2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(83d) Numerical Investigation of Mixing Strategies in Multiphase Loop Reactors
Authors
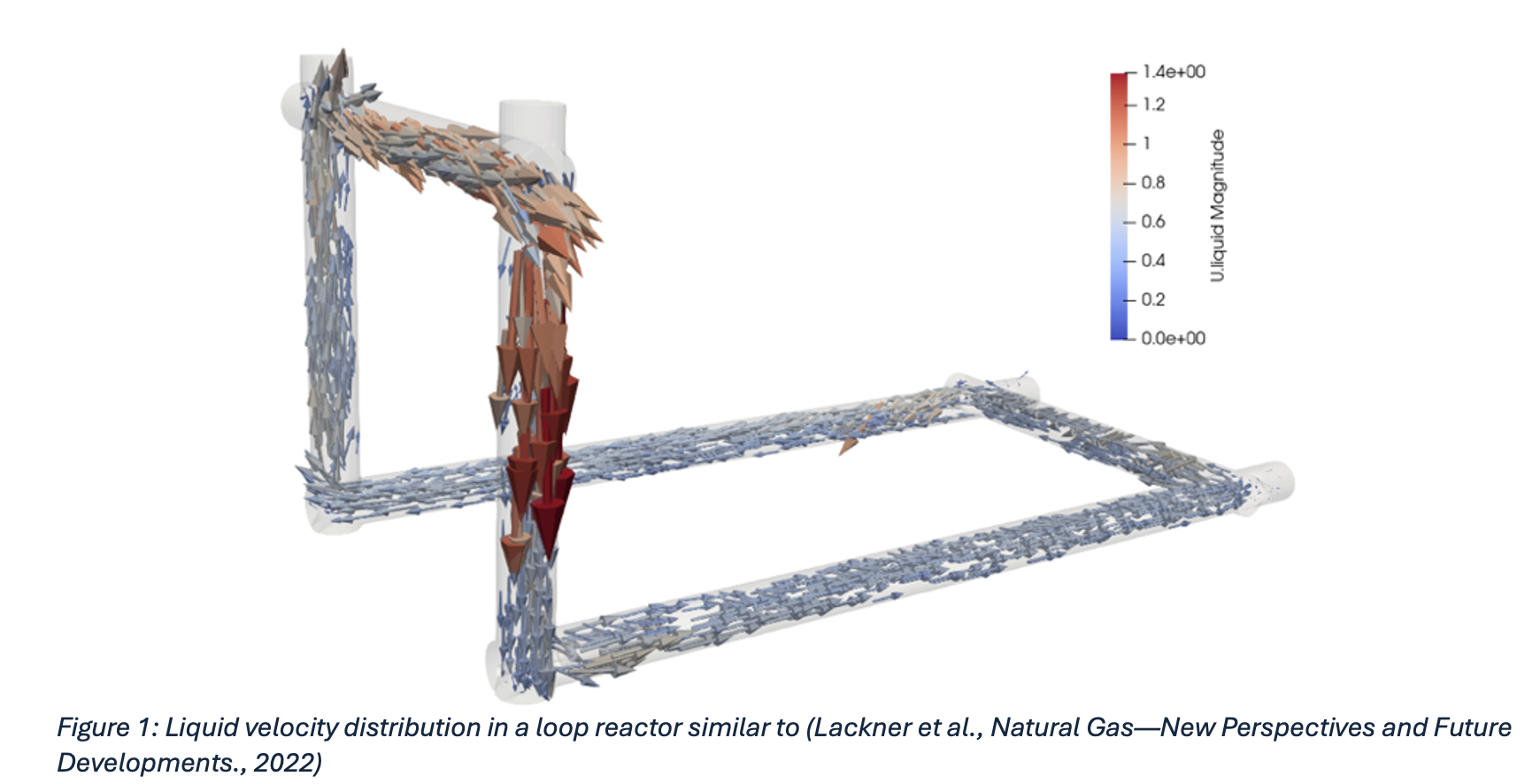
The performance of gas fermentation reactors at-scale (~ million liters) strongly depends on the efficient mass transfer of species from the gas to the liquid phase. To address this challenge, we investigate loop reactor designs with strategically placed static and dynamic mixing elements for improving mass transfer at scale. Loop reactors (Fig. 1) typically are more compact than stir tanks, and enable greater control of gas residence times. However, the design of loop reactors at scale, that simultaneously achieves adequate mass transfer of gas mixtures and reduces inhomogeneous species distribution is a challenging research problem.
In loop reactors, mixing is best achieved through the strategical placement of static/dynamic mixers and spargers. The objective of this work is to optimize the spatial locations of mixers and spargers to maximize interphase mass transfer while minimizing power consumption. To solve this optimization problem, we will use an ensemble of simulations of loop reactor designs using our validated high-fidelity multiphase computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model (Rahimi et al., Chem. Eng. Res. Design, 139, 2018, https://github.com/NREL/BioReactorDesign). The effect of the placement and the type of mixer adopted will be described, and an optimal mixing strategy will be described.