2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(199b) Alloying Effects in Pt-Ag Catalysts Towards Selective Ethylene to 1-Propanol Direct Conversion Via Tandem Catalysis
Authors
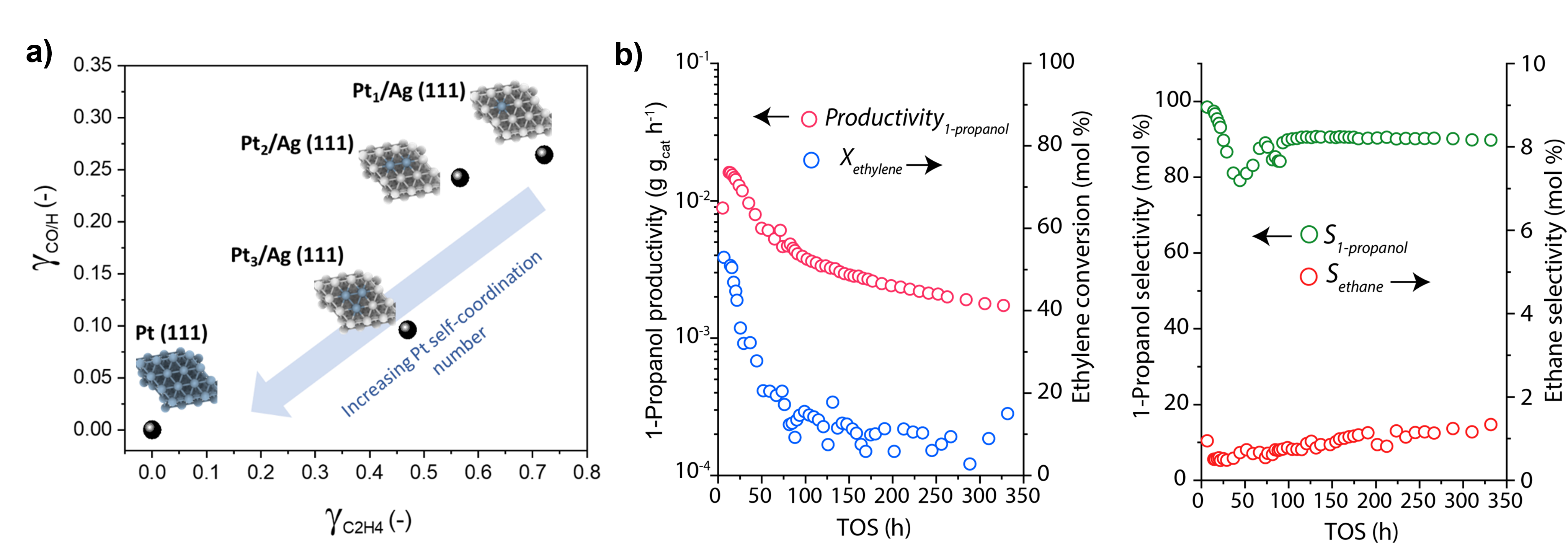
Firstly, we have computationally screened diluted and single-atom Pt-Ag alloys for the selective hydrogenation of propanal to 1-propanol in the presence of ethylene and CO. Isolated Pt1 centers and Pt2 dimers are predicted to provide the most advantageous features, with barrierless H2 dissociation, low ethylene adsorption energies and lower CO/H binding energy ratio (Figure 1a), in good agreement with the results obtained experimentally. For the optimal hydrogenation catalyst identified (i.e. 1 at% Pt), ethylene reductive hydroformylation tests were performed in combination with Rh1/SnO2. As illustrated in Figure 1b, the system can reach very high 1-propanol selectivity (>90%) at high ethylene conversion levels (>50%) for more than 300 hours on-stream with negligible ethane formation. These results showcase the potential of atomically precise active sites and tandem catalysis approaches to attain a gas-solid reductive hydroformylation process with selectivity levels comparable to those thus fur restricted to homogeneous catalysis.