2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(88b) CFD Modelling of a Mixing Vessel Configured with One or Two Impellers Using a Novel GPU Solver
Authors
Luke Munholand - Presenter, Fluent Inc.
Hossam Metwally, Ansys
Mohana Gurunadhan, Ansys Inc.
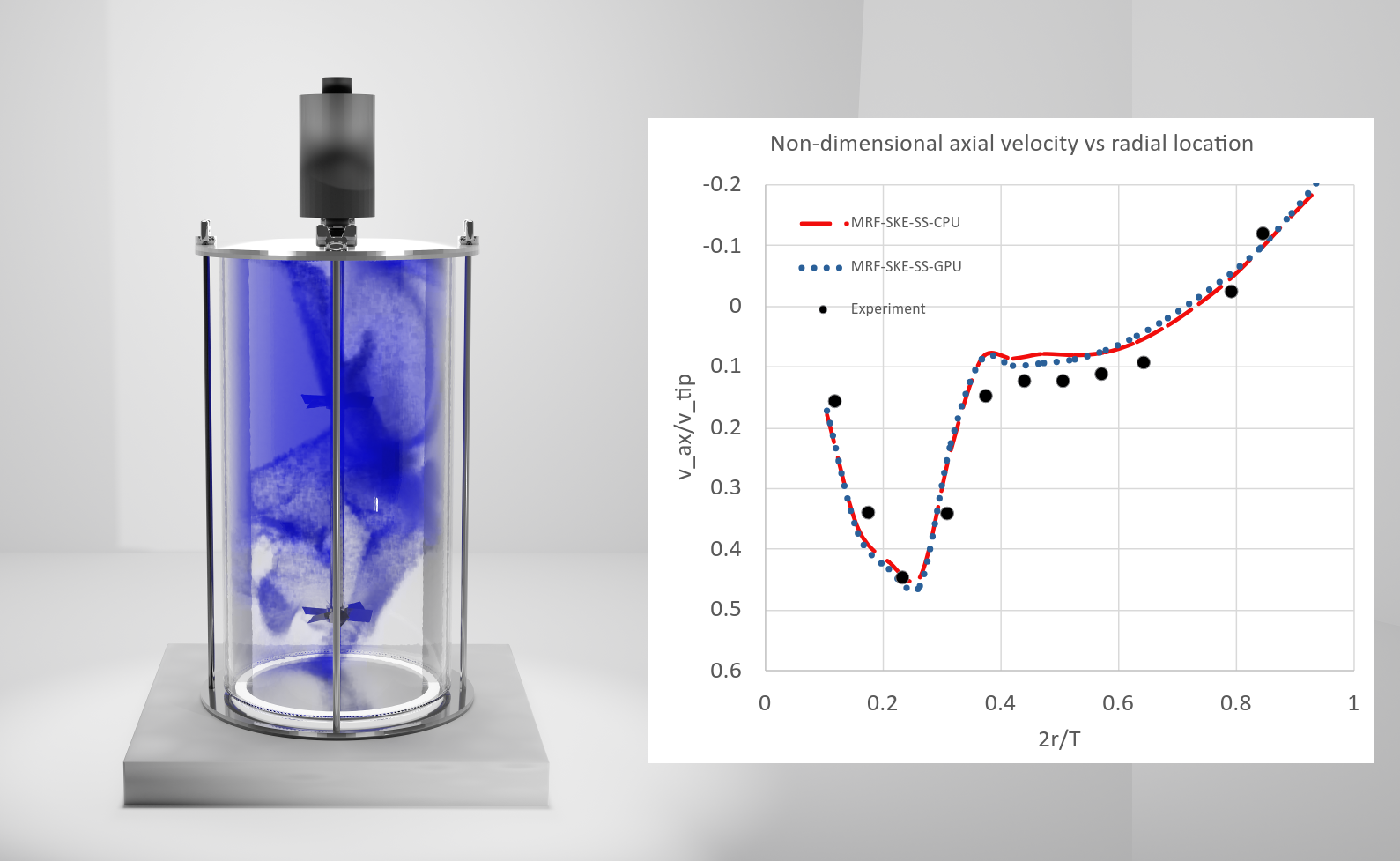
This work demonstrates how GPU compute is dramatically changing accuracy and time expectations in the mixing industry. A typical flat bottom mixing tank is studied with the novel Ansys Fluent GPU native solver. Multiple simulations are reported which characterize the mixing vessel in both low and high fill configurations using different sets of impellers. High resolution Large Eddy Simulation (LES) for turbulence using Sliding Mesh (SM) impeller rotation is compared to the legacy Multiple Reference Frame (MRF) approach with two equation turbulence models. Experimental data from the literature is used to validate all results from the GPU simulations. Power and flow number, axial and radial mean velocity and species tracked blend time are reported. Specific GPU hardware attributes that provide maximum speed up for mixing applications are summarized. GPU speed up of greater than 4x are demonstrated over competing CPU solutions.