2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(7d) Well-Defined Ptsn Alloyed Clusters for Highly Efficient Propane Dehydrogenation
Authors
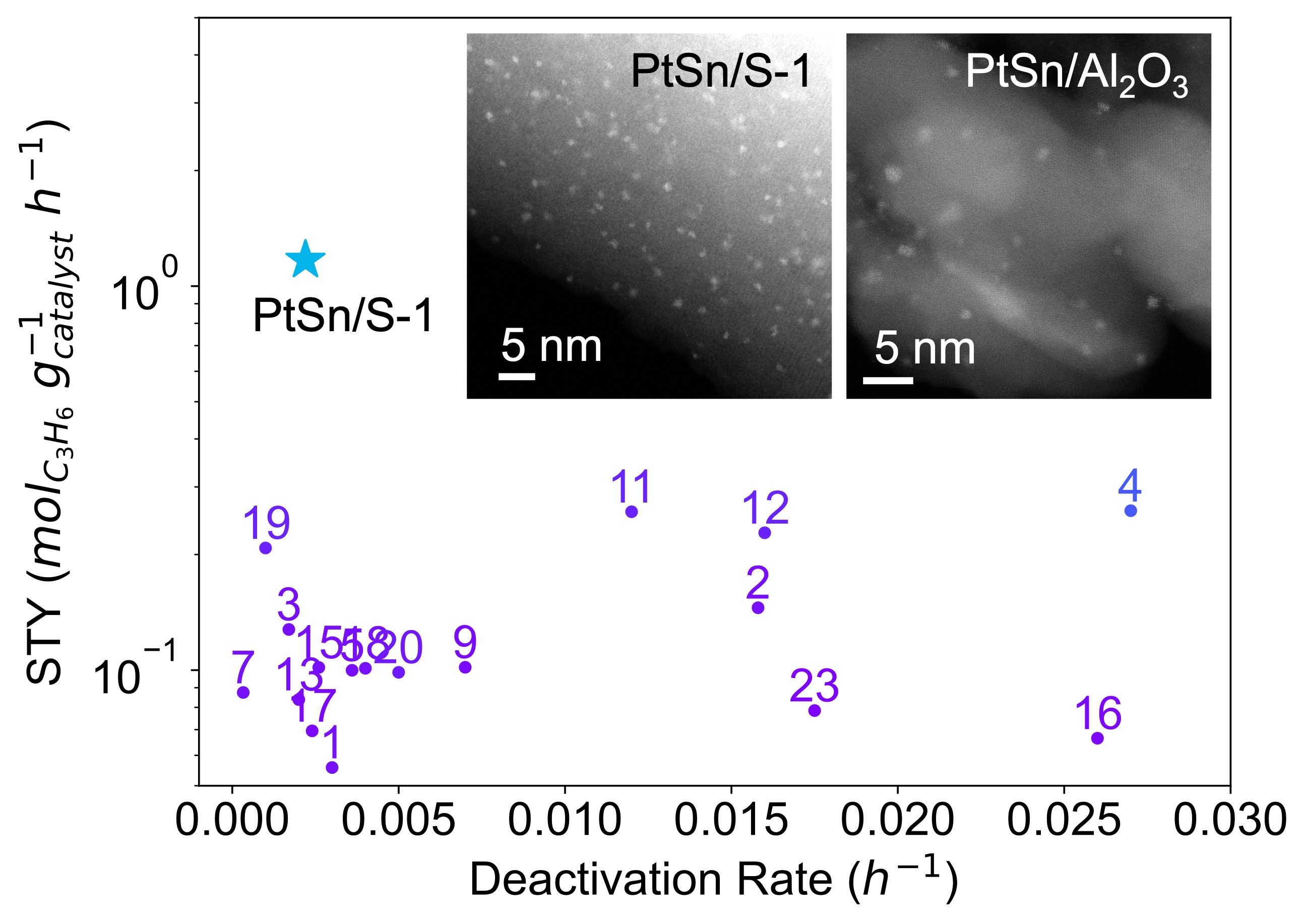
Through comprehensive characterization, including aberration-corrected AC-STEM studies, alongside atomistic simulations via ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) and density functional theory (DFT), we unveiled that the alloyed clusters possess unique active sites that differ significantly from those offered by single metal atoms or bulk metal alloys. These findings suggest that the outstanding catalytic performance of the PtSn clusters may also stem from their dynamic structures under reaction conditions. Our work not only sheds light on the unseen potential of widely-known PtSn catalysts but also underscores the importance of controlled synthesis in developing highly efficient and stable catalysts for industrial processes.
- Sattler, et al., Chem. Rev. 114, 10613–10653 (2014).
- Xu, et al., Appl. Catal. B 341, 123285 (2024).
- Lu, et al., Encapsulated Sub-nm Alloys for Highly Efficient Propane Dehydrogenation. submitted (2024)
Figure caption
Top panel: Representative STEM-HAADF images of the PtSn/Al2O3 and PtSn/Silicalite-1 catalysts prepared from stannous platinum complexes. Bottom panel: The space-time-yield of the PtSn/Silicalite-1 catalyst (star) and its deactivation rate, compared with the best ones reported in literature.