2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(387l) Automated Detection of Crystallization Outcomes Via Deep Learning Image Analysis in the CMAC Crystallization Screening Datafactory
Authors
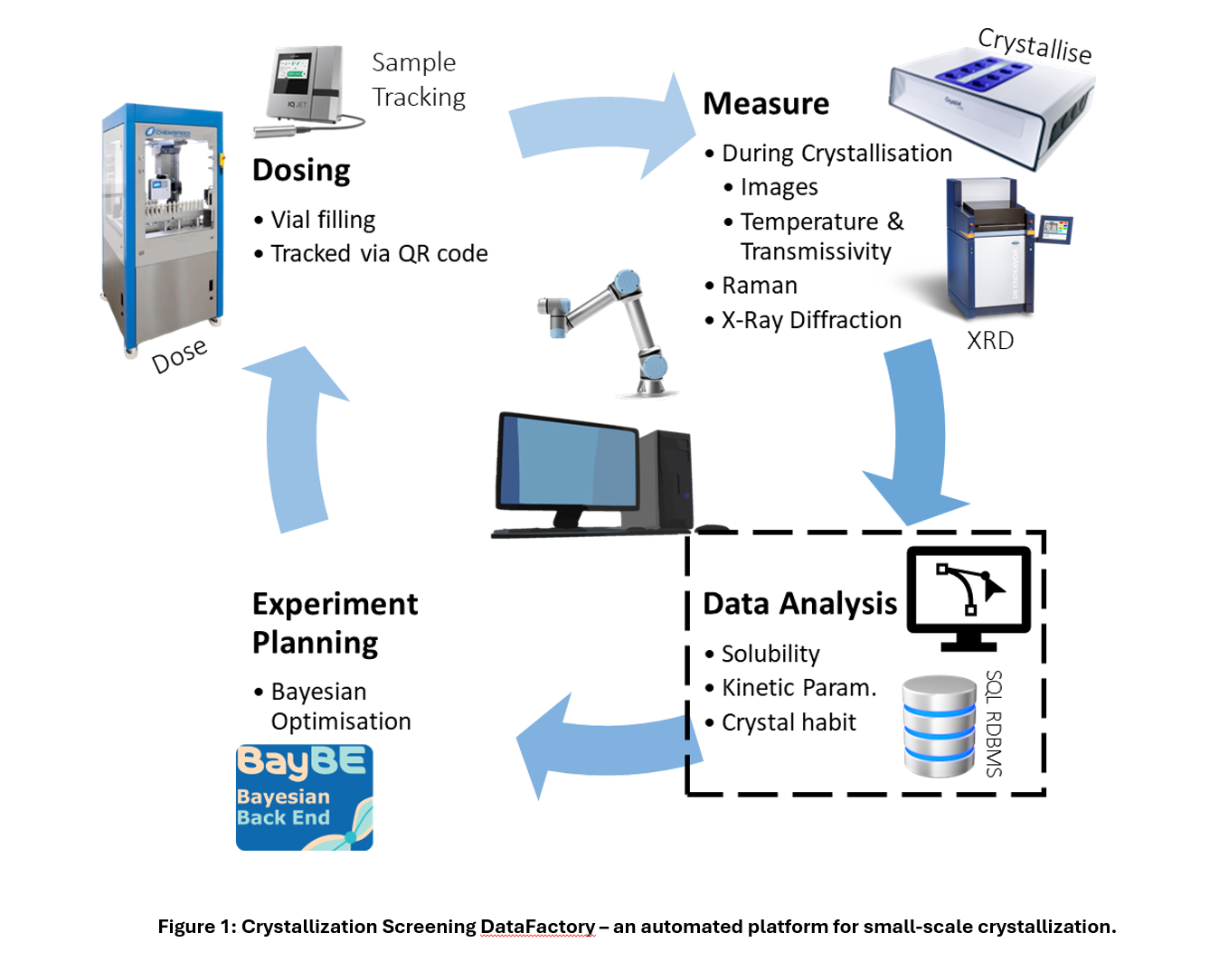
Crystallization plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing, as the properties of drug crystals—such as their size, shape, and form—significantly influence subsequent processes like filtration, drying, and formulation [1]. To address these challenges, high-throughput crystallization screening platforms have become valuable tools in modern pharmaceutical development. These systems enable researchers to explore a wide range of crystallization conditions rapidly, accelerating the identification of optimal process parameters while reducing material usage and development timelines [2]. The CMAC Crystallization Screening DataFactory (CSDF) is state-of-the-art, automated platform for small-scale crystallization, designed to accelerate process development through high-throughput experimentation and real-time analysis (see Figure 1). By automating the analysis of large volumes of crystallization data, the CSDF supports informed decision-making and improves consistency, efficiency, and product quality at an industrial scale.The platform operates through four key stages:1) Dosing, where drug and solvent are precisely dispensed; 2) Measurement, which uses the Technobis Crystalline system to carry out and monitor crystallization in real time, with additional analytical probes, such as Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD), used to provide further experiment insights; 3) Data Analysis, where artificial intelligence (AI) extracts parameters such as solubility, nucleation and growth kinetics, and crystal habit; and 4) Experiment Planning, which uses Bayesian optimization to refine conditions based on real-time data.
Research Interests:
Throughout my PhD journey, I have developed a strong passion for integrating data-driven techniques with in-line imaging in crystallization processes. I am particularly interested in applying modern AI methods to enhance our understanding and control of crystallization in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Moving forward, I aim to explore the capabilities and limitations of AI solutions in crystallization screening and work towards improving their overall efficiency by continuously retraining models on new datasets. I hope to build practical tools that allow faster decision-making with better outcomes to improve the quality and efficiency of drug manufacturing. I am particularly interested in implementing these tools in an industrial setting with cross-functional teams and would welcome the opportunity to test data-driven tools in a real work setting. Close interaction with industry will allow feedback on the usability and efficacy of these tools, as well as inform future directions in practical, impactful approaches that improve manufacturing practices and speed process development.
References:
1] Conrad Meyer, Arjun Arora, and Stephan Scholl. A method for the rapid creation of AI driven crystallization
process controllers. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 186:108680, 2024.
[2] Parisa Shiri, Veronica Lai, Tara Zepel, Daniel Griffin, Jonathan Reifman, Sean Clark, Shad Grunert, Lars P.E.
Yunker, Sebastian Steiner, Henry Situ, Fan Yang, Paloma L. Prieto, and Jason E. Hein. Automated solubility
screening platform using computer vision. iScience, 24(3):102176, 202