2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(369a) A Design Framework for Optimizing Ligand Spatial Arrangement in Affinity Membranes
Authors
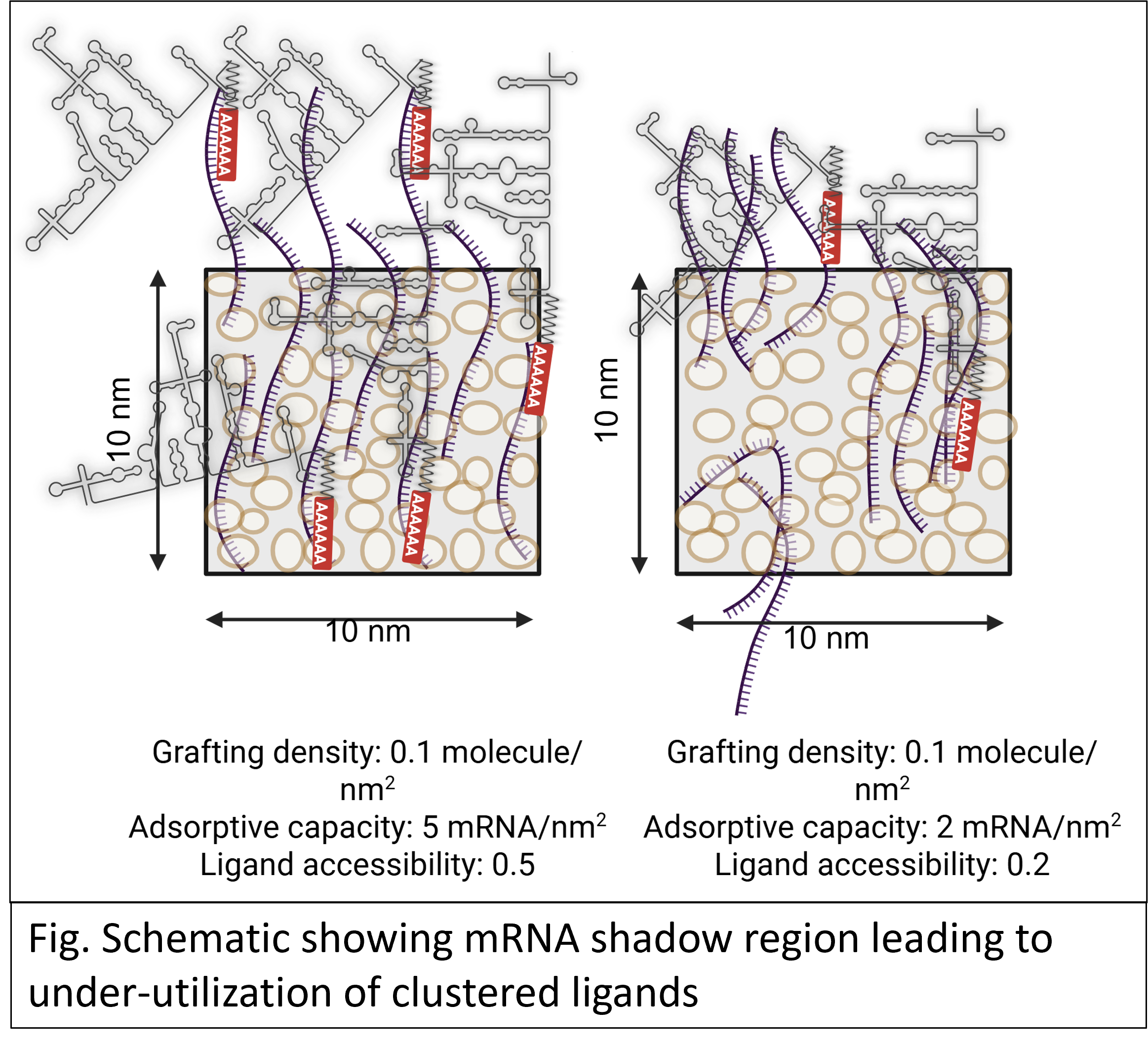
This study introduces a new class of convective affinity membranes where ligand spacing is tailored to match the molecular dimensions of mRNA, thereby reducing steric hindrance. The membranes are functionalized via Single-Electron Transfer Living Radical Polymerization (SET-LRP), where grafting kinetics are controlled by manipulating solvent polarity to modulate the balance between comproportionation and disproportionation of copper ions in reaction. By systematically slowing down polymerization using unfavorable solvents, we achieve optimal ligand spacing. Super-resolution microscopy (STORM, ~10 nm resolution) is used to quantify ligand distribution, while real-time kinetic analysis assess mRNA adsorption efficiency.
This work establishes a design framework for optimizing ligand spatial arrangement in affinity membranes, offering a scalable strategy for enhancing mRNA purification efficiency. Additionally, it provides fundamental insights into surface grafting kinetics, expanding the scope of controlled radical polymerization in biomolecular separations.
References
- Bilodeau, C. L.; Lau, E. Y.; Roush, D.; Garde, S.; Cramer, S. M., Formation of Ligand Clusters on Multimodal Chromatographic Surfaces. Langmuir 2019, 35 (51), 16770-16779.