Current drug delivery systems account for the biomolecules involved (e.g., small molecules, peptides, antibodies, nucleic acids, live cells, etc.), the bioavailability of the drug molecule, environmental factors (e.g., pH, permeability, intracellular interactions, etc.), and devices compatible with said therapeutic molecules (e.g., microneedle patches, micro/nanoparticles, polymer films, implants, etc.). A major challenge, however, in drug delivery centers on overcoming physiological, chemical, and biological barriers when entering the human body. Silk-elastin-like protein polymers (SELPs) offer a promising solution due to their chemical stability, easily tunable physicochemical structures, and biocompatibility. Leveraging silk's abundance in nature and uniform properties, SELPs serve as a promising sustainable drug delivery platform.
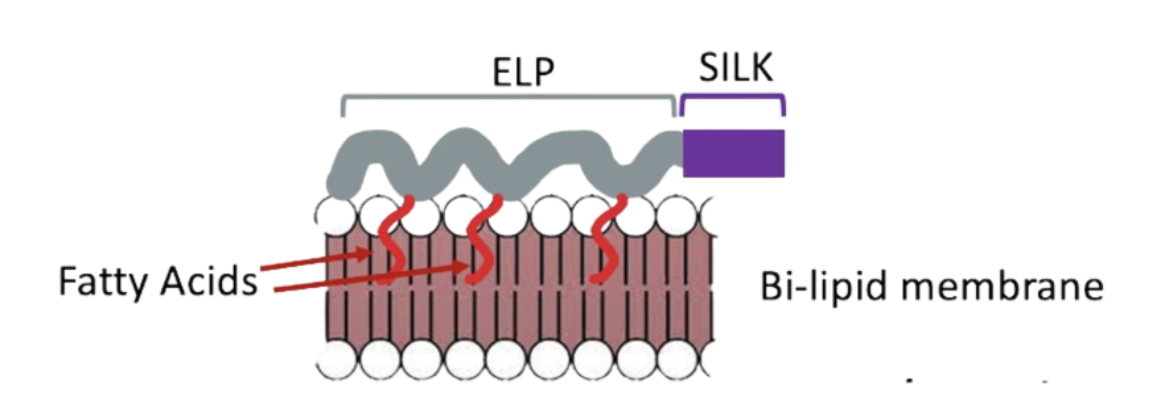
This study focuses on developing the SELP system and demonstrating its versatility with various biomolecules, which includes coating lipid membranes and silk protein-based nanoparticles (SNPs) with SELPs. The SELP platform, augmented with fatty acid groups, has been successfully proven to be biocompatible with live human cells and capable of covalently binding with silk-based nanoparticles. Upon refining these models, SELPs can be engineered with cell-targeting oligopeptides such as GE11 and LT6 to target specific cell types like EGFR high-expressing cancer cells. Future iterations of the SELP-fatty acid conjugate platform can be improved by adjusting parameters such as temperature, incubation time, and fatty acid composition to enhance cellular binding. Additionally, SELP-SNP results suggest that an alternative coating method (e.g., layer-by-layer assembly of oppositely charged particles) may offer better optimization for SELPs and SNPs.
[Attached: Figure 1: Simplified schematic of SELP platform with fatty acid conjugate]