2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(387s) A High Throughput Microfluidic Platform for Accelerated Lipid Nanoparticles Synthesis and Screening: A First Step Towards Self-Driven Labs for Pharmaceutical Industries
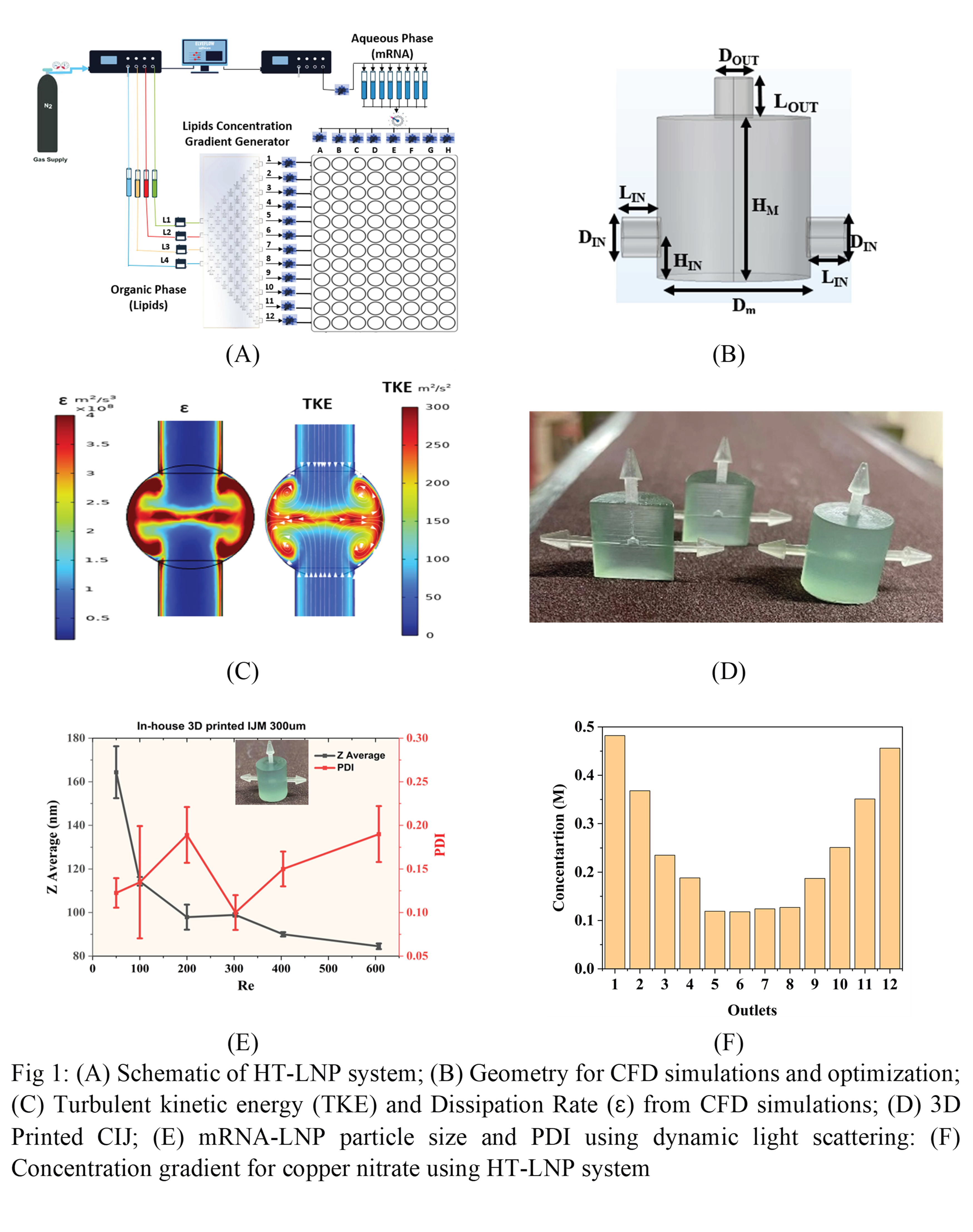
The global success of mRNA vaccines1,2 has established lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) as a gold standard for delivering nucleic acid therapeutics, including mRNA, siRNA, and DNA. However, traditional batch mixing approaches remain limited by low throughput, poor reproducibility, and inefficient optimization workflows, hindering rapid clinical translation. To address these limitations, we developed a novel High-Throughput Lipid Nanoparticle (HT-LNP) platform3 (Fig 1A), developed in-house, that integrates physics-informed Confined Impinging Jet (CIJ) micromixers4, an automated lipid composition generator (LCG), and a multiplexed pressure-driven fluid delivery system. This integrated platform is designed for rapid, scalable, and reproducible LNP synthesis with real-time control over critical quality attributes (CQAs) such as particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), and encapsulation efficiency5.
CIJ stands out for its capability to achieve mixing times below a millisecond due to turbulent mixing with higher energy dissipation rates6,7. However, the optimum design of CIJ depends upon design parameters (inlet tube diameter, mixer diameter, mixer height, outlet diameter) and process parameters (Reynolds number of inlet streams, inlet/outlet flow rate ratio). The energy dissipation rate is the most critical parameter for identifying the extent of mixing. However, it is difficult to quantify this using experimental techniques. CIJ micromixers were systematically optimized through 3D Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations8,9 to maximize turbulent kinetic energy and energy dissipation (Fig 1C). Optimized designs were fabricated via high-resolution 3D printing (Fig 1D) and validated experimentally. The lipid composition generator, also 3D-printed, enables automated blending of lipid components; its functionality was initially validated using copper nitrate solutions.
Key findings are:
- Measured using the Dynamic light scattering, particle size decreases with Re, while PDI increases. A sharp PDI rise occurs beyond Re > 300.
- Measured using the Ribogreen assay, both encapsulation efficiency and RNA concentration decrease with increasing Re.
- Measure using UV spectrometry: The concentration decreases towards the central channels as compared to the channels at the end.
The HT-LNP platform represents a significant leap forward in LNP process intensification, offering both throughput and precision. More importantly, it lays the foundation for self-driven laboratories in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where closed-loop optimization, real-time analytics, and modular automation converge to accelerate therapeutic development.