2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(22g) AI-Assisted Immune Cell Phenotyping Via Biopolymer Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: A Novel Approach to Disease Fingerprinting and Profiling
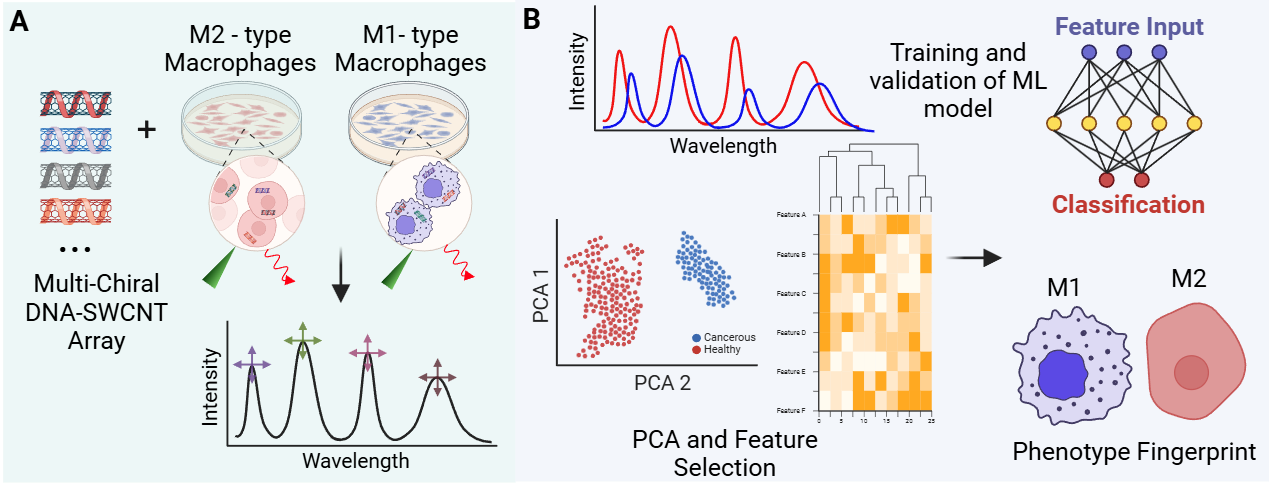
A key finding in this study highlights the importance of DNA sequence length in maintaining the stability of DNA-SWCNT complexes. Shorter sequences (e.g., GT6) foster stronger interactions with proteins, lipids, metabolites and other biomolecules in the endosomal microenvironment, leading to improved classification accuracy (>87%). Collectively, these insights underscore the potential of SWCNT and NIR spectral fingerprinting, especially when integrated with machine learning, as a robust and noninvasive platform for real-time cell phenotype characterization. This innovative approach opens new avenues for phenotype fingerprinting, disease profiling, in vivo monitoring of dynamic cellular processes, disease progression, biomarker discovery and therapeutic response. By bridging the gap between spectral analysis and cellular dynamics, our methodology provides a significant advance in bio-nanotechnology-based diagnostics, offering heightened sensitivity and specificity for next-generation biomedicine and clinical interventions.