2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(417b) Development of a Fully Automated Supercapacitive Swing Adsorption (SSA) Process for Carbon Capture
Authors
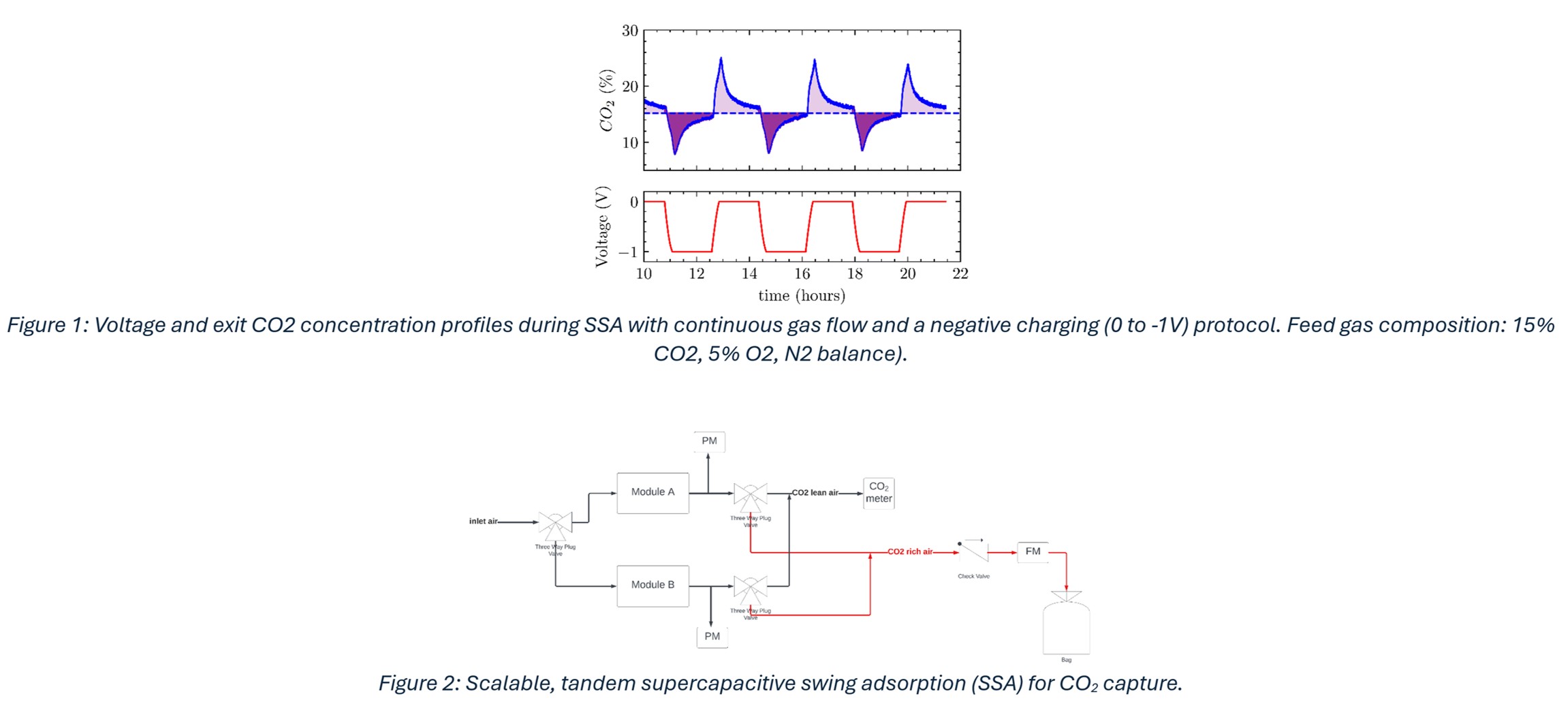
The capture of CO2 via SSA has been demonstrated in recent studies. These characterization studies provide insight into the effects of electrode material2,3, electrolyte composition4, oxygen content in feed gas5 and charging parameters6 on adsorption capacity and efficiency. However, the continuous production of a high purity CO2 stream via SSA for sequestration (or conversion into valuable chemicals) as in a commercial-scale plant, is yet to be addressed. To achieve this objective, we developed an automated SSA system (Figure 2) that extracts high purity CO2 from a continuous gas feed. Automated coordination between charge/discharge protocols of the dual module system and gas flow sequence is achieved with a programmable microcontroller. We present experimental results using this design with gas feed concentrations ranging from 15% to 400 part per million CO2. Valuable insight gleaned from our architecture will accelerate the development of pilot-scale and ultimately, commercial point source and direct air capture applications.
References
- Kokoszka, B., Jarrah, N.K., Liu, C., Moore, D.T., Landskron, K.: Supercapacitive swing adsorption of carbon dioxide. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 53(14), 3698–3701 (2014).
- Bilal, M., Li, J., Landskron, K.: Enhancing supercapacitive swing adsorption of CO2 with advanced activated carbon electrodes. Advanced Sustainable Systems 7(11), 2300250 (2023)
- Xu, Z., Mapstone, G., Coady, Z., Wang, M., Spreng, T.L., Liu, X., Molino, D.,Forse, A.C. Enhancing electrochemical carbon dioxide capture with supercapacitors. Nature Communications 15(1), 7851 (2024)
- Zhu, S., Li, J., Toth, A., Landskron, K.: Relationships between the elemental composition of electrolytes and the supercapacitive swing adsorption of CO2. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2(10), 7449–7456 (2019)
- Bilal, M., Li, J., Kumar, N., Mosevitzky, B., Wachs, I.E., Landskron, K.: Oxygen-assisted supercapacitive swing adsorption of carbon dioxide. Angewandte Chemie 136(39), 202404881 (2024)
- Binford, T.B., Mapstone, G., Temprano, I., Forse, A.C.: Enhancing the capacity of supercapacitive swing adsorption CO2 capture by tuning charging protocols. Nanoscale 14(22), 7980–7984 (2022)