2025 AIChE Annual Meeting
(194h) 2D Nanomaterials Prepared By Chelating Agent-Assisted Electrodeposition for Efficient Electrochemical Oxidation of Biomass-Derived Aldehydes Coupled with CO2 Reduction
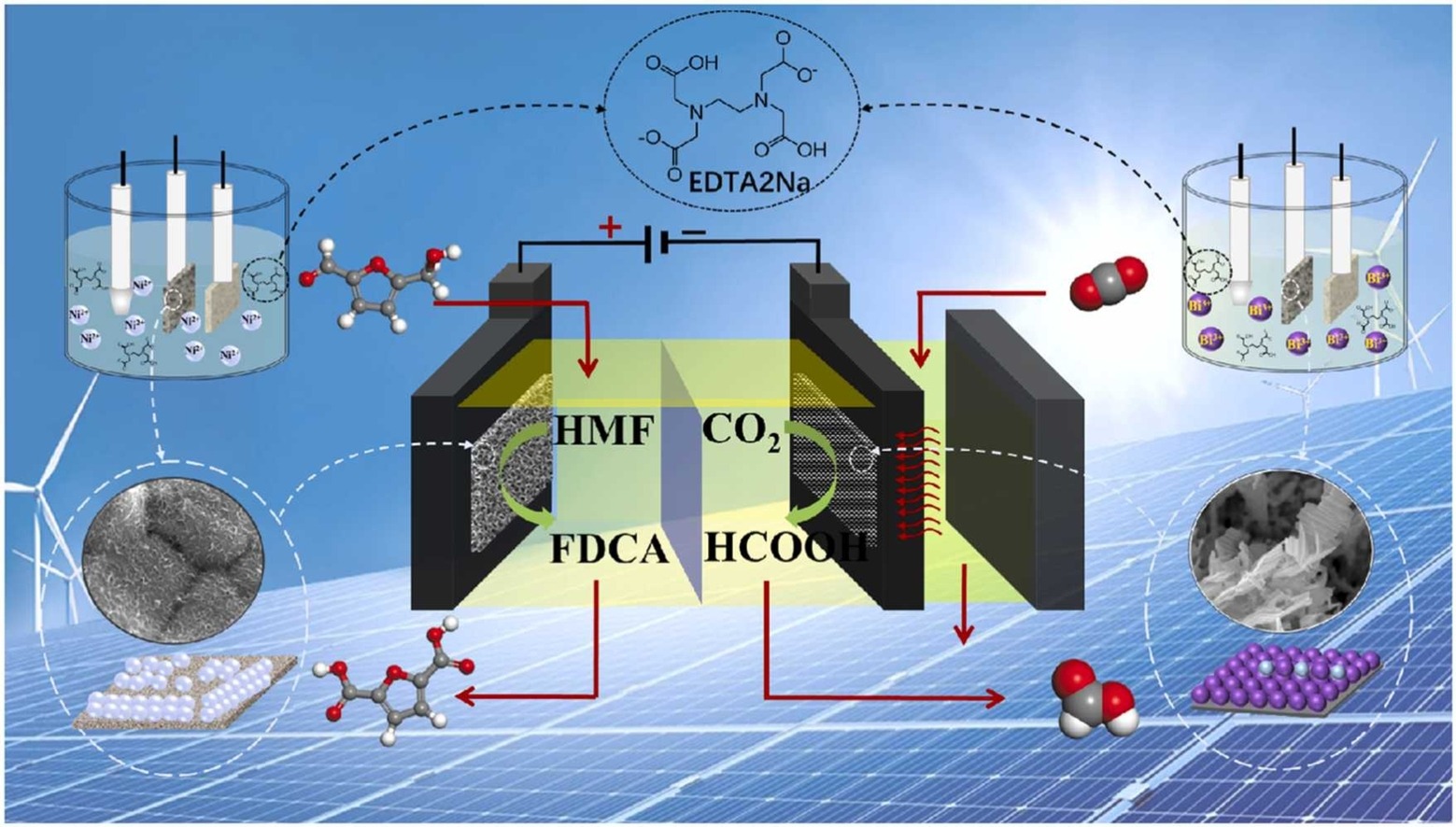
In this work, we developed a facile met hod of electrodeposition based on chelating agents for preparing two-dimensional nanosheet electrocatalysts on both the anode and cathode. It was found that the Ni-based electrocatalyst prepared by using EDTA2Na had the best performance for electrooxidation of biomass derived aldehydes (e.g. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF)). When the ratio of Ni2+ to EDTA2Na is 1:0.25, the electrocatalyst is dispersed scaly structure, which can achieve nearly 100% FDCA yield and FEFDCA. 98.7 % average FDCA yield and 93.9 % FEFDCA were obtained with FDCA concentration reaching 159.1 g/L after ten cycles.
In the cathode, Bi-based electrocatalysts prepared by electrodeposition with different chelating agents have different morphologies. The cathode catalyst (Bi-EDTA2Na) has two-dimensional sheets with nano-corrugated paper morphology, which showed good performance for CO2RR to produce formate with FE of higher than 90 % in a potential range from −1.4 to −1.8 V vs. Ag/AgCl. And Bi-EDTA2Na can be stably cycled for 24h.
Compared with the traditional OER-CO2RR coupling system, the new system can reduce the energy by 7.02%. By using a paired electrolysis system, 50.7 g/L FDCA and 10.8 g/L formate were obtained, with both FDCA yield and cathode FE being higher than 90 %. The value of FDCA produced by the anode HMFOR is greatly increased by hundreds of times compared with the traditional system of OER. This work developed a renewable electricity-driven new system of biomass electrooxidation coupled with CO2RR.