, Y. A mixed-integer linear programming-based scheduling model for refined-oil shipping. Comput Chem Eng 99, 106–116 (2017).
5. Hagberg, A. A., Schult, D. A. & Swart, P. J. Exploring Network Structure, Dynamics, and Function using NetworkX. in Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference (eds. Varoquaux, G., Vaught, T. & Millman, J.) 11–15 (Pasadena, CA USA, 2008).
6. Hart, W. E., Watson, J.-P. & Woodruff, D. L. Pyomo: modeling and solving mathematical programs in Python. Math Program Comput 3, 219–260 (2011)