2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
Development of Agarose-Based Hydrogel Composites for Enterosorptive Removal of PFAS
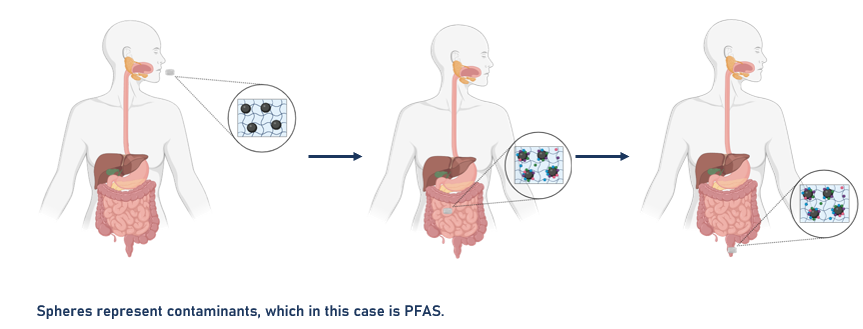
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), or “forever chemicals,” are persistent anthropogenic chemicals linked to various health disorders and accumulate in the body. Agarose-based hydrogels were investigated as a candidate for removing PFAS from the body to tackle the issue of PFAS accumulation. In vitro sorption studies with model dyes were conducted to determine if they could be used for PFAS enterosorption (orally administering sorbents to remove contaminants using undigested sorbents that are excreted). The results of the in vitro binding of model compounds suggest that agarose-based hydrogel systems are effective in removing PFAS due to their aqueous sorption behavior. Furthermore, preliminary research shows that hydrogel behavior is maintained within human-simulated conditions. Future research will focus on continuing studies in simulated human conditions and quantifying PFAS removal in vitro with the potential to conduct in vivo studies.