2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(180ay) An Experimental and Modeling Study of Triethylenetetramine Functionalized Carbon Nanofibers for CO2 Capture
Author
Puspendu Sardar - Presenter, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Kharagpur
Clean air to breathe is a fundamental need for all living creatures. Global environmental issues
have arisen as a consequence of the excessive release of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon
dioxide (CO2) pollution [1]. One of the most effective ways to fight climate change and global
warming while also encouraging long-term economic growth is not only by capturing CO2 from
source but also from ambient air i.e., Direct Air Capture (DAC) [2]. CO2 adsorption in the open
air is essential for reducing the atmospheric CO2 concentration and averting global climate change.
The structural modification of adsorbents with amine is a new attractive strategy to enhance their
CO2 uptake capacity under low pressure. In this study, the copper nanoparticles grown carbon
nanofibers supported on activated carbon fiber (Cu-CNF/ACF) integrated Nano adsorbent was
selected as the base material owing to its outstanding CO2 uptake capacity, large specific surface
area, and excellent thermal and chemical stability. The nanocomposite was synthesized and
functionalized with triethylenetetramine (TETA) at varying loadings (20%, 30%, and 40%) via a
wet impregnation process. The nanomaterials were thoroughly characterized using a
comprehensive set of analytical techniques, including HRXRD, Micro-Raman spectroscopy,
FTIR, FESEM, HRTEM, EDS, XPS, BET, and CHNS analysis. CO2 adsorption performance was
assessed using an iSorb HP2 high-pressure sorption system under variable pressure (0-30 bar) and
temperature (25-80 °C) conditions. Experimental CO2 uptake data were correlated and predicted
using various mathematical isotherm models. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) based on the
Box-Behnken Design (BBD) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) supervised the experimental
design, which aimed to optimize three variables: adsorption temperature, CO2 partial pressure,
and TETA content. Notably, the 30% TETA incorporated Cu-CNF/ACF exhibited a remarkable
CO2 uptake capacity of 4.876 mmol/g, marking an enhancement of roughly 1.58-fold over the unmodified Cu-CNF/ACF nanocomposite (3.085 mmol/g) under standard conditions of 25 ᵒC and
1 bar.
Keywords: TETA functionalized Cu-CNF/ACF nanocomposite; CO2 adsorption; Modeling;
Breakthrough analysis; Heat of adsorption study.
have arisen as a consequence of the excessive release of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon
dioxide (CO2) pollution [1]. One of the most effective ways to fight climate change and global
warming while also encouraging long-term economic growth is not only by capturing CO2 from
source but also from ambient air i.e., Direct Air Capture (DAC) [2]. CO2 adsorption in the open
air is essential for reducing the atmospheric CO2 concentration and averting global climate change.
The structural modification of adsorbents with amine is a new attractive strategy to enhance their
CO2 uptake capacity under low pressure. In this study, the copper nanoparticles grown carbon
nanofibers supported on activated carbon fiber (Cu-CNF/ACF) integrated Nano adsorbent was
selected as the base material owing to its outstanding CO2 uptake capacity, large specific surface
area, and excellent thermal and chemical stability. The nanocomposite was synthesized and
functionalized with triethylenetetramine (TETA) at varying loadings (20%, 30%, and 40%) via a
wet impregnation process. The nanomaterials were thoroughly characterized using a
comprehensive set of analytical techniques, including HRXRD, Micro-Raman spectroscopy,
FTIR, FESEM, HRTEM, EDS, XPS, BET, and CHNS analysis. CO2 adsorption performance was
assessed using an iSorb HP2 high-pressure sorption system under variable pressure (0-30 bar) and
temperature (25-80 °C) conditions. Experimental CO2 uptake data were correlated and predicted
using various mathematical isotherm models. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) based on the
Box-Behnken Design (BBD) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) supervised the experimental
design, which aimed to optimize three variables: adsorption temperature, CO2 partial pressure,
and TETA content. Notably, the 30% TETA incorporated Cu-CNF/ACF exhibited a remarkable
CO2 uptake capacity of 4.876 mmol/g, marking an enhancement of roughly 1.58-fold over the unmodified Cu-CNF/ACF nanocomposite (3.085 mmol/g) under standard conditions of 25 ᵒC and
1 bar.
Keywords: TETA functionalized Cu-CNF/ACF nanocomposite; CO2 adsorption; Modeling;
Breakthrough analysis; Heat of adsorption study.
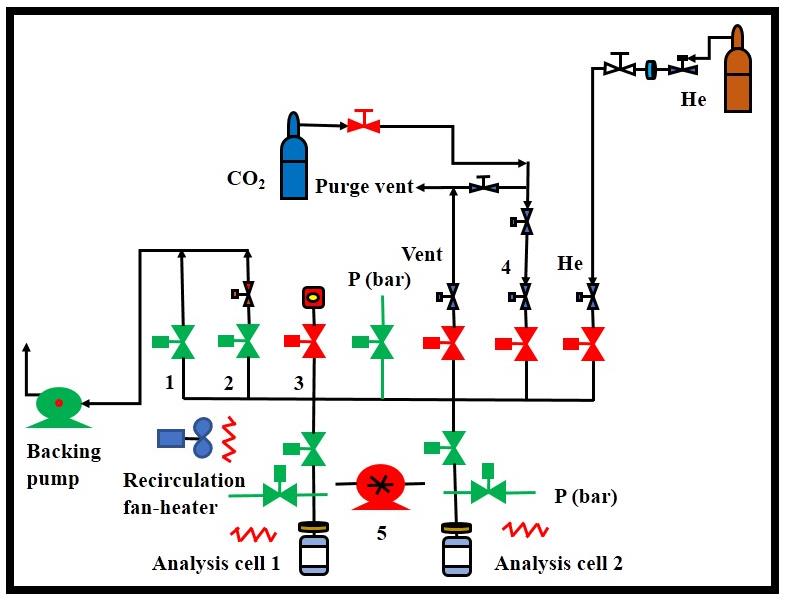
The iSorbHP2 schematic is depicted in the main window of the software: (1) Coarse vacuum, (2)
Fine vacuum, (3) Calibrated sampler cell, (4) CO2 adsorbate gas, (5) Thermostatic circulator.
References
[1] P. Sardar, G. Bhattacharya, R. Manna, S. Raj, S. Rahut, A. Nath Samanta, Excellent CO2
adsorption performance of amine-impregnated highly porous ZIF-8 adsorbent:
Experimental and isotherm modeling studies, Adv. Powder Technol. 35 (2024) 104344.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2024.104344.
[2] N. Bera, P. Sardar, A.N. Samanta, N. Sarkar, Arginine-Based Ionic Liquid in a WaterDMSO
Binary
Mixture
for
Highly
Efficient
CO2
Capture
from
Open
Air,
Energy
and
Fuels.
38
(2024)
1281–1287.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c03647.