2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
Exploring Irreversible Protease Inhibition: Using Yeast Surface Display and Genetic Code Expansion to Engineer Covalent MMP Inhibitors
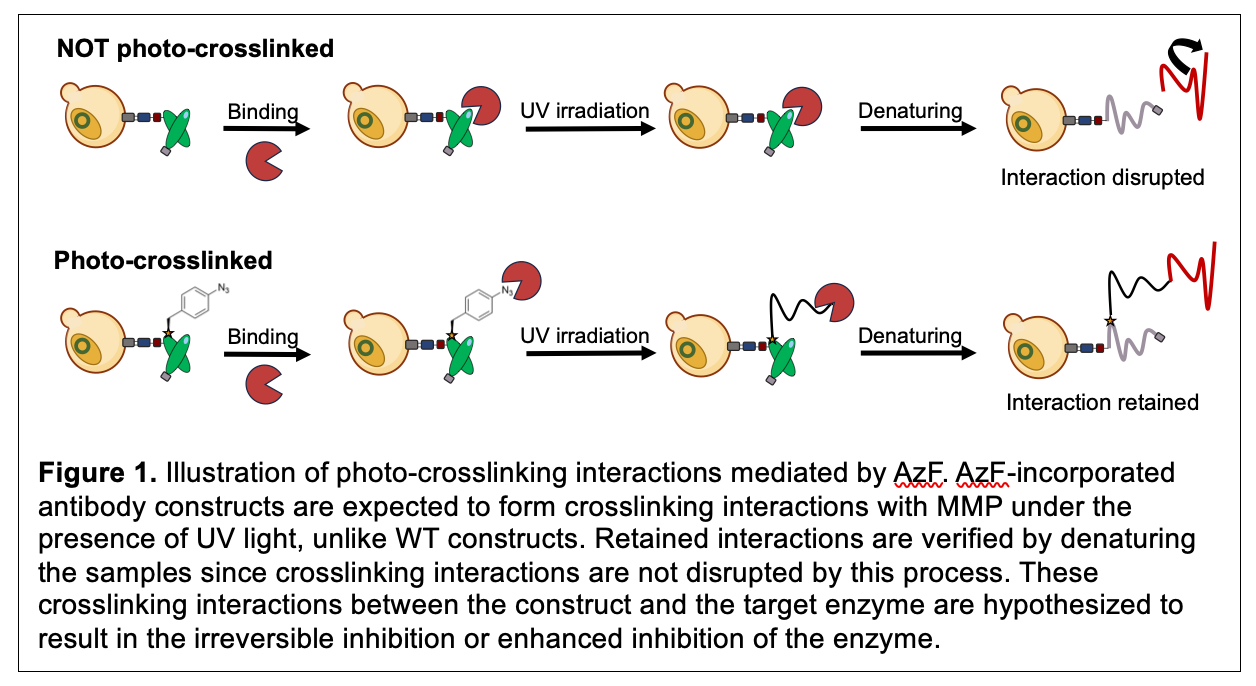
A challenge in drug discovery is the need to develop irreversible enzyme inhibitors with high specificity; genetic code expansion through the incorporation of noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) into antibodies is a potential solution. ncAAs have more chemically diverse functional groups than canonical amino acids (cAAs), enabling the incorporation of chemical reactivities not found in the standard genetic code. This project aims to discover antibodies capable of forming photo-induced covalent (photo-crosslinking) interactions with an MMP, which belongs to a class of enzymes with diverse roles in physiological functions, using yeast-displayed antibodies containing ncAAs. Stop codon suppression is a tool used to introduce noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) into antibodies in place of a TAG codon. This desired interaction is expected to be achieved by substituting a canonical amino acid (cAA) on an antibody with p-azido-L-phenylalanine (AzF), an ncAA, that becomes a highly reactive species when irradiated with light and crosslinks with other chemical groups.