2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(735q) Production of Curcumin Nanoparticles Via Self-Assembly in Supersaturated Solution
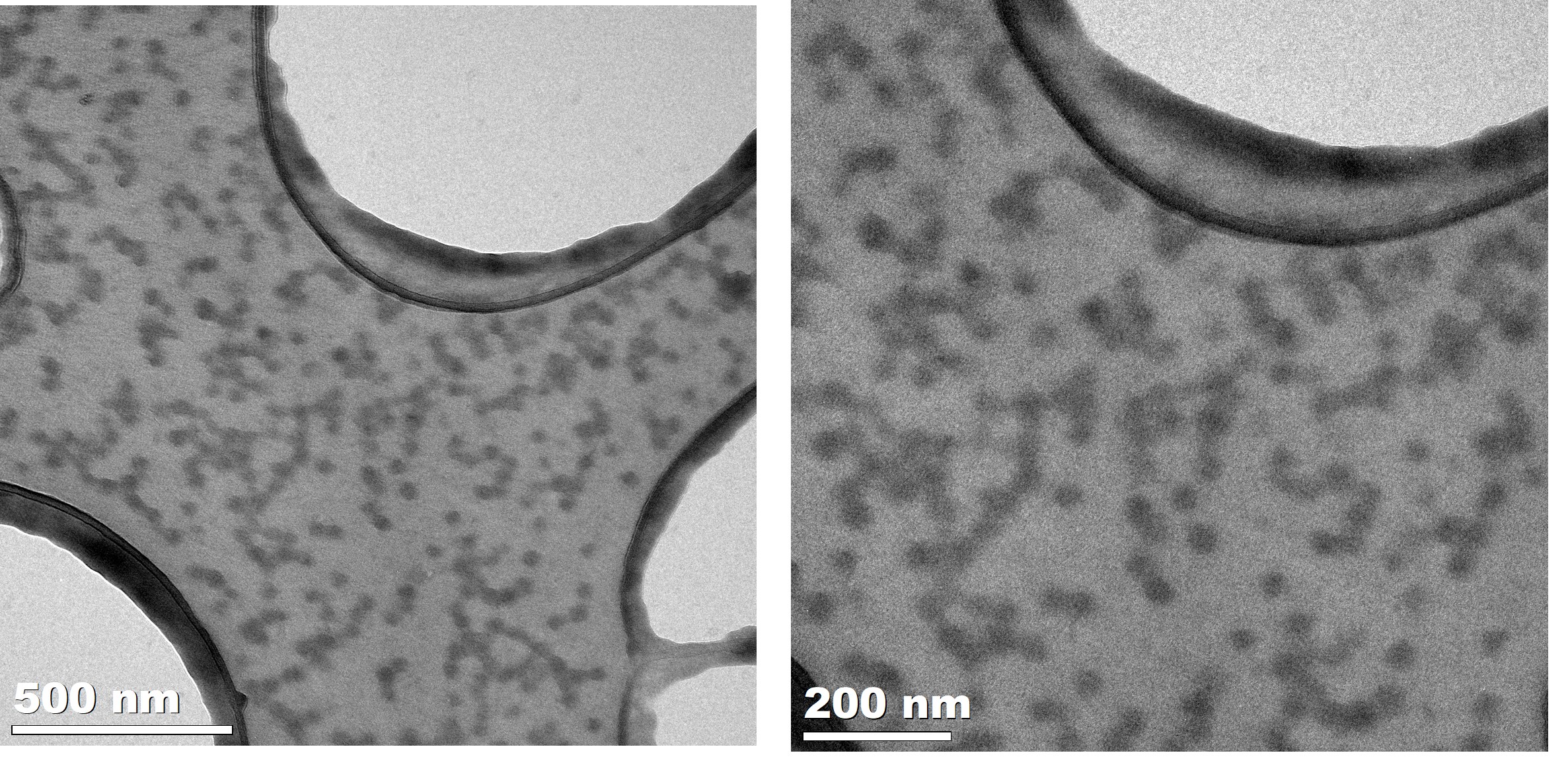
TEM analysis revealed that the curcumin nanoparticles were well dispersed in the solution (see Figure). These nanoparticles were isolated using vacuum filtration to form to micron sized particles through the adsorption of curcumin particles onto the surface of MMT clay particles. Then the adsorbed curcumin was filtered using PTFE membrane filter with 0.2 micron pore size. The concentration of curcumin in the filtrate was determined using UV-Vis spectroscopy and the drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of each sample was determined. The maximum drug loading achieved was 49 % and the maximum drug release achieved was 55 %.
To further improve drug loading and drug release spray drying was employed. In this process, drug loading of approx. 70 % and drug release of 70 % was achieved. The spray drying initially was used as a semi-continuous process. Experiments to produce curcumin nanoparticles in fully continuous mode using spray drying produces slightly larger (90 nm) curcumin nanoparticles compared to the nanoparticles (60-80 nm) in the semi-batch process.