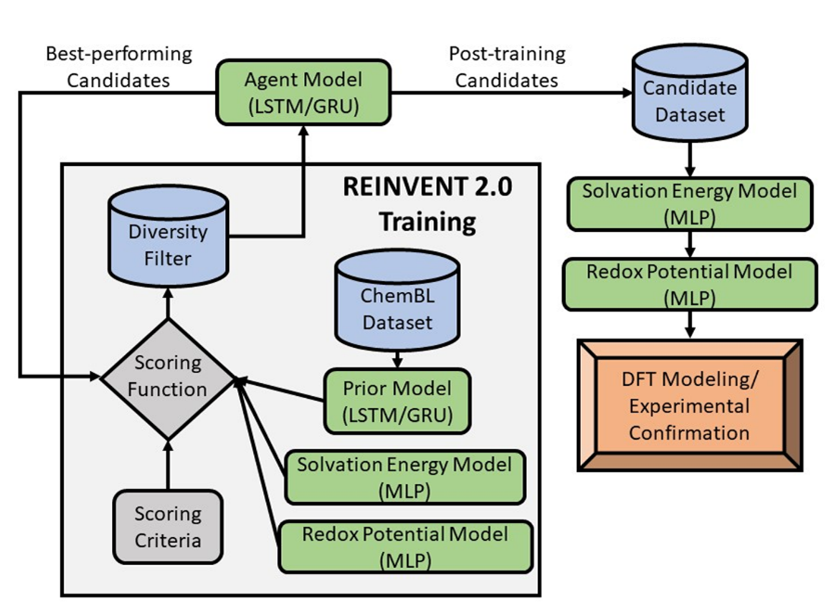
Organic molecule design with multiple target properties is a combinatorically hard problem in that the vast structure-property outcomes of molecular scaffolds preclude exhaustive search from
ab initio computational methods (e.g., density functional theory, DFT) and experimental characterization. Machine learning (ML) models have been used to generate molecules and explore structure-property relationships for applications in a high-throughput fashion, yet many molecular design problems tasked for generative ML have target property ranges that are rare events in the underlying chemical space [1]. In this study, we use reinforcement learning of generative ML models applied to one such rare-event sampling problem in molecular design
—finding soluble, redox-active organic electrolytes for aqueous redox flow battery (RFB) energy storage [2].
Organic electrolytes have garnered interest for use in RFB energy storage applications, but these electrolytes must satisfy a set of key properties, such as a sufficiently negative reduction potential and stability under operating conditions. Quinone- and phenazine-based molecules have been explored for this application, but their stabilities are sub-optimal in terms of their capacity fade rate [3]. Based on our experimental measurements, we narrow our electrolyte search to a benzo[c]cinnoline (BZC) scaffold, a relatively underexplored class of molecule that we hypothesize as being a promisingly stable chemical space due to a ring-constraining bond across from the hydrazo bridge of the core scaffold. The stability of the core benzo[c]cinnoline scaffold is explored with DFT via thermodynamic measures of degradation for lab-tested molecules compared to their unconstrained azobenzene analogues.
A recurrent neural network is leveraged to first generate BZC molecules irrespective of their chemical properties (i.e., a prior model). Property-guided reinforcement learning is applied onto the model to train a new iteration of the model (i.e., an agent model) via the REINVENT 2.0 framework, which biases an ML model towards generation of preferable molecules via explicit penalties to the loss function [4]. For effective property reinforcement, we develop a structure-property ML model for redox potential trained on estimates of the potentials via thermodynamic cycle—the states of which we compute with DFT. Also, a structure-property ML model for solubility is trained by using solvation energy as a thermodynamic proxy. Screening results of the proposed candidates are discussed. This work ultimately leverages a generative ML workflow to efficiently explore the chemical space and propose promising benzo[c]cinnoline electrolytes for further downstream synthesis and characterization for aqueous RFB energy storage.
References:
- Bilodeau, Camille, et al. "Generative models for molecular discovery: Recent advances and challenges." Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science 12.5 (2022): e1608.
- Luo, Jian, et al. "Status and prospects of organic redox flow batteries toward sustainable energy storage." ACS Energy Letters 4.9 (2019): 2220-2240.
- Kwabi, David G., Yunlong Ji, and Michael J. Aziz. "Electrolyte lifetime in aqueous organic redox flow batteries: a critical review." Chemical Reviews 120.14 (2020): 6467-6489.
- Blaschke, Thomas, et al. "REINVENT 2.0: an AI tool for de novo drug design." Journal of chemical information and modeling 60.12 (2020): 5918-5922.