2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(39b) Dry Surfactant-Modified Carbon Additives on the Electrical and Compaction Behaviour of Dry Mix for Dry Battery Electrode Coating
Authors
Rajasekar Krishnamoorthy, The University of Sheffield
Guo Jung Lian, The University of Sheffield
Rachel Smith, University of Sheffield
Denis Cumming, The University Of Sheffield
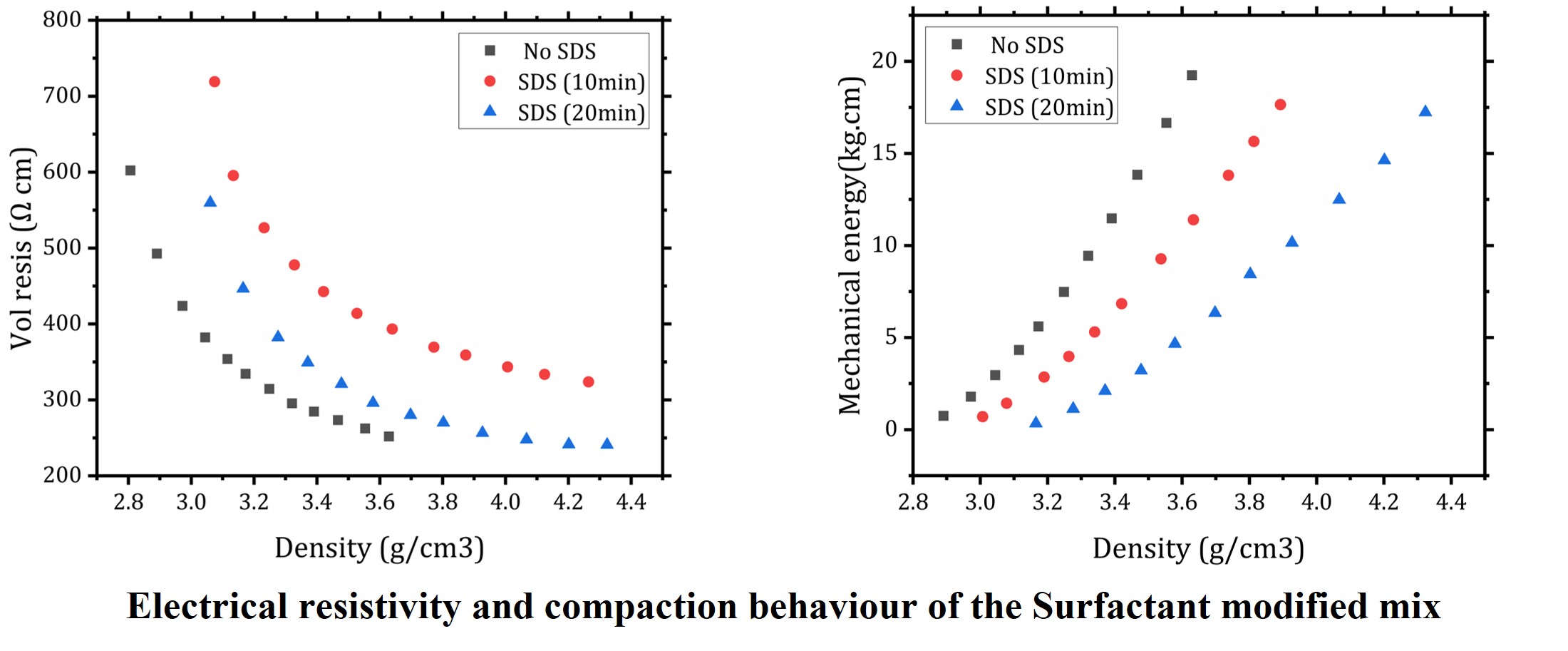
Electrical conductivity and rearranging of the active material particles during calendaring play a vital role in the dry-coated electrodes' mechanical and electrochemical properties and performance. The Van der Waals force and high surface energy of the carbon black leads to agglomerates of carbon with carbon and carbon with binder particles. The amphiphilic nature of the surfactants helps modify the carbon additives and their interaction with the active material. The present study used sodium dodecyl sulfate (0.3 Wt%) as a surfactant due to its interaction with carbon additives that favor the situation. Initially, the carbon additive is subjected to mechanical modification using the surfactant before it's added to the active material. The mix of surfactant-modified carbon additive, active material, and binder was subjected to high shear through a conventional dry mixing procedure with nobilta mechano-fusion. The formulated dry mix was then tested for its compression energy requirements, resistivity and compared with the traditional dry mix, showed the compression energy to achieve identical density is reduced by 25 to 30% from the traditional dry mix with very little compromise in the conductivity.