2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(632a) AI-Driven Computational Material Screening for CO2 Utilization: Optimal Amine for Low-Temperature Methanol Production
Authors
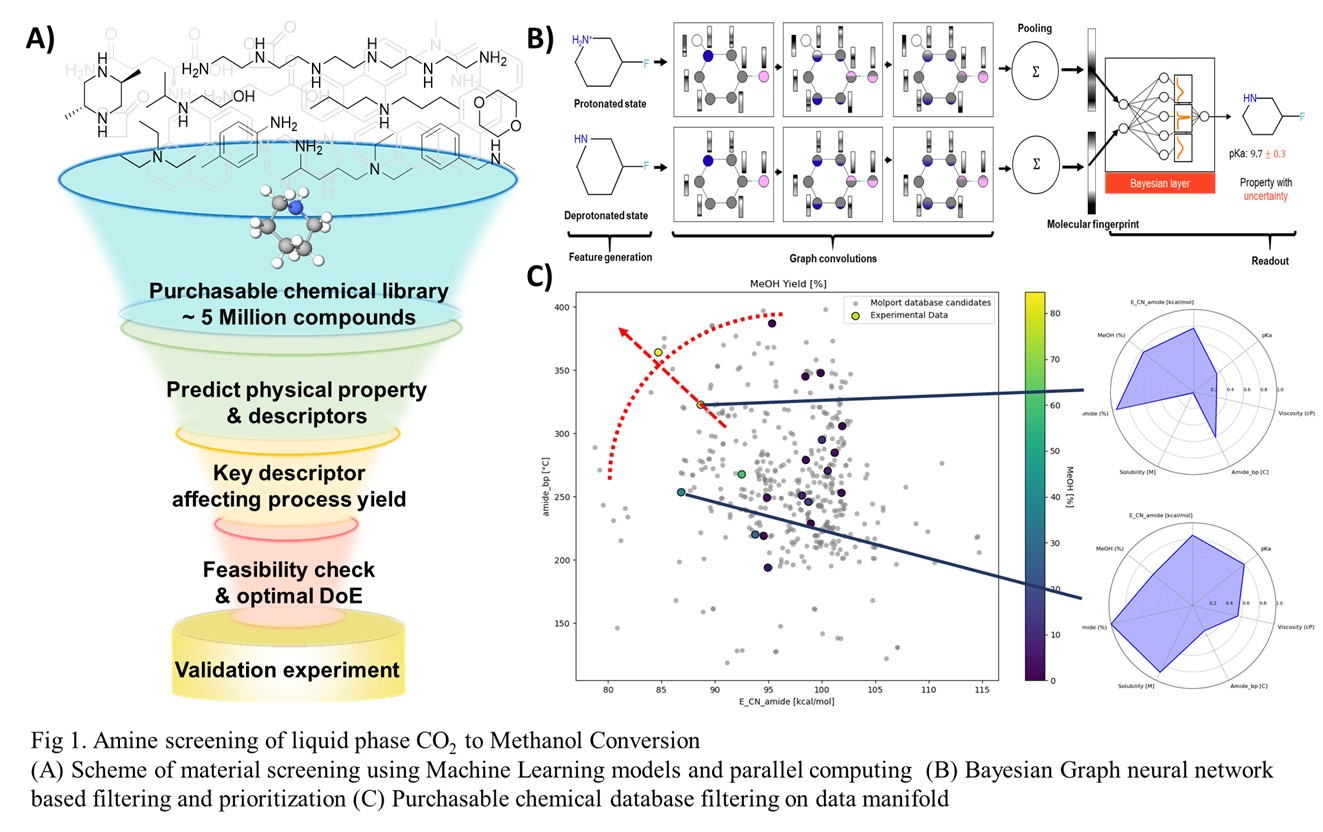
To efficiently identify optimal amine candidates, we developed a scalable, AI-driven material screening platform powered by a Bayesian Graph Isomorphism Network (BGIN). This model predicts key molecular properties—such as pKa and bond dissociation energy (BDE)—with over 90% accuracy while also providing uncertainty estimates. By analyzing correlations between these molecular descriptors and experimental methanol yields, we systematically selected and refined descriptors that best align with the reaction's mechanistic insights.
Our experimental design process, as illustrated in Fig. A, leverages Bayesian optimization combined with Design of Experiments (DoE) methodologies to streamline workflows. This iterative approach—comprising predictive modeling, targeted descriptor identification, experimental testing, and optimization—not only substantially accelerates the discovery of high-performance amine materials for CO₂ conversion, but also emphasizes the importance of building models that do not overfit to small datasets.
Through this AI-driven computational approach, we identified an optimal amine candidate capable of achieving approximately 80% methanol yield from CO₂ at temperatures below 160 °C. The effectiveness and efficiency of our methodology demonstrates its potential as a powerful strategy for accelerating the development of practical CO₂ utilization technologies. In addition, a pilot-scale verification confirmed continuous methanol production at rate of 1 kg/day, further validating the real-world applicability of the materials and conditions identified through our DoE-guided workflow.
References:
1. Kar, S.; Sen, R.; Kothandaraman, J.; Goeppert, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Munoz, S. B.; Haiges, R.; Prakash, G. K. S. Mechanistic Insights into Ruthenium-Pincer-Catalyzed Amine-Assisted Homogeneous Hydrogenation of CO₂ to Methanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3160–3170.
2. Xu, P.; Ji, X.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W. Small Data Machine Learning in Materials Science. npj Comput. Mater. 2023, 9, 42.