2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(342b) Chemo-Enzymatic Conversion of Phytic Acid to High-Value Enantio-Pure Myo-Inositol Containing Biomolecules
Myo-Inositol phosphates (InsPs) and phosphoinositides (PtdInsPs) are crucial metabolites in eukaryotic organisms and facilitate a multitude of signaling pathways. Impairment of the InsP and PtdInsP metabolism has severe consequences on proper cell functioning. The availability of InsPs, PtdInsPs, and phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) is modest which influences research and industrial applications, thus novel synthetic approaches of production are of high value.
Results and discussion:
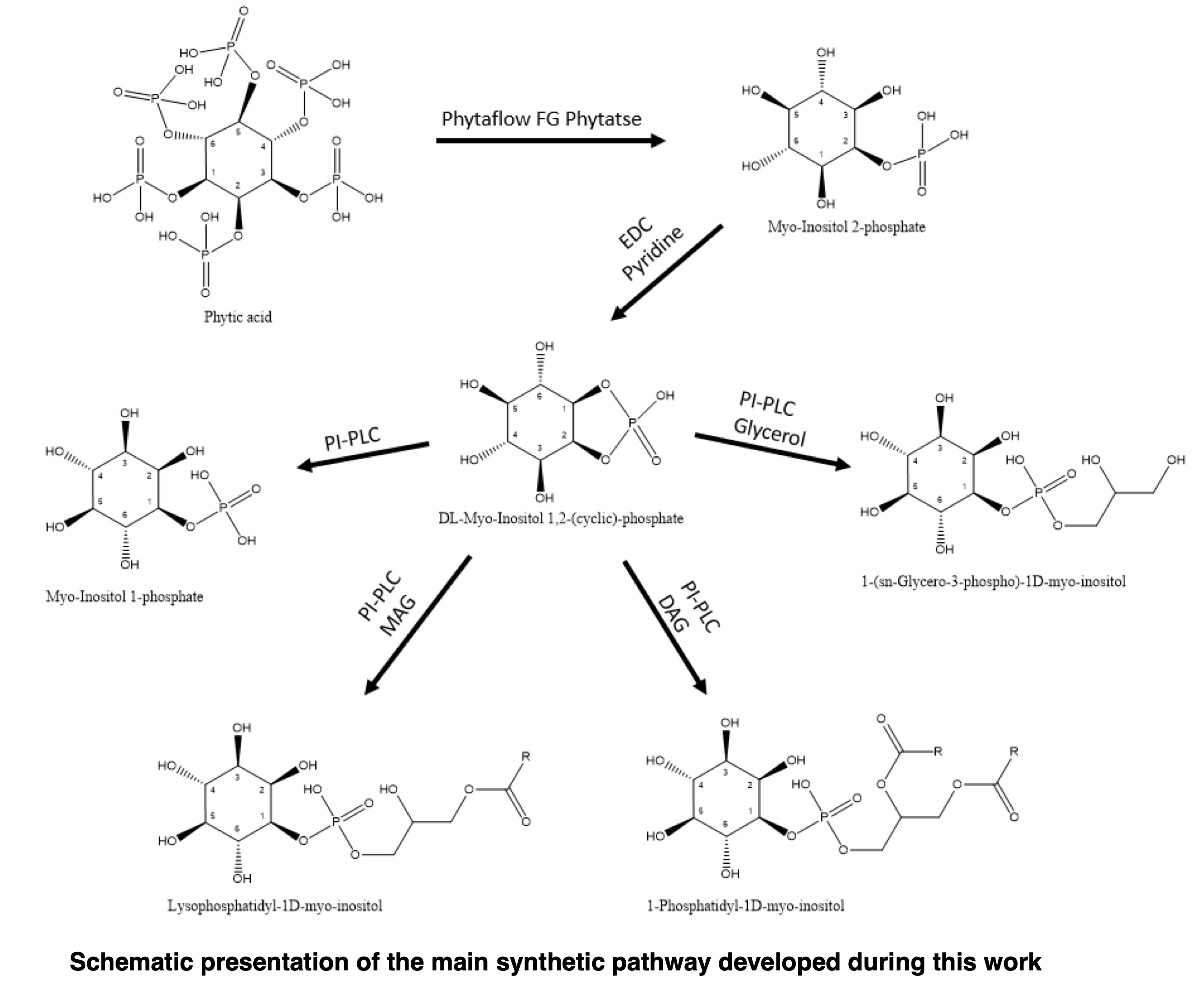
In this study, A novel three-step chemo-enzymatic pathway of Lyso-PtdIns synthesis has been developed, utilizing low-cost and easily accessible phytic acid as starting material. In the first step, phytases dephosphorylate phytic acid to Myo-Inositol 2 phosphate Ins(2)P with 53% isolated yield. Ins(2)P is cyclized to DL-Myo-Inositol 1,2(cyclic)-phosphate (DL-cIP) by 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) with 67% isolated yield. D-cIP coupling to Monooleate is facilitated by the phosphatidylinositol-specific Lipase C (PI-PLC) from Bacillus thuringiensis in a sodium deoxycholate-based micelle reaction system, albeit at low conversions of 7%. Strategies involving reaction condition optimization by altering the micelle components and addition of water-miscible organic co-solvents, and construction of a bi-enzymatic cascade reaction system are being discussed. Lastly, strategies involving the expansion of PI-PLCs substrate scope to synthesize PtdInsPs and synthesis of Myo-Inositol 1,2(cyclic)-polyphosphate substrates are being proposed.
Conclusion:
In the present work, we have successfully established a chemo-/bio-synthesis pathway for regio-/enantio-selective synthesis of phosphatidyl inositol, Myo-Inositol phosphate(s) and Lyso-PtdIns using plant-based building blocks (such as phytic acid, monoglycerides, lecithin etc) and chemical catalyst / biocatalyst tools such as coupling reagent, phytase, and phospholipase C (PLC) etc.