2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
Electrochemical Water Splitting Using MnO2 and TiO2 for H2 Generation
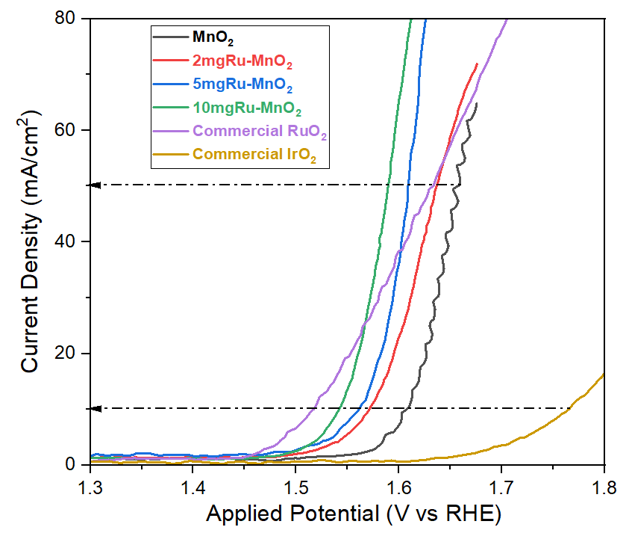
Hydrogen represents a clean and powerful energy carrier, but large-scale production remains limited by the high cost of water-splitting catalysts. While noble metals offer excellent activity, their expense restricts commercial viability. Transition-metal-based catalysts provide a promising alternative by lowering reaction energy barriers at reduced cost. This study investigates MnO2 combined with RuO2 and TiO2 as potential oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts. Under alkaline conditions, MnO2 performance improved markedly when integrated with Ru, forming a Ru–MnO2 hybrid catalyst. Among all tested samples, pure MnO2 and commercial IrO2 exhibited the lowest OER activity, whereas Ru–MnO2 hybrids (2 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg loadings) achieved the highest performance. The enhanced electron transfer and favorable surface properties of the Ru–MnO2 hybrids highlight their potential for efficient and sustainable hydrogen generation.