2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(392ax) Bollinger Band-Guided, Event-Driven Reinforcement Learning Control of Multivariable Process Systems Under Uncertainty
Author
Monzure-Khoda Kazi - Presenter, South Dakota School of Mines and Technology
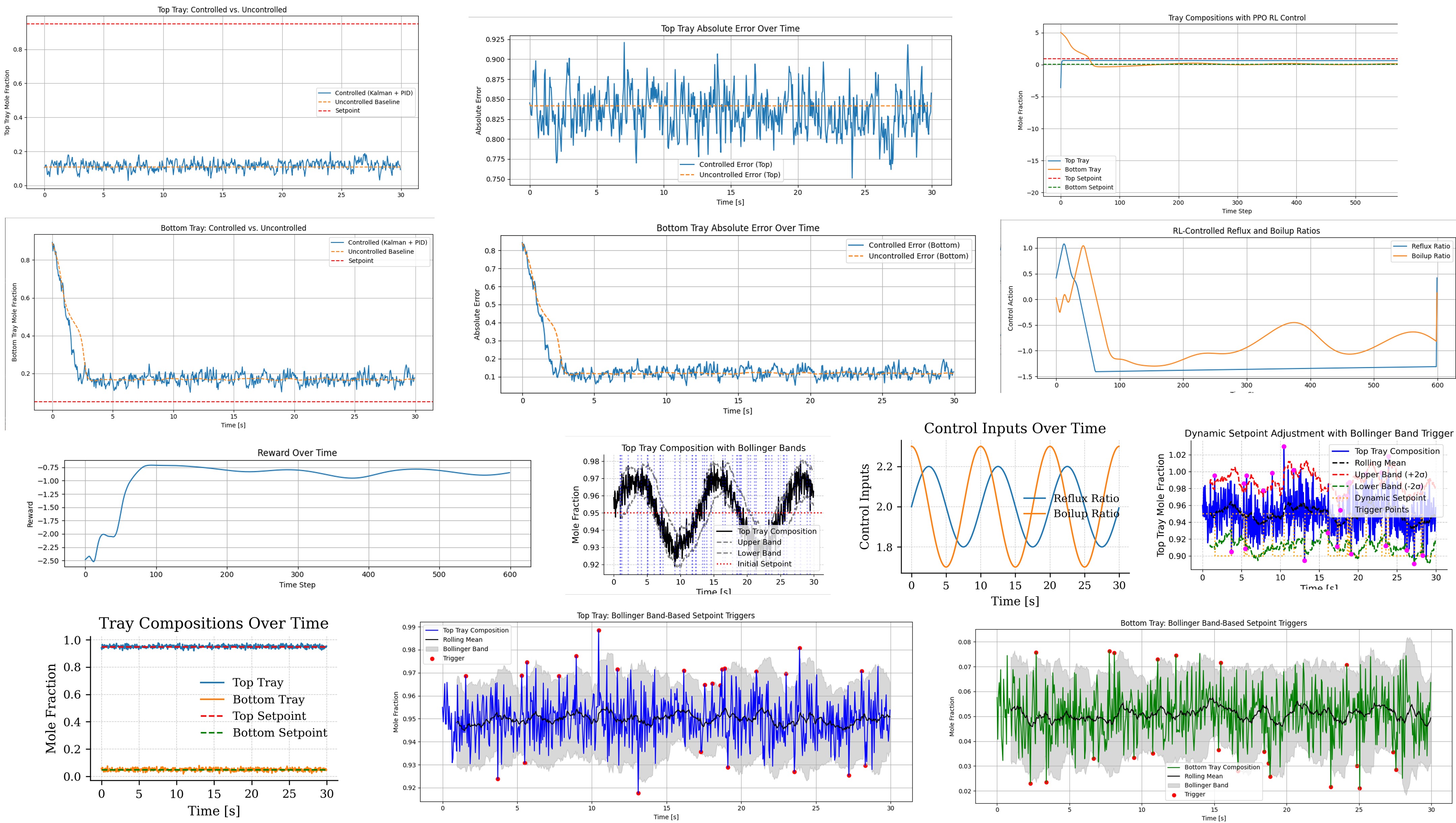
Chemical process systems, especially multivariable units like distillation columns, face increasing demands for resilient and adaptive control under stochastic disturbances, nonlinear dynamics, and fluctuating operating conditions [1]. With the rise of novel column configurations enabled by process intensification and customized design, many emerging systems are difficult to control using conventional first-principles models due to structural complexity and limited mechanistic insight [2]. Traditional PID controllers, while industry standard, often struggle to maintain optimal performance under such uncertainty [3]. Hybrid machine learning approaches have thus emerged as promising alternatives for control tasks where partial process knowledge exists. In this work, we present a Bollinger Band-guided, event-driven reinforcement learning (RL) framework tailored for real-time control of a 25-stage distillation column. Drawing inspiration from high-frequency trading strategies, this approach leverages statistical volatility bands—originally used in financial markets—to trigger dynamic setpoint shifts when process variability breaches learned confidence thresholds. We develop a hybrid control environment using OpenAI Gym and Stable-Baselines3, combining Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)-based RL with physics-informed process dynamics, variable volatility vapor-liquid equilibrium, and Kalman filtering. Control actions include reflux and boilup ratio adjustments based on dynamic observations of tray compositions and event-based setpoint updates. Comparative simulations under stochastic noise and step disturbances reveal important trade-offs between conventional PID and RL-based controllers. While PID controllers exhibited lower Integral of Absolute Error (IAE) in baseline tracking performance, the proposed RL controller—augmented with Bollinger Band-based event triggers—demonstrated stronger adaptability to dynamic process fluctuations and unforeseen events. Moreover, the RL agent offers a scalable and model-flexible strategy that is particularly useful when controlling novel column configurations where mechanistic knowledge is incomplete. These results underscore the potential of volatility-aware reinforcement learning as a complementary control paradigm rather than a direct replacement of PID strategies in certain process environments. This study not only introduces a novel control paradigm at the intersection of financial modeling and process engineering but also establishes a scalable methodology for volatility-aware, hybrid-learning-driven control in complex or poorly modeled chemical systems. The framework is broadly applicable across industries where data-driven, resilient, and event-sensitive control strategies are vital.
References
[1] C. Kim, M. Shah, A.M. Sahlodin, Design of multi-loop control systems for distillation columns: review of past and recent mathematical tools, Chemical Product and Process Modeling 17(2) (2022) 171-197.
[2] B. Decardi-Nelson, A.S. Alshehri, A. Ajagekar, F. You, Generative AI and process systems engineering: The next frontier, Computers & Chemical Engineering (2024) 108723.
[3] M.A. Ahmad, G. Yoganathan, M.I.M. Rashid, M.R. Hao, M.H. Suid, M.Z.M. Tumari, Improved Smoothed Functional Algorithms-Optimized PID Controller for Efficient Speed Regulation of Wind Turbines, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications (2025) 1-15.