2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(662h) Advancing Molecular Sieving Via ?-Scale Pore Tuning in Bottom-up Graphene Synthesis
Authors
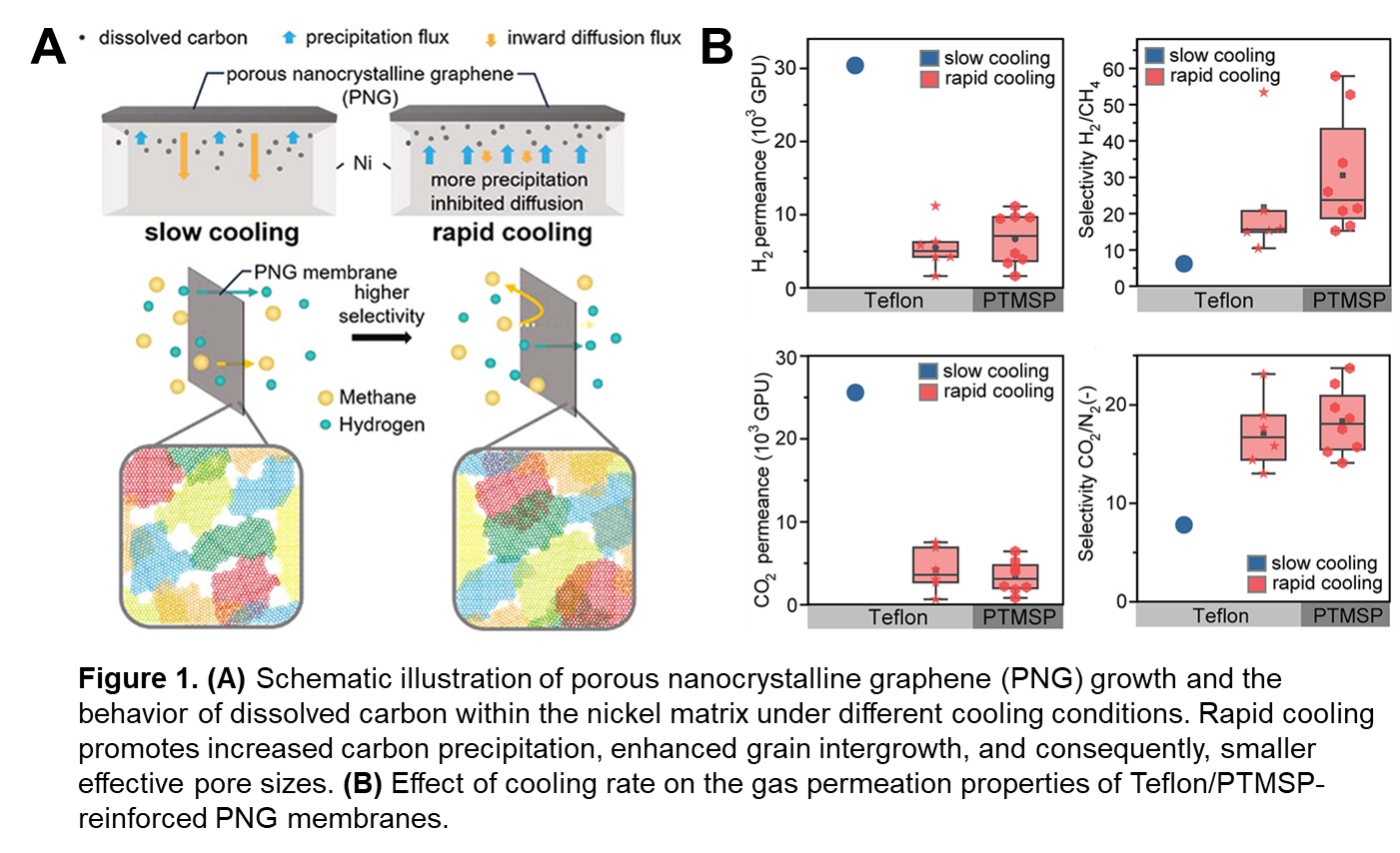
Comprehensive characterizations revealed that carbon precipitation from the nickel bulk during cooling governed PNG formation. A dissolution-precipitation model captured carbon behavior in a 25 μm-thick nickel foil, revealing that the cooling rate critically modulated pore nanostructure. Rapid cooling enhanced carbon precipitation, promoted PNG crystallization and the intergrowth of graphene grains, and ultimately reduced the effective pore size.
Gas permeation data showed that increasing the cooling rate from 1 °C/min (slow cooling) to over 180 °C/min (rapid cooling) significantly increased the H2/CH4 selectivity of resulting PNG membranes from 6.8 to over 50, while decreased H2 permeance from over 30,000 GPU to 1,600 GPU. Notably, rapid-cooled membranes also exhibited attractive CO2/N2 selectivity (23.7) with a CO2 permeance around 4,000 GPU.
This work presents a tunable and scalable strategy for pore engineering in graphene membranes via a dissolution–precipitation mechanism. The approach may extend to other crystallization-driven 2D systems, including CVD-grown transition metal dichalcogenides and porous crystalline materials such as MOFs and COFs.
Acknowledgments
We thank Shell for funding this work. A part of the work was funded by European Research Council Starting Grant (805437-UltimateMembranes).
References
[1] Villalobos, L. F.; Van Goethem, C.; Agrawal, K.V. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118 (37).
[2] Van Goethem, C.; Shen, Y.; Agrawal, K.V. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7, 5730-5740.