2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(461e) Insights into the Adsorption Configurations of Para-Chloronitrobenzene and Its Impact on the Rates and Selectivities Towards Its Hydrogenation to Chloroaniline
Authors
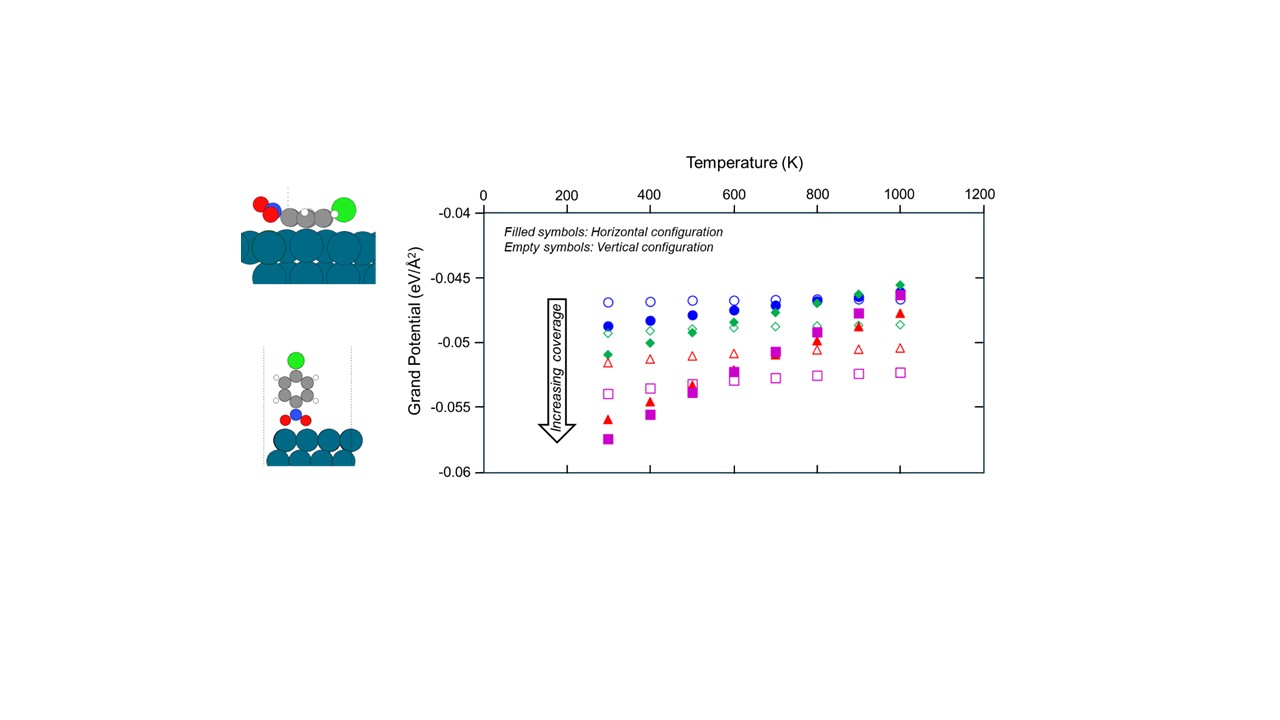
Experiments show that nitrobenzene adsorbs vertically on Pd through the oxygen atoms.1 However, our low-coverage density functional theory (DFT) calculations show that PCNB prefers to adsorb on Pd (111) such that the phenyl ring is parallel to the Pd slab at increasing coverages (from 1/24 ML to 1/6 ML) which contradicts the IR results. Grand potential calculations indicate that PCNB bound in a horizontal configuration remains more stable than the vertical mode at lower coverage at all temperatures (298-1000 K). The vertical mode becomes more stable at elevated temperatures with increasing coverage because of lower entropy loss at higher temperatures as compared to horizontal PCNB. Additionally, attractive interactions among vertically bound PCNB such as π-π interactions between adjacent phenyl rings and electrostatic interactions between neighbouring -NO2 groups further stabilize PCNB in the vertical mode as compared to the destabilizing repulsive interactions in the horizontal mode. These results illustrate the underlying reasons for the preference of PCNB to adsorb in a vertical binding configuration instead of horizontal even though the low-coverage DFT calculations suggest otherwise.
1. McCullagh, A.M., Gibson, E.K., Parker, S.F., Refson, K., Lennon, D., Chem. Chem. Phys., 2023, 25, 25993.