2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(57d) Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Propane with Novel High-Active Chromium Based Catalyst
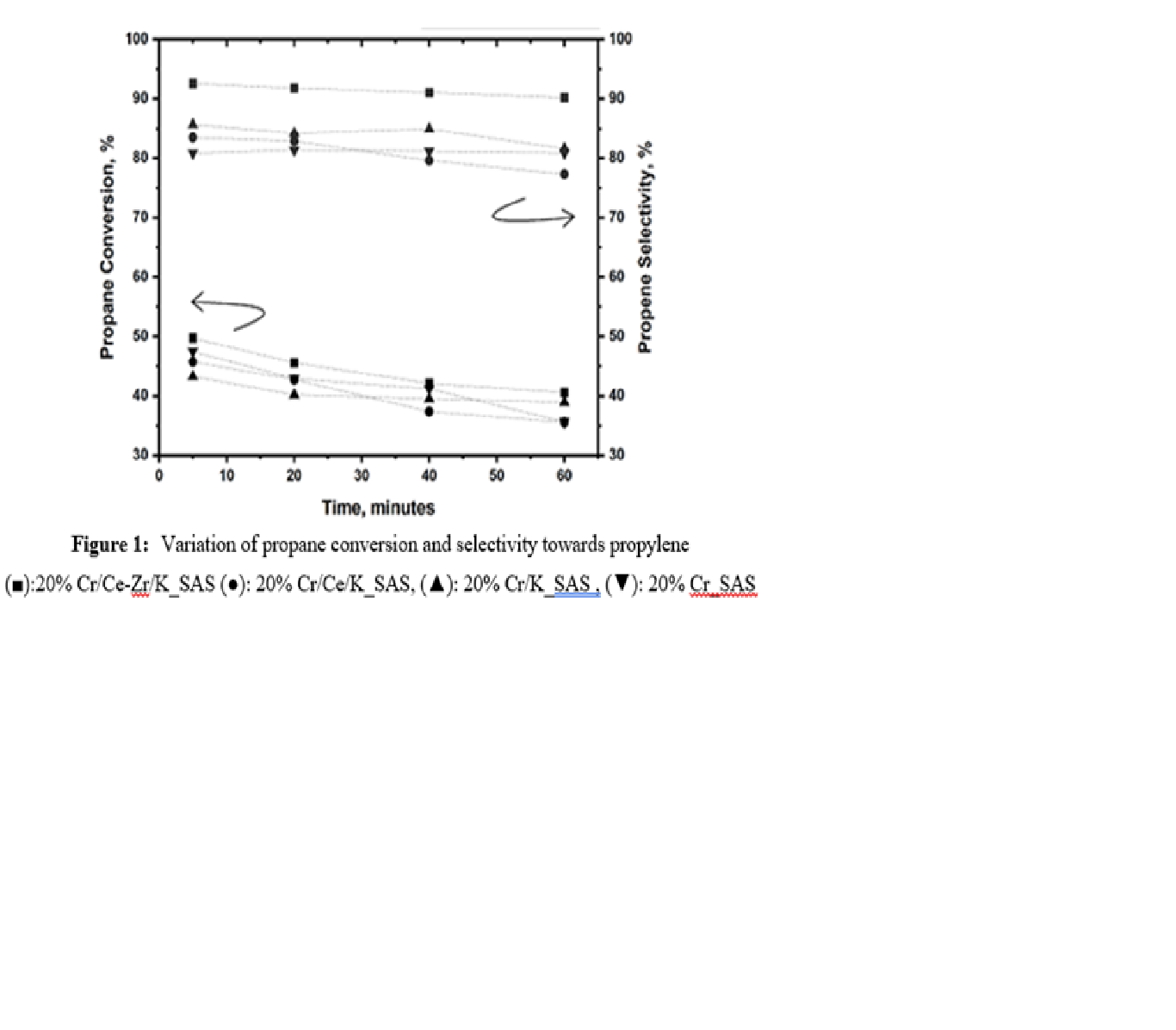
Propane dehydrogenation technology stands as a pivotal solution in meeting the escalating demand for petrochemical feedstock. However, inherent challenges such as low conversion rates and elevated operating temperatures impede its efficiency. In response to these challenges, our study introduces a novel CrOx-based catalyst in to mitigate these limitations. Experimental investigations demonstrate a notable enhancement in propane conversion rates and propene selectivity, offering promising avenues for advancing propane dehydrogenation technology. A CrOx-based catalyst on silica-alumina support was synthesized via sequential wetness impregnation. It was characterized for surface area, pore structure, and active sites. Performance was tested in a bench-scale fixed bed reactor using propane at 550–650°C, 1 atm, and WHSV of 1–10 hr⁻¹. Each 60-minute run included gas sampling at 5, 20, 40, and 60 minutes, analyzed by online GC. Catalyst performance analysis (Figure 1) indicates that the 20%-Cr catalyst exhibits the least favorable performance, emphasizing the necessity of adding Ce, Zr, and K promoters for efficient propane dehydrogenation with high selectivity and yield. Potassium (K) addition significantly enhances catalyst stability, maintaining higher conversion rates by suppressing coke formation, neutralizing acid sites, and minimizing deactivation. Incorporating cerium (Ce) introduces oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) pathways, utilizing lattice oxygen from the catalyst. However, the Ce⁴⁺/(Ce³⁺ + Ce⁴⁺) ratio and associated oxygen capacity influence the initial conversion and propylene yield, while its high reactivity promotes by-product formation. Further enhancement with zirconium (Zr) substantially improves structural stability, redox characteristics, and acidity control in the 20%-Cr/Ce-Zr/K catalyst, thereby optimizing lattice oxygen utilization, reducing coke formation, and achieving superior propene selectivity compared to other promoter combinations.